Preparation method for molybdenum disulfide nanometer film with preset patterns
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and nano-film, which is applied in the manufacture of semiconductor/solid-state devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious, damage or pollution of molybdenum disulfide film, and achieve the effect of uniform crystal quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
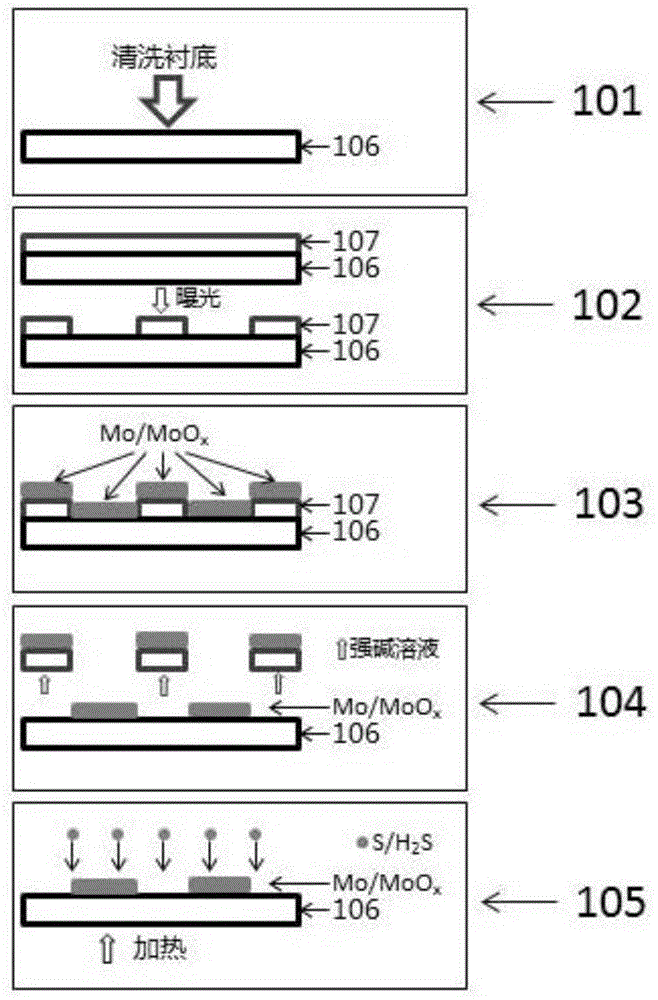
[0030] figure 1 The process flow of the method for preparing the molybdenum disulfide film with preset graphics in the present invention includes:
[0031] Step 101: Cleaning the substrate. The substrate can be a silicon substrate, a germanium substrate, a silicon carbide substrate, a sapphire substrate, etc., which mainly serve as a support for the precursor and the molybdenum disulfide sample generated later;
[0032] Step 102: Spin-coat a layer of photoresist on the substrate with a coater (it can be glue for ultraviolet exposure, ion beam exposure, and electron beam exposure, etc., depending on the specific process requirements), and use a mask with a corresponding pattern The film plate exposes and develops the substrate coated with photoresist, and removes the photoresist at the preset pattern part;
[0033] Step 103: Deposit a layer of metal molybdenum film or molybdenum oxide film on the substrate by using magnetron sputtering technology, electron beam evaporation or ...
Embodiment 1
[0038] A kind of molybdenum disulfide CVD preparation method that can preset pattern, comprises following specific steps:
[0039] Step 101: Cleaning the substrate. The substrate is a thermally oxidized silicon substrate, which mainly serves as a support for the precursor and the later-generated molybdenum disulfide sample.
[0040] Step 102: Spin-coat a layer of photoresist positive resist on the clean silicon substrate with a coater, use a mask plate to expose the pre-baked sample, and develop the sample after post-baking;
[0041] Step 103: using a magnetron sputtering device to deposit a layer of metal molybdenum as a precursor on the sample substrate. The process parameters used in the sputtering process were argon gas flow rate of 20 sccm, sputtering pressure of 2.0 Pa, sputtering power of 10 W, and sputtering time of 1 min. The thickness of the obtained molybdenum film is about 5nm;
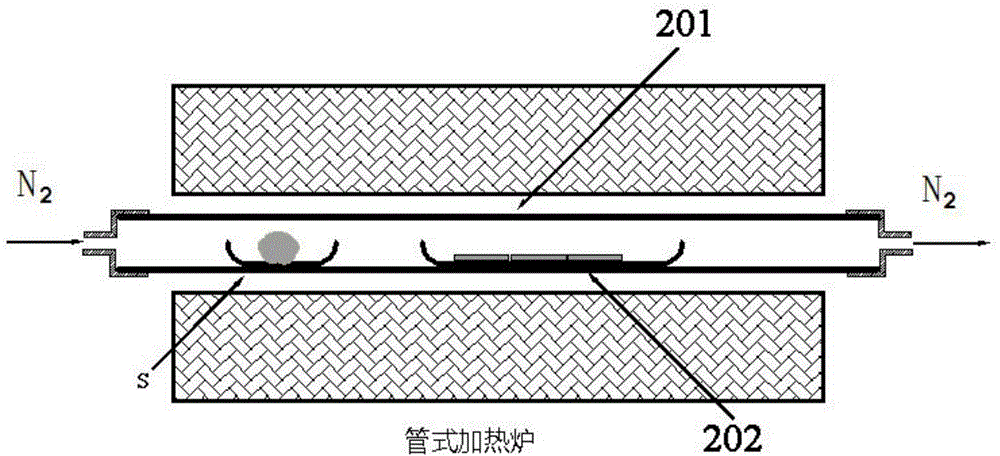
[0042] Step 104: Soak the sample coated with molybdenum film in acetone solvent for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com