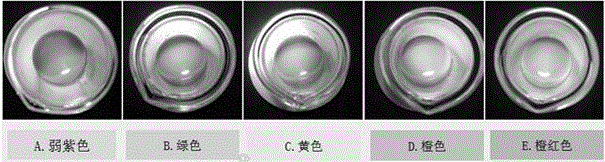
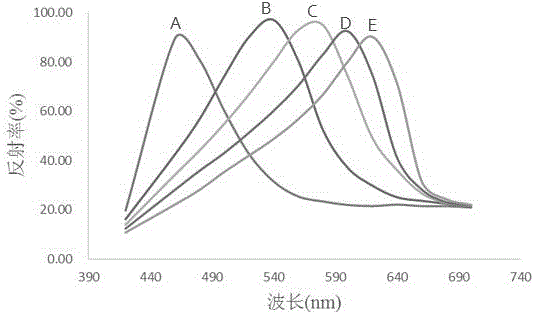
Preparation method of magnetic molecular imprinting photonic crystal sensor for detecting melamine
A magnetic molecular imprinting and melamine technology, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions, can solve the problems of destroying molecular imprinting sites and long template assembly time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
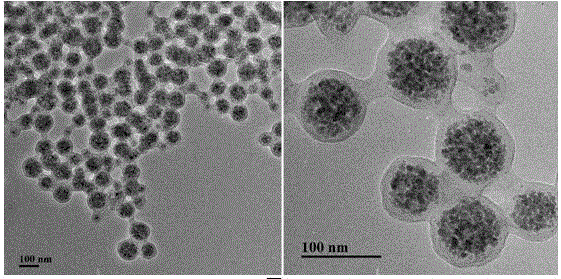
[0028] (1) Preparation of ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified with oleic acid: the ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified with oleic acid were prepared by co-precipitation method. Add 0.01mol of ferric chloride and 0.01mol of ferrous sulfate into 150mL of ultrapure water that has been treated with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, and ultrasonically dissolve at 50-60KHz to obtain a mixed solution. The resulting mixed solution was transferred to a 250 mL three-necked flask, and placed in a 60°C oil bath. Add 20 mL of ammonia water and 0.5 g of oleic acid in sequence, pass nitrogen to remove oxygen throughout the reaction, and react for 0.5 h. After the reaction, a magnet was placed at the bottom of the flask to absorb the particles. The collected particles were washed to neutral with deionized water, and dried in a vacuum oven at 40° C. to obtain oleic acid-modified ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles.
[0029] (2) Preparation of melamine magnetic m...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Preparation of ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified with oleic acid: the ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified with oleic acid were prepared by co-precipitation method. Add 0.01mol of ferric chloride and 0.01mol of ferrous chloride to 120mL of ultrapure water that has been treated with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, and ultrasonically dissolve at 50-60KHz to obtain a mixed solution. The resulting mixed solution was transferred to a 250 mL three-necked flask, and placed in a 90°C oil bath. Add 30 mL of ammonia water and 1 g of oleic acid in sequence, pass nitrogen to remove oxygen throughout the reaction, and react for 2 hours. After the reaction, a magnet was placed at the bottom of the flask to absorb the particles. The collected particles were washed with deionized water until neutral, and dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. to obtain oleic acid-modified ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles.
[0039] (2) Preparation of melamine magnetic...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Preparation of ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified with oleic acid: the ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified with oleic acid were prepared by co-precipitation method. Add 0.01mol of ferric chloride and 0.01mol of ferrous sulfate into 90mL of ultrapure water that has been treated with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, and ultrasonically dissolve at 50-60KHz to obtain a mixed solution. The resulting mixed solution was transferred to a 250 mL three-necked flask, and placed in an 80°C oil bath. Add 10 mL of ammonia water and 0.1 g of oleic acid in sequence, pass nitrogen to remove oxygen during the whole reaction, and react for 1 h. After the reaction, a magnet was placed at the bottom of the flask to absorb the particles. The collected particles were washed with deionized water until neutral, and dried in a vacuum oven at 45° C. to obtain oleic acid-modified ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles.
[0047] (2) Preparation of melamine magneti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com