A kind of preparation method of nanoscale porous carbon microsphere
A porous carbon and nano-scale technology, applied in the direction of nano-carbon, can solve the problems of porous carbon microspheres easy to agglomerate, high production cost, difficult to disperse, etc., and achieve the effect of wide sources, increased specific surface area, and favorable loading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
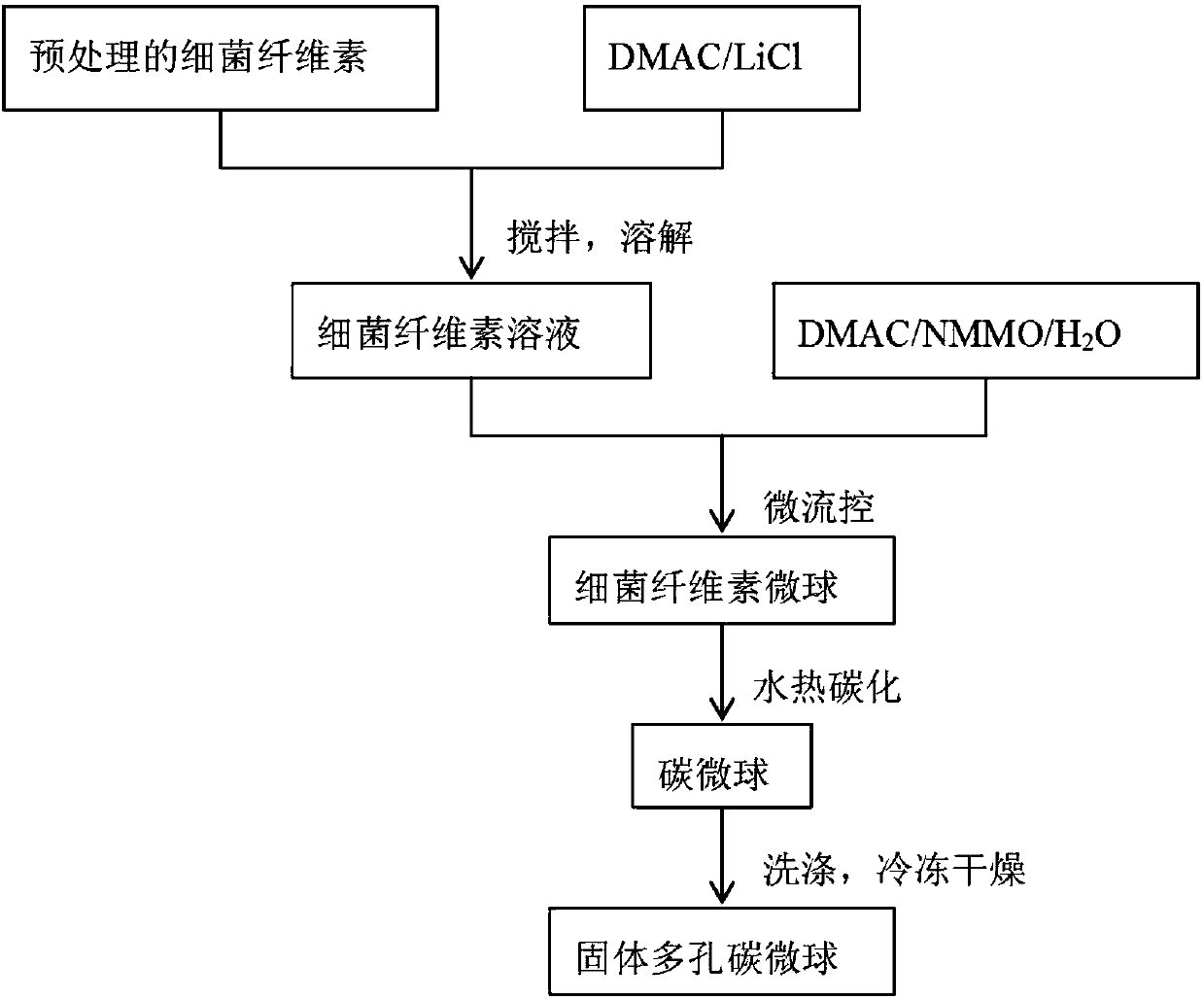
[0021] A kind of preparation method of nanoscale porous carbon microsphere of the present invention, flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0022] Step 1, the dissolution of bacterial cellulose: Dissolve the bacterial cellulose powder obtained by alkali treatment, washing and drying in LiCl / DMAC solution, stir until completely dissolved, and centrifuge to obtain LiCl / DMAC / BC solution;
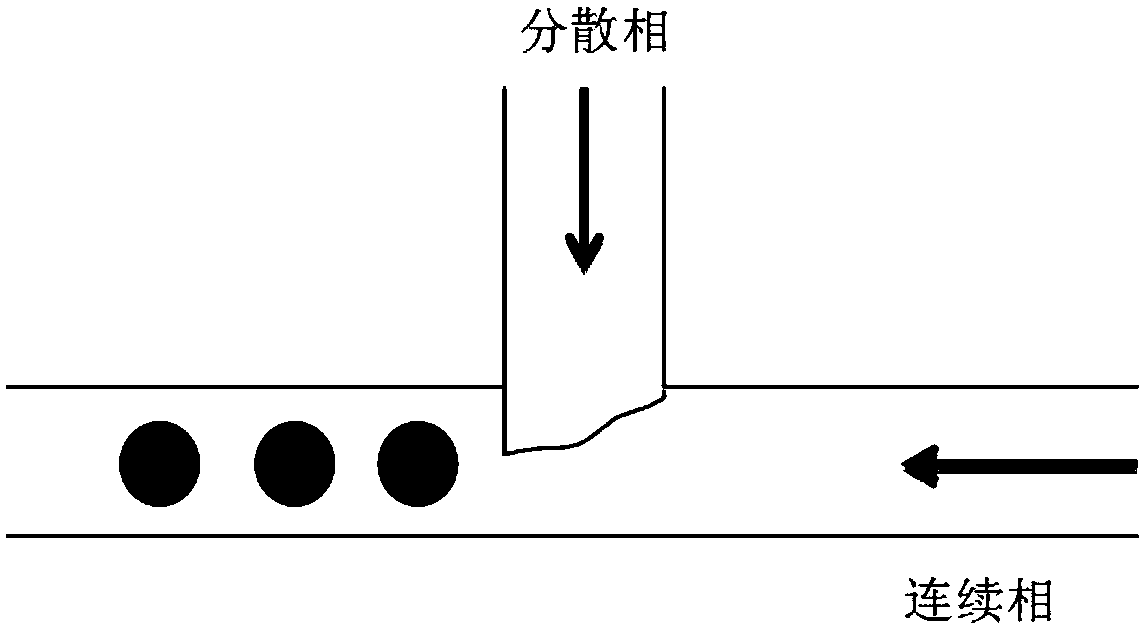
[0023] Step 2, preparation of microspheres by microfluidic technology: use LiCl / DMAC / BC solution as the dispersed phase, DMAC / NMMO / H 2 The O solution is the continuous phase, the flow rate ratio of the dispersed phase to the continuous phase is 1:10-80, and the bacterial cellulose microspheres are prepared by using a microfluidic device with T-shaped vertically interlaced microchannels;
[0024] Step 3, hydrothermal carbonization: put the microsphere solution in a reaction kettle, and react at 160°C-200°C for 4h-30h to obtain a carbon microsphere solution;
...
Embodiment 1
[0031] The first step: the dissolution of bacterial cellulose: put the bacterial cellulose into a 6% NaOH aqueous solution, activate it at room temperature for 3 hours, vacuum filter, rinse repeatedly with deionized water until the washing liquid is neutral, and then wash with ethanol Repeated soaking three times, each time for 1 hour, vacuum filtration, and then placed in a vacuum drying oven at 80°C to dry to obtain bacterial cellulose powder. Accurately 1g of pretreated bacterial cellulose powder was uniformly dispersed into 100mL of anhydrous LiCl / DMAC system with a mass fraction of 8%, magnetically stirred at 100°C for 1h, and then mechanically stirred for 6h at room temperature to fully dissolve it. Centrifuge and defoam for 20 min to obtain LiCl / DMAC / BC solution.
[0032] Step 2: Prepare microspheres using microfluidic technology: use the solution obtained in the first step as the dispersed phase, DMAC / NMMO / H 2 O was the continuous phase, and bacterial cellulose micros...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The first step: the dissolution of bacterial cellulose: put the bacterial cellulose into a 6% NaOH aqueous solution, activate it at room temperature for 3 hours, vacuum filter, rinse repeatedly with deionized water until the washing liquid is neutral, and then wash with ethanol Repeated soaking three times, each time for 1 hour, vacuum filtration, and then placed in a vacuum drying oven at 80°C to dry to obtain bacterial cellulose powder. Accurately 1g of pretreated bacterial cellulose powder was uniformly dispersed into 100mL of anhydrous LiCl / DMAC system with a mass fraction of 8%, magnetically stirred at 100°C for 1h, and then mechanically stirred for 6h at room temperature to fully dissolve it. Centrifuge and defoam for 20 min to obtain LiCl / DMAC / BC solution.
[0038] Step 2: Prepare microspheres using microfluidic technology: use the solution obtained in the first step as the dispersed phase, DMAC / NMMO / H 2 O was the continuous phase, and bacterial cellulose micros...
PUM
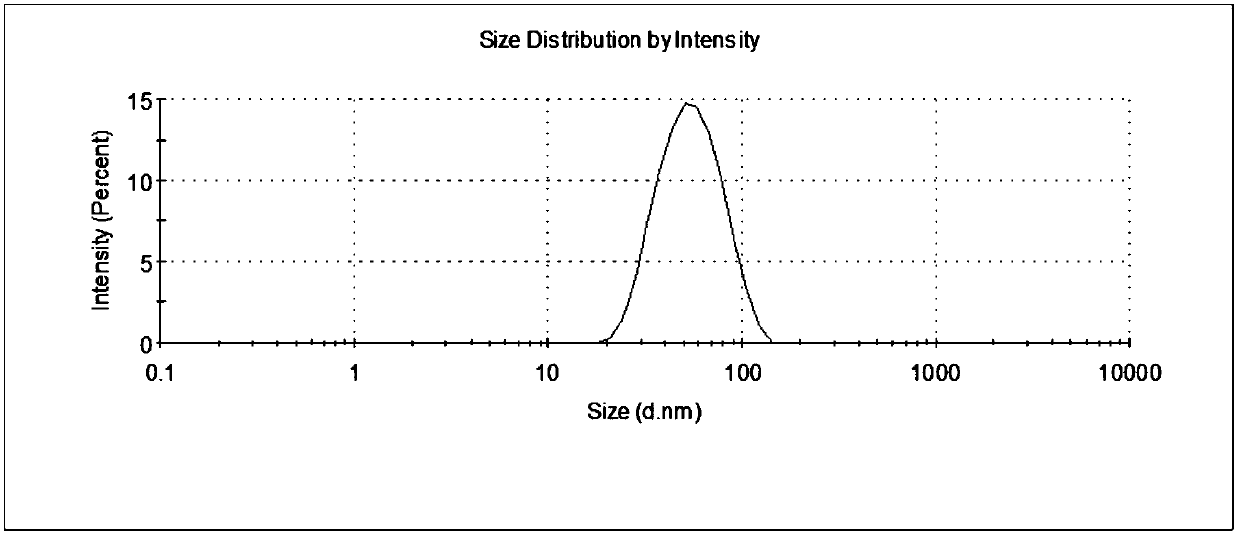
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com