Production method for preparing isomahooligosaccharide from waste residues of sweet potatoes
A technology of isomaltooligosaccharides and sweet potato waste residues, which is applied in the field of preparation of isomaltooligosaccharides, can solve the problems of insufficient utilization of sweet potato residue resources, and achieve the effects of reducing enzyme addition costs, improving hydrolysis efficiency, and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
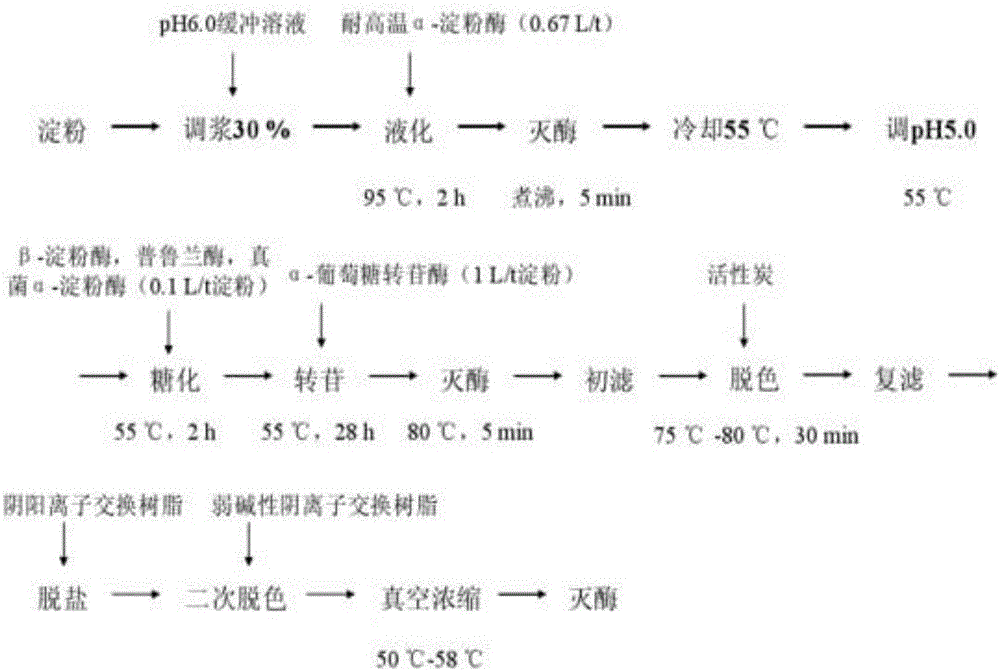
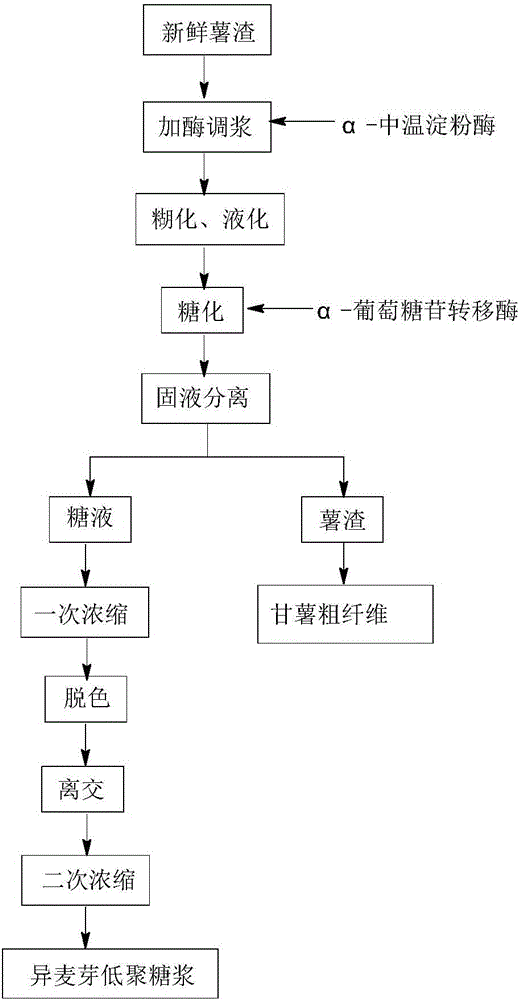
[0051] Get fresh potato dregs 10kg (production of sweet potato starch processing, water content 88%, starch content 50.5% (dry basis), β-amylase activity 166U / g fresh potato dregs, add α-amylase (BAN480L) 0.3g / kg starch, After stirring evenly, heat to 88°C, keep warm for 5min, measure the DE value as 22.0%, cool down to 60±2°C, keep warm for saccharification for 2 hours, add α-glucosidyl transferase (enzyme activity is 3×10 5 u / mL) 0.6mL, after stirring evenly, continue to incubate at 60±2°C for 8h. After the incubation, the temperature was raised to 80°C for 10 minutes to inactivate the enzyme. Filter and separate the potato residue after deenzyme removal, wash the filter residue with a small amount of water, and combine the filtrates to obtain a total of 12.4 L. The solid content is 4.6%. The sugar solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to a solid content of 22%. Add 6g of activated carbon to the concentrated sugar solution, raise the temperature to 80°C, and ke...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Take 20kg of fresh potato dregs (produced by sweet potato starch processing, water content 89%, starch content 49.5%, β-amylase activity 137U / g), add α-amylase (BAN480L) 0.4g / kg starch, after stirring evenly, heat to Incubate at 88°C for 10 minutes, measure the DE value as 24.5%, lower the temperature to 60°C, and heat for saccharification for 2 hours, add α-glucosidyl transferase 1.1mL, stir well and continue to incubate at 60°C for 10 hours. After the incubation, heat-inactivation treatment was carried out, and the incubation was carried out at 90°C for 5 minutes. Filter the sugar solution from sweet potato residue after deactivation, wash the filter residue with 1.5L of water, and combine the filtrates to obtain a total of 19.3L. The solid content is 5.6%. The sugar solution is concentrated to a solid content of 25%. Add activated carbon to the concentrated sugar solution, keep warm and decolorize. The decolorized sugar solution is ion-exchanged, and the conductan...
Embodiment 3
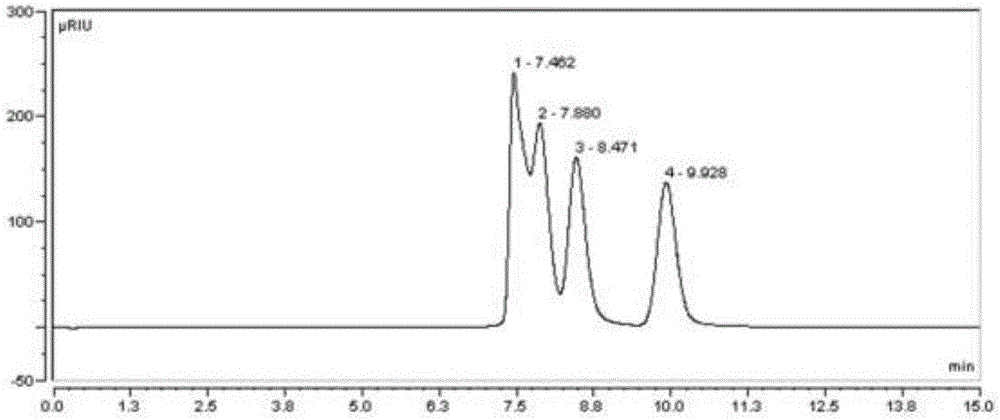
[0055] Take 20kg of fresh potato dregs (produced by sweet potato starch processing, water content 90%, starch content 50.2%, β-amylase activity 184U / g), add α-amylase (BAN480L) 0.5g / kg starch, heat to 90°C, keep warm After 5 minutes, the DE value was determined to be 28.2%, the temperature was lowered to 60°C, α-glucosidyl transferase was added, and the glycosyltransferase was incubated for 10 hours. After the incubation, heat-up enzyme treatment was carried out. Sweet potato dregs are filtered to obtain sugar liquid. After the sugar solution is concentrated, it is decolorized and ion exchanged to remove impurities. The impurity-removing sugar solution is concentrated under pressure to a solid content of 80%. The proportion of isomaltooligosaccharides was detected by HPLC to be 52.8%. The potato residue obtained by filtering is dried to obtain crude fiber.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com