Method for removing orange yellow I in printing and dyeing wastewater by using sulfurized modified zero-valent iron material under effect of low-intensity magnetic field
A technology for printing and dyeing wastewater and zero-valent iron, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, harsh preparation conditions for nano-zero-valent iron, and unsatisfactory practical applications, and achieve Increased efficiency, ease of application, and accelerated electron transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Preparation of vulcanized modified zero-valent iron material
[0046] Nitrogen was passed through 250mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution with a pH of 6.0 until the dissolved oxygen was zero, and then 1g of zero-valent iron was quickly added to seal it and placed in a shaker with a speed of 120r / min to rotate and shake for 10min. Middle Fe 2+ When it is 50mg / L, add 1M Na 2 S solution 1.5mL, then placed in a shaker and rotated at 25°C for 12h. Finally, filter and vacuum freeze-dry for 2h. The sulfur-iron molar ratio of the obtained vulcanized modified zero-valent iron material is 0.084. About 0.95 g of product was obtained. This was repeated 8 times to give about 7.6 g of product.
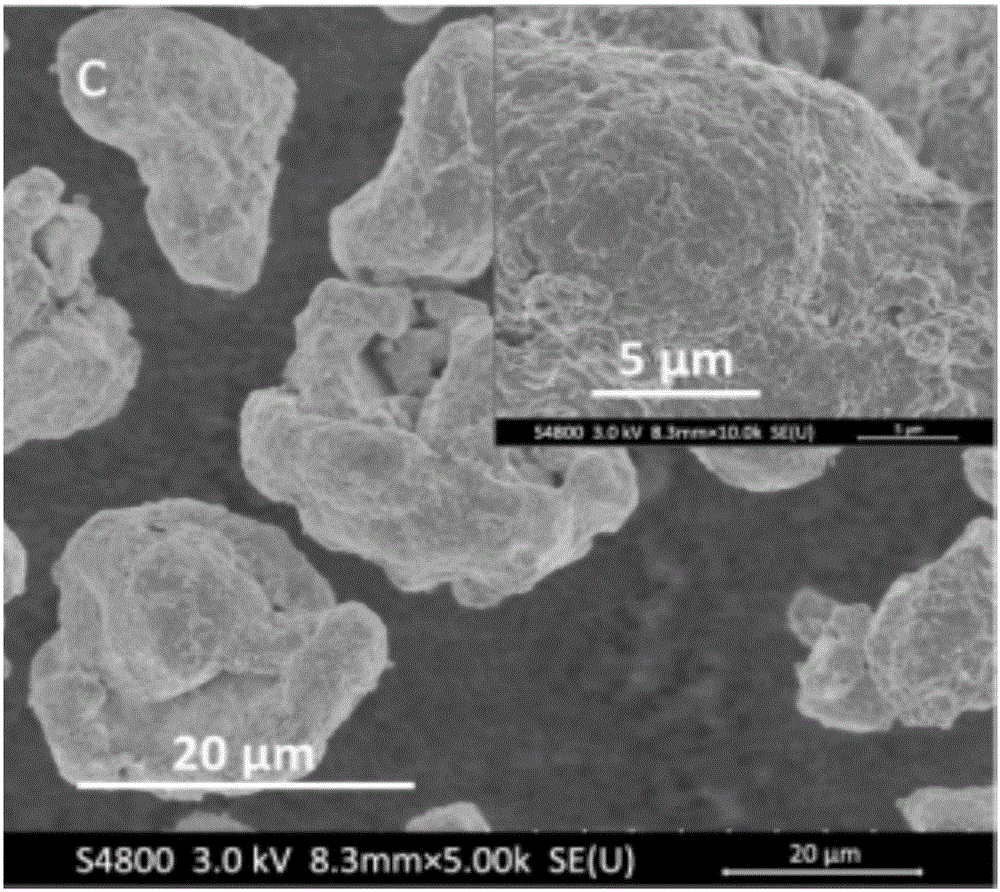
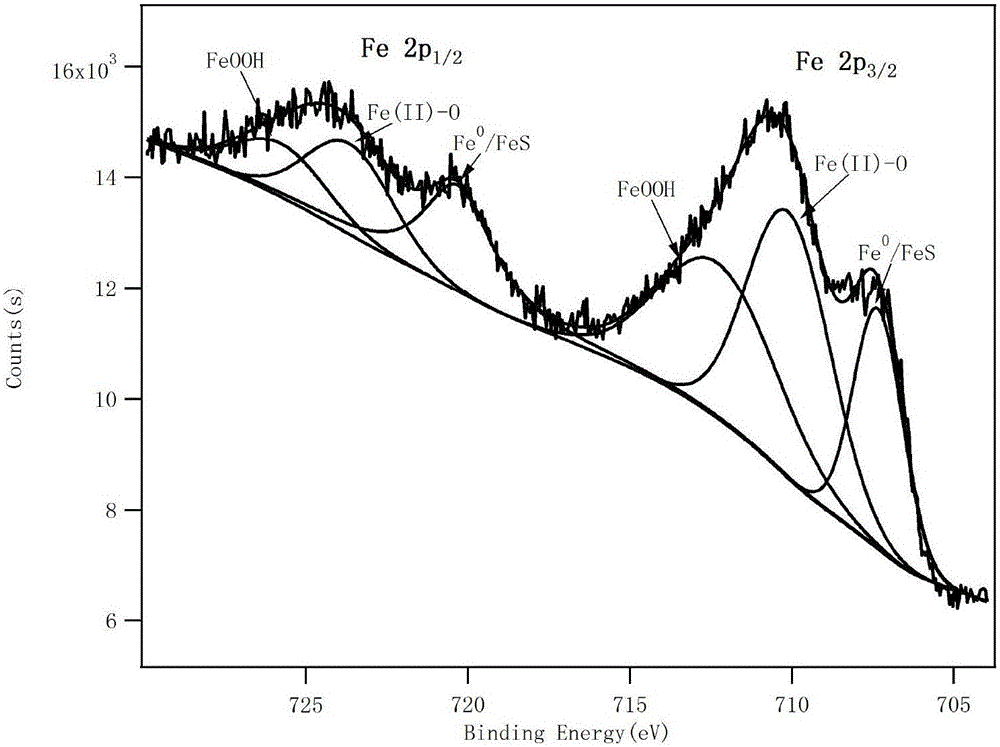
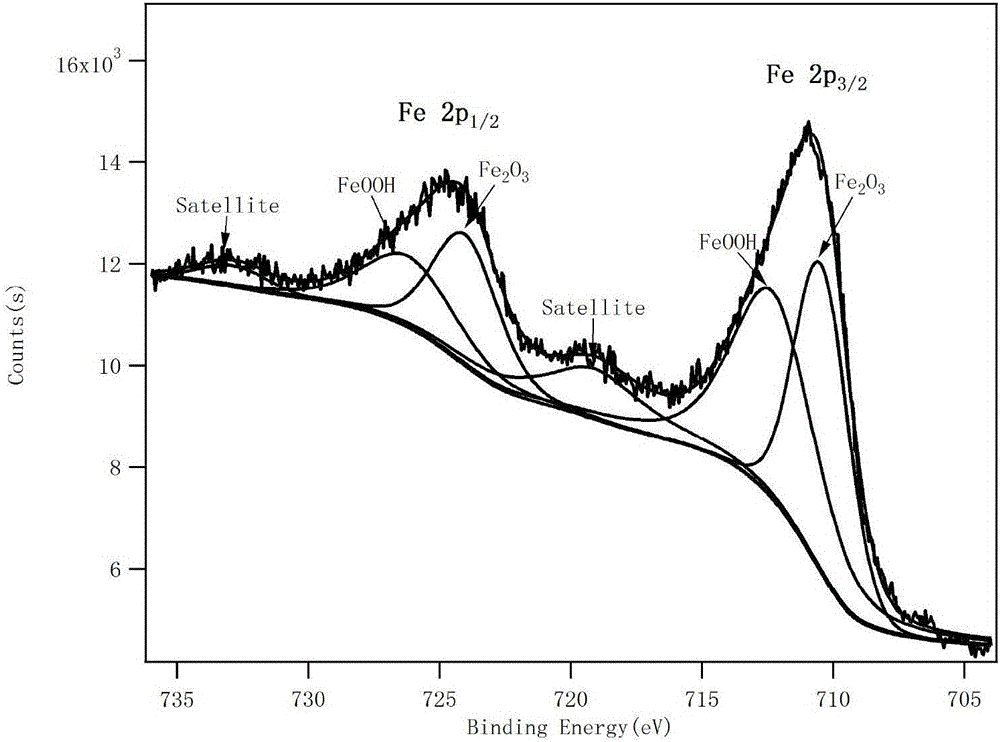
[0047] The X-ray photoelectron spectrum (XPS) of gained vulcanization modified zero-valent iron is as follows figure 1 As shown in the scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of image 3 shown. Depend on figure 1 , image 3 It can be seen that the vulcanized ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Utilize the vulcanized modified zero-valent iron material prepared in Example 1 to remove the orange I in the printing and dyeing wastewater under the effect of an externally applied weak magnetic field, the orange I content in the wastewater is 100mg / L wastewater, the steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) Take 1L of printing and dyeing wastewater containing Orange I, put it in a reactor, add 2.383g buffer HEPES (concentration 10mmol / L) and adjust the pH=7 with a 20% NaOH solution;
[0052] (2) Add 2g / L of the vulcanized modified zero-valent iron material prepared in Example 1, place a ring magnet at the bottom of the reactor, provide a non-uniform weak magnetic field with a magnetic field strength≤20mT, and use 400r / min under the action of the weak magnetic field The reaction was stirred at a rotating speed for 15 minutes, and the removal rate of Orange I was over 98.2%. Continue to stir the reaction at 400r / min for 20min, and the removal rate of Orange I is approximately...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: The experiment of removing orange I in printing and dyeing wastewater by sulfurized modified zero-valent iron material under the action of weak magnetic field.
[0054] (1) Dissolve the analytically pure orange I reagent in distilled water, configure the simulated printing and dyeing wastewater containing orange I of different concentration gradients, and utilize a UV-visible spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the simulated orange I wastewater with different concentration gradients at a wavelength of 476nm, Make concentration-absorbance standard curve;
[0055] Use the buffer agent HEPES and sodium hydroxide to adjust, so that the configured simulated printing and dyeing wastewater with different concentration gradients has a pH of 7;
[0056] The above-mentioned simulated orange yellow I wastewater of different concentrations is that the orange yellow I content is 50, 100 and 200mg / L respectively;
[0057] (2) Place a ring magnet at the bottom o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com