Hard alloy blade and preparation method thereof
A technology of carbide inserts and tools, applied in metal processing equipment, turning equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problem of low versatility of cutting inserts, achieve excellent edge strength and impact resistance, achieve optimization, improve Effects of hardness and high temperature properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
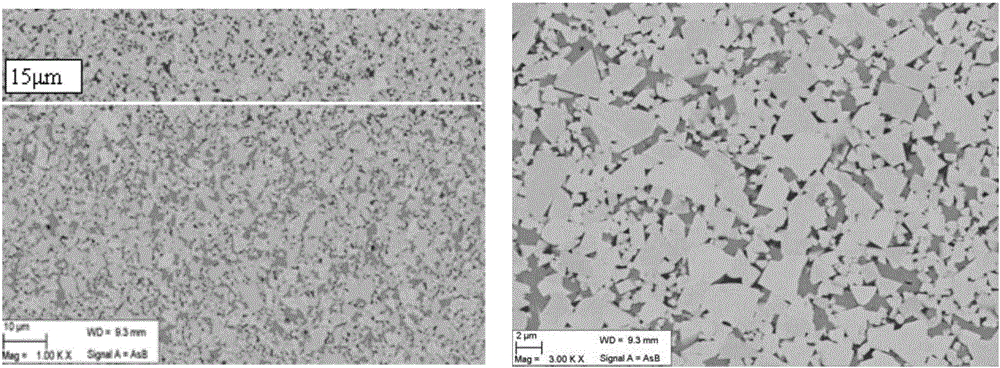
[0049] A cemented carbide blade of the present invention, the blade model is WNMG080408. The cemented carbide blade includes a cemented carbide blade substrate and a coating provided on the cemented carbide blade substrate. See Table 1 and Table 2 for the matrix composition of the cemented carbide insert in this embodiment. 5.6wt.% (not including solid solution W and Cr) Co metal is used as the binding phase, WC and titanium-containing cubic phase compound are used as the hard phase, and the balance is WC. In the bonding phase, there are W and Cr elements in solid solution, and the solid solution content of Cr in the bonding phase is 3.2wt.% (Cr element accounts for the mass fraction of the bonding phase), and the Cr element is represented by Cr 3 C 2 Added in form, the W solid solution content is 5.6wt.% (the W element accounts for the mass fraction of the binder phase). The cemented carbide insert substrate has a surface structure lacking titanium-containing cubic phase c...
Embodiment 2
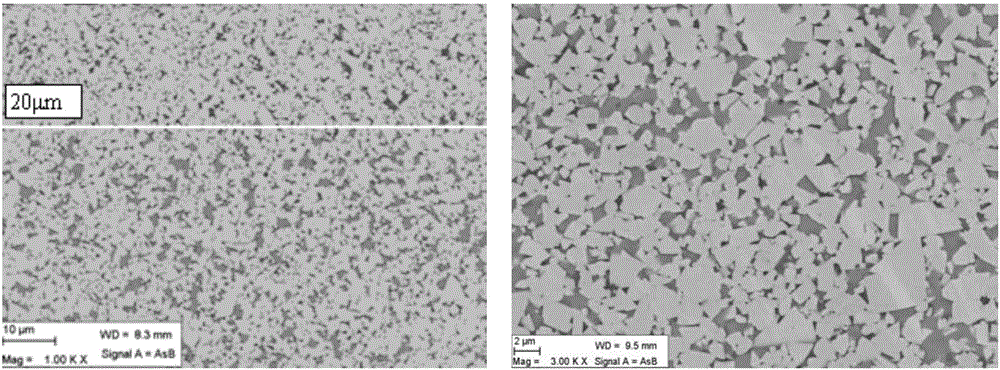
[0067] A cemented carbide blade of the present invention, the blade model is WNMG080408. The cemented carbide blade includes a cemented carbide blade substrate and a coating provided on the cemented carbide blade substrate. The matrix composition of the cemented carbide insert in this embodiment is shown in Table 1 and Table 2, 6.8wt.% Co metal is used as the binder phase, WC and titanium-containing cubic phase compound are used as the hard phase, and the balance is WC. In the bonding phase, there are W and Cr elements in solid solution, and the solid solution content of Cr in the bonding phase is 4.8wt.%, and the Cr element is represented by Cr 3 C 2 Form added, W solid solution content of 6.5wt.%. The cemented carbide insert substrate has a surface structure lacking titanium-containing cubic phase compounds whose average binder phase content is 1.7 times the nominal Co binder phase content, and the thickness of the surface structure is 20 μm. The average particle size of ...
Embodiment 3
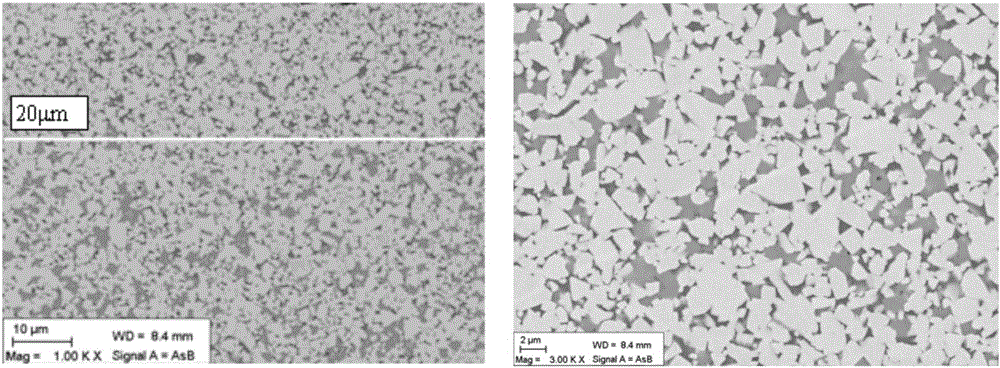
[0074]A cemented carbide blade of the present invention, the blade model is WNMG080408. The cemented carbide blade includes a cemented carbide blade substrate and a coating provided on the cemented carbide blade substrate. The matrix composition of the cemented carbide insert in this example is shown in Table 1 and Table 2, 8.4wt.% Co metal is used as the binder phase, WC and titanium-containing cubic phase compound are used as the hard phase, and the balance is WC. W and Cr elements are dissolved in the binder phase, and the solid solution content of Cr in the binder phase is 6.8wt.%. The Cr element is represented by Cr 3 C 2 Form added, W solid solution content of 6.3wt.%. The cemented carbide insert substrate has a surface structure lacking titanium-containing cubic phase compounds with an average binder phase content of 1.8 times the nominal Co binder phase content, with a thickness of 20 μm. The average particle size of the titanium-containing cubic phase compound in t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com