Lithium ion battery composite membrane and preparation method thereof
A lithium-ion battery and composite diaphragm technology, which is applied in secondary batteries, battery pack components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of complex process and difficult control of process conditions, and achieve simple process, excellent thermal stability, and improved thermal stability. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
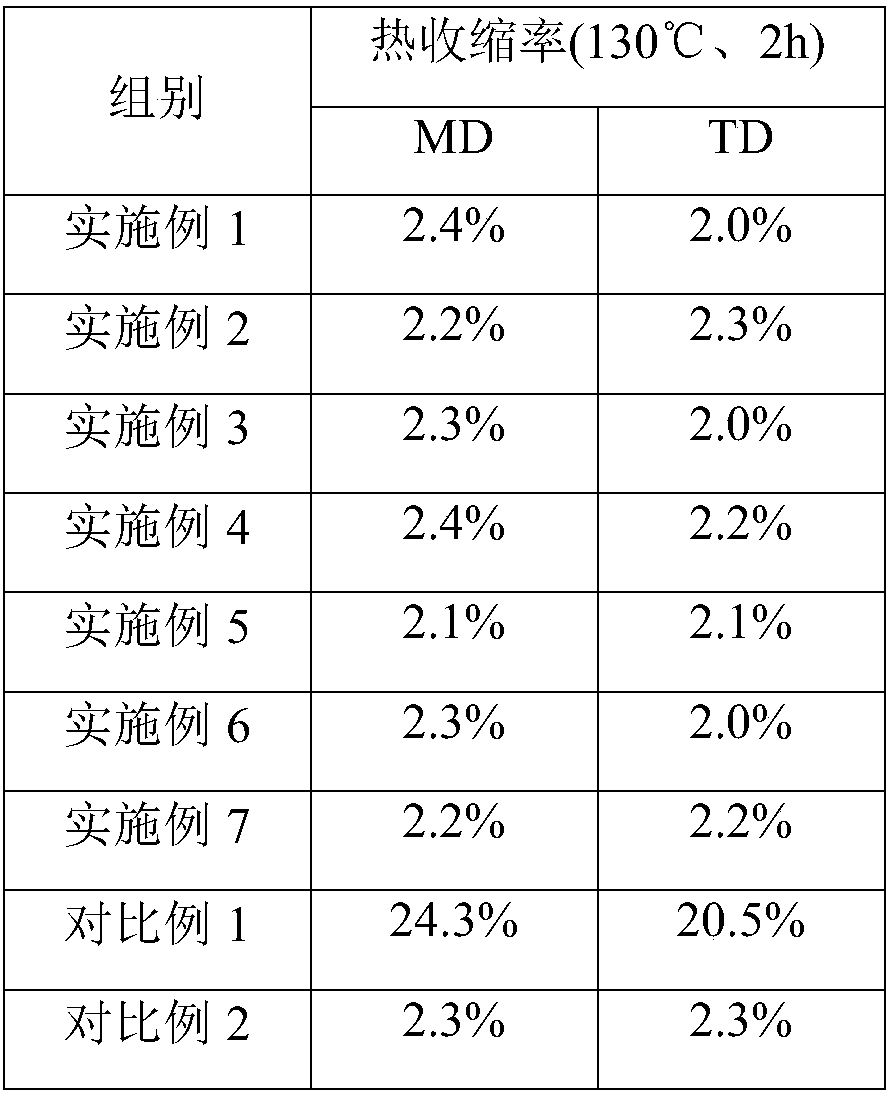
Embodiment 1
[0031] Preparation of positive electrode sheet:
[0032] Lithium cobaltate (positive electrode active material), conductive agent superconducting carbon (Super-P), and binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) were uniformly mixed at a mass ratio of 96:2.0:2.0 to make positive electrode slurry, and the slurry Coated on the aluminum foil of the current collector, and then dried at 110°C, then cold-pressed, slitting, trimmed, and tab-welded to make the positive electrode sheet of the lithium-ion battery.
[0033] Preparation of negative electrode sheet:
[0034] Graphite and conductive agent superconducting carbon (Super-P), thickener sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and binder styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) are made into negative electrode slurry at a mass ratio of 96:1.5:1.0:1.5 The slurry is coated on the copper foil of the current collector, and then dried at 85°C, then cold-pressed, stripped, trimmed, and tab-welded to make a lithium-ion battery negative electrode sheet. ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Different from Example 1 is the preparation of composite diaphragm:
[0043] Preparation of composite diaphragm:
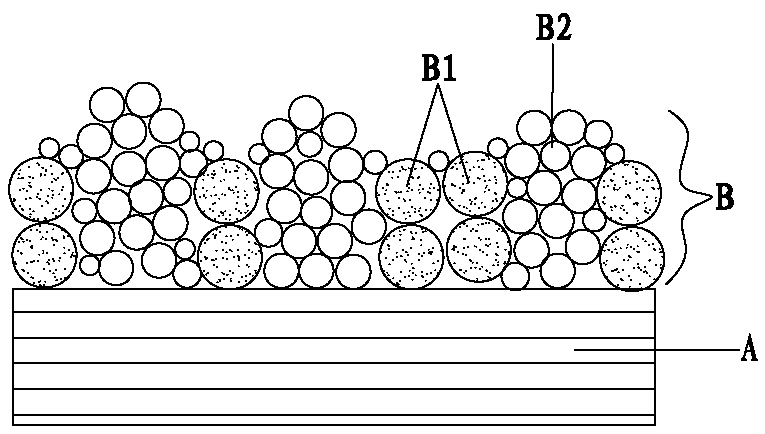
[0044] 1) Take a polyethylene microporous film with a thickness of 9 μm as the diaphragm substrate;
[0045] 2) Add polyoxyethylene and styrene-butadiene to deionized water, stir at 50°C for 2 hours, wherein the mass ratio of polyoxyethylene and styrene-butadiene is 92:8, and agglomerate into large particles Suspension dispersion; then add ZrO 2 The particles were stirred for 1h, and then added polyacrylate emulsion (the content of polyacrylate in the aqueous solution was 25wt%) and continued to stir for 1h, wherein, ZrO 2 The mass ratio to polyacrylate is 85:15, ZrO 2 The mass ratio to polyoxyethylene is 60:40 to obtain a mixed slurry of inorganic particles and binding polymer, and the solid content of the mixed slurry is 40wt%;
[0046] 3) Coating the mixed slurry obtained in step 2) on both sides of the diaphragm substrate by gravure coating, and dry...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Different from Example 1 is the preparation of composite diaphragm:
[0050] Preparation of composite diaphragm:
[0051] 1) Take a polyethylene microporous film with a thickness of 9 μm as the diaphragm substrate;
[0052] 2) Add polymethyl methacrylate and styrene-butadiene to deionized water, stir at 40°C for 2h, wherein the mass ratio of polymethyl methacrylate and styrene-butadiene is 94: 6. Agglomerate into a suspension dispersion of large particles; then add boehmite particles and stir for 1 hour, then add carboxymethyl cellulose sodium and continue stirring for 1 hour, wherein the mass ratio of boehmite to carboxymethyl cellulose sodium is 90:10, the mass ratio of boehmite and polymethyl methacrylate is 70:30, obtain the mixed slurry of inorganic particles and binding polymer, the solid content of this mixed slurry is 45wt%;
[0053] 3) Coating the mixed slurry obtained in step 2) on one side of the diaphragm substrate by screen printing, and drying to obtain ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size distribution range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com