Method for improving paper strengthening effect of bacterial cellulose-based paper strengthening agent
A bacterial cellulose and enhancer technology, applied in the direction of synthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paper, enhancer addition, fiber raw material treatment, etc., can solve the problem of reducing paper air permeability, increasing paper production cost, bacterial cellulose In order to achieve the effect of improving the enhancement effect, reducing the dosage, and improving the effect of enhancing the physical properties of the paper
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
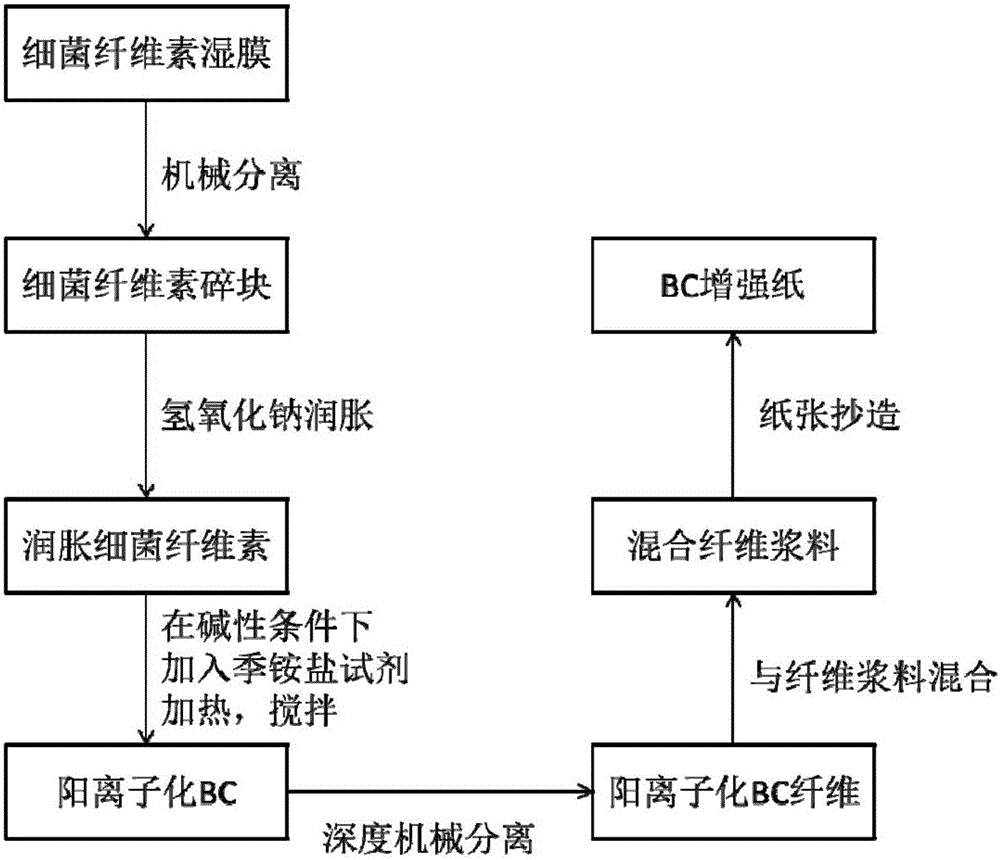
[0028] Cut 20 g of bacterial cellulose wet film secreted by Glucoacetobacter xylinus cultured by static fermentation into small pieces, add it to 100 mL of water, use a tissue grinder to separate into small pieces, and let it stand for a while After the solution is still not suspended in water, add 100 mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 4.5% to make the solid content of bacterial cellulose in the system reach 0.15%, and stir the system with a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 30 min; add 0.024 mL of 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride 65wt% aqueous solution, so that the molar ratio of glucose monomer in bacterial cellulose to 0.1:1, heated to 40 ° C in a magnetic stirrer Under the conditions, the reaction was stirred for 6 hours; the system was separated from the solid and liquid using a centrifuge at 5000 rpm, and 200 mL of 0.005 M hydrochloric acid solution was added to wash the cationized bacterial cellulose for several times until ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Cut 10 g of bacterial cellulose wet film secreted by Glucoacetobacter xylinus cultured by static fermentation into small pieces, add it to 100 mL of water, use a tissue grinder to separate into small pieces, and let it stand for a while Afterwards, it was still not suspended in water, and then 100 mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 3% was added to make the solid content of bacterial cellulose in the system reach 0.075%, and the system was stirred for 30 min with a magnetic stirrer at room temperature; 0.24 mL of 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride 65 wt% aqueous solution, so that the molar ratio of glucose monomer in bacterial cellulose to 0.5:1, heated to 50 °C in a magnetic stirrer Under the conditions of stirring for 4 hours; the system was separated from the solid and liquid using a centrifuge at 5000 rpm, and 200 mL of 0.005 M hydrochloric acid solution was added to wash the cationized bacterial cellulose several times until the l...
Embodiment 3
[0032]Cut 30 g of bacterial cellulose wet film secreted by Glucoacetobacter xylinus cultured by static fermentation into small pieces, add it to 100 mL of water, use a tissue grinder to separate into small pieces, and let it stand for a while Afterwards, it was still not suspended in water, and then 100 mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 6% was added to make the solid content of bacterial cellulose in the system reach 0.225%, and the system was stirred with a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 30 min; 0.72 mL of 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride 65 wt% aqueous solution, so that the molar ratio of glucose monomer in bacterial cellulose to 1:1, heated to 60 °C in a magnetic stirrer Under the conditions of stirring for 2 hours; the system was separated from the solid and liquid using a centrifuge at 5000 rpm, and 200 mL of 0.005 M hydrochloric acid solution was added to wash the cationized bacterial cellulose several times until the liqu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com