Resource utilization zero-emission recycling process method of chemical waste nickel liquid
A process method, chemical nickel technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing waste liquid treatment costs, rising costs, burdens, etc., to reduce social Environmental capacity, reduced environmental pressure, and high operational safety factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
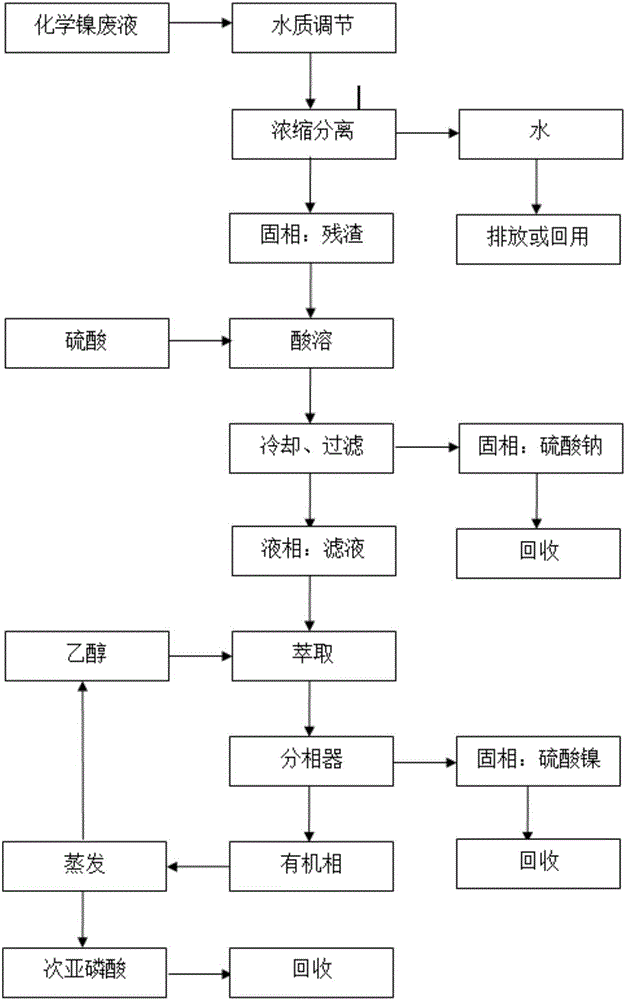
[0042]Example 1: A zero-discharge recycling process for chemical nickel waste liquid
[0043] The resource-based zero-emission recovery process method consists of the following steps:
[0044] The first step is to concentrate and separate the chemical nickel waste liquid:
[0045] Adjust the pH value of the chemical nickel waste liquid to 3~5, so that the ammonia nitrogen in the chemical nickel waste liquid exists in the form of ammonium salt; , the external heating temperature is 100°C, and the negative pressure condition is -0.09MPa. When heating, ensure that the boiling temperature of the chemical nickel waste liquid does not exceed 70°C. When the volume of the chemical nickel waste liquid is 10% of the original volume, stop evaporation. The chemical nickel residue is obtained, and the evaporated water vapor is condensed and turned into condensed water to be discharged. The COD content of the condensed water does not exceed 200mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen content of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: A zero-discharge recycling process for chemical nickel waste liquid
[0053] The resource-based zero-emission recovery process method consists of the following steps:
[0054] The first step is to concentrate and separate the chemical nickel waste liquid:
[0055] The pH value of the chemical nickel waste liquid is adjusted to 3~5, so that the ammonia nitrogen in the chemical nickel waste liquid exists in the form of ammonium salt; The external heating temperature is 95°C, and the negative pressure condition is -0.1MPa. When heating, ensure that the boiling temperature of the chemical nickel waste liquid does not exceed 70°C. When the volume of the chemical nickel waste liquid is 12% of the original volume, stop evaporation, and get Chemical nickel residue, the evaporated water vapor is condensed and then discharged into condensed water. The COD content of the condensed water does not exceed 200mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen content of the condensed water do...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com