Device and method for measuring soil water flow velocity on basis of thermal pulse method
A soil water and heat pulse technology, applied in the direction of using thermal variables to measure fluid velocity, etc., can solve the problems affecting measurement accuracy, distance influence, inability to use, etc., and achieve the effects of accurate measurement, stable heat transfer, and simple analysis method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. However, it should be understood that the accompanying drawings are provided only for better understanding of the present invention, and they should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
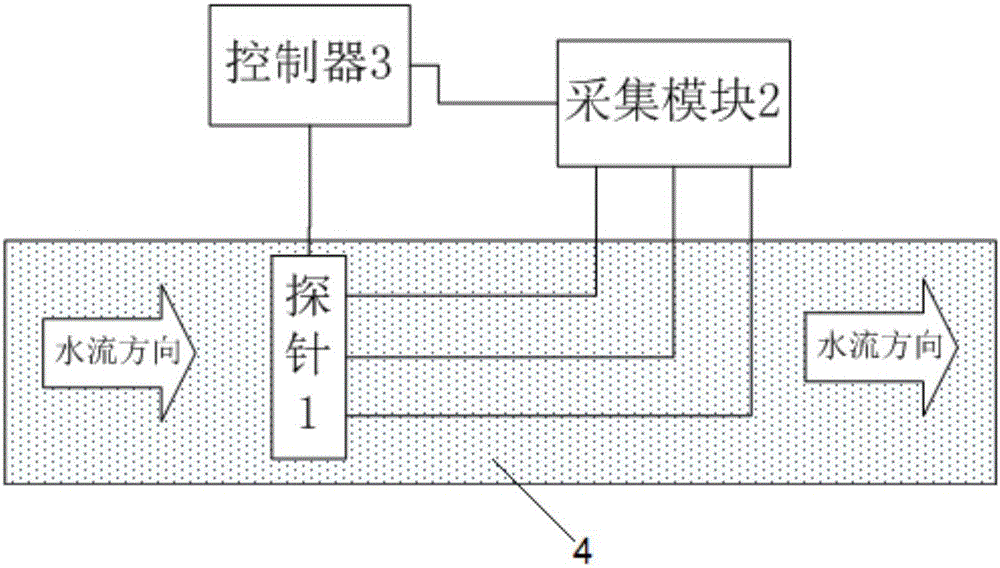
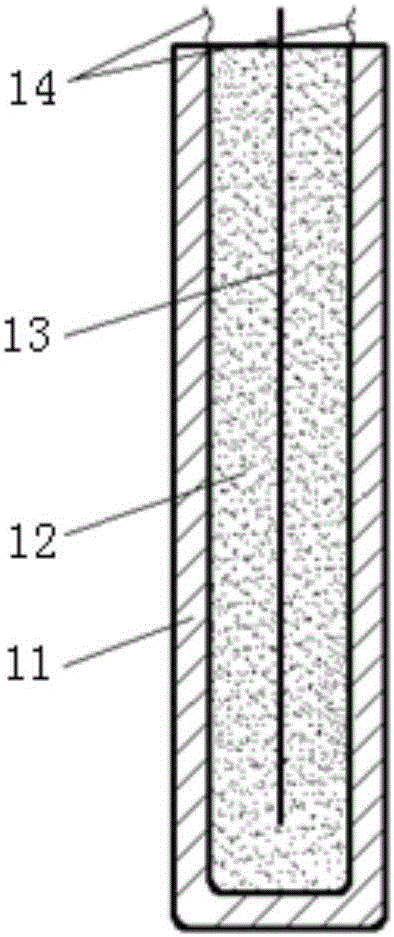
[0026] like Figure 1~2 As shown, the device for measuring soil water flow rate based on thermal pulse method of the present invention includes a probe 1, an acquisition module 2 and a controller 3; the probe 1 is all vertically inserted into the soil 4, and is in close contact with the soil 4, and the probe 1 includes Heat-conducting metal steel shell 11, insulating and heat-conducting material 12, heating resistance wire 13 and thermocouple bare wire 14, heat-conducting metal steel shell 11 is filled with high-temperature-resistant insulating and heat-conducting material 12 such as magnesium oxide, and insulating and heat-conducting material 12 is used for conduction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com