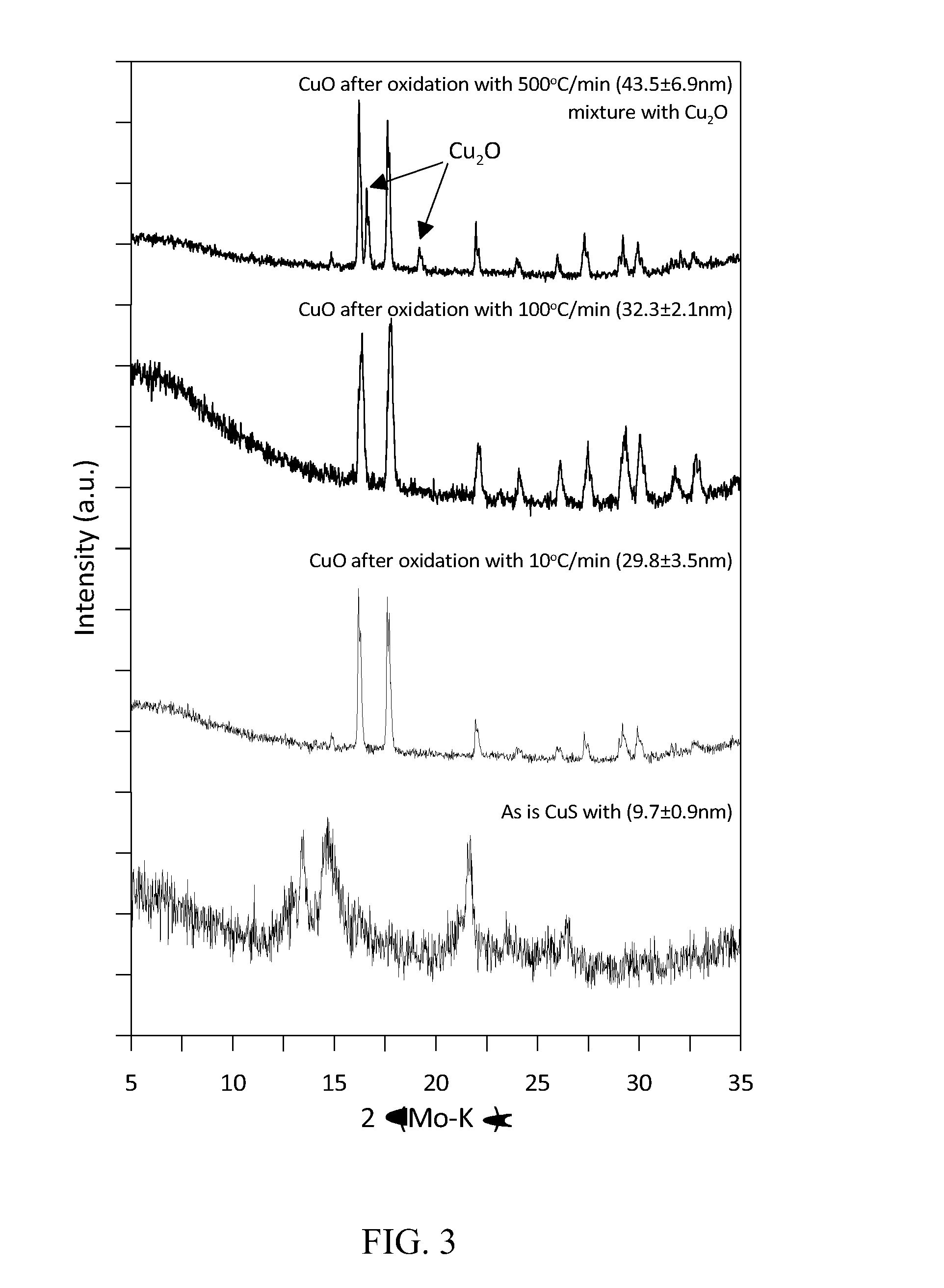
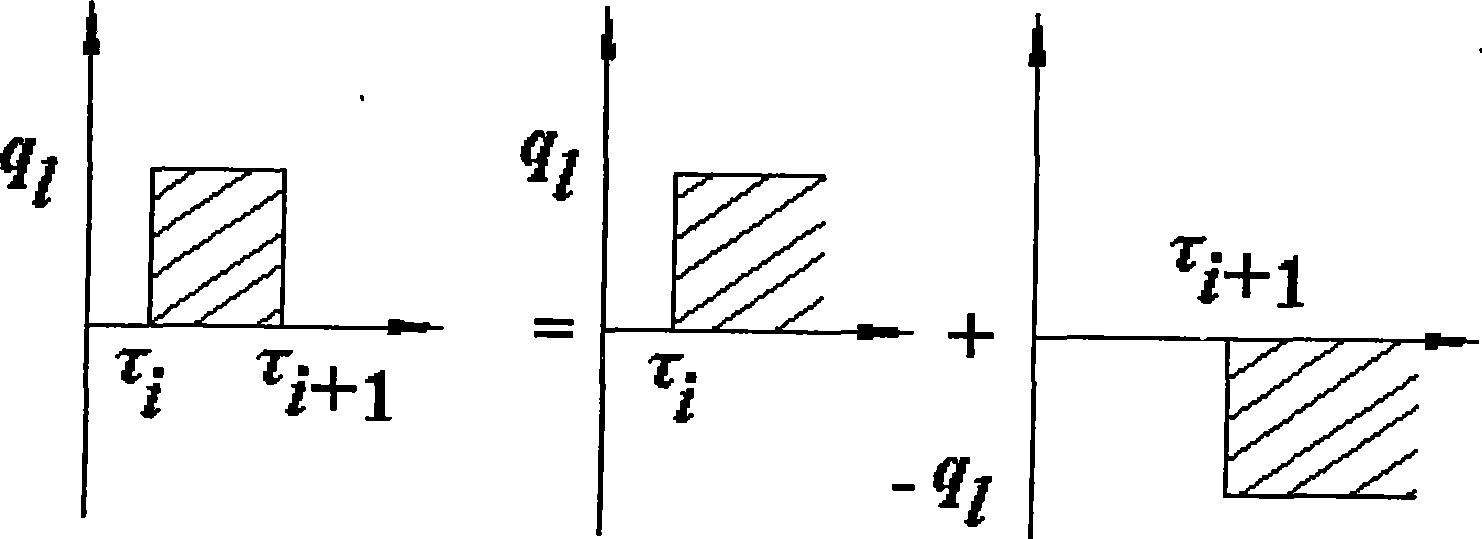Patents
Literature
46 results about "Thermal pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
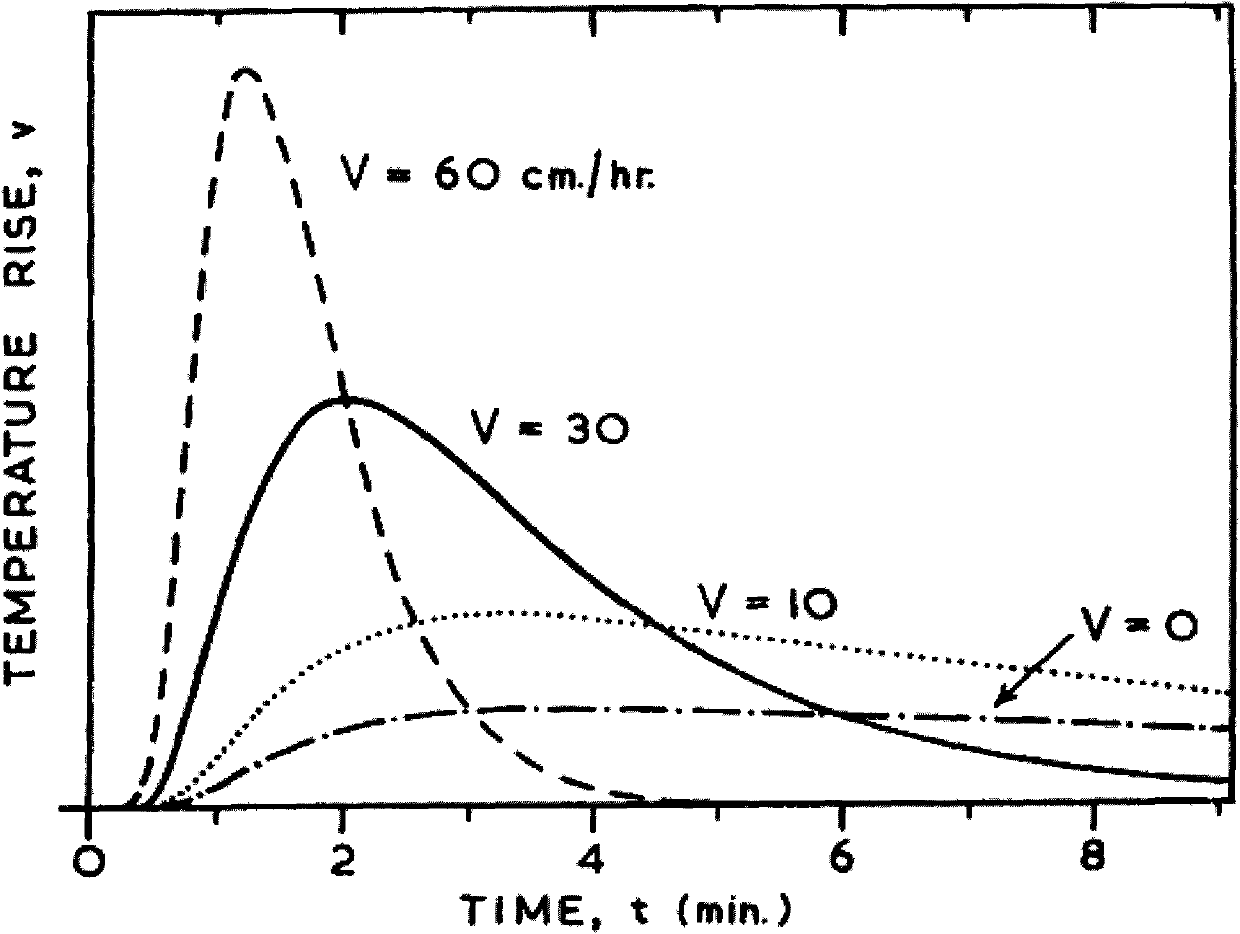
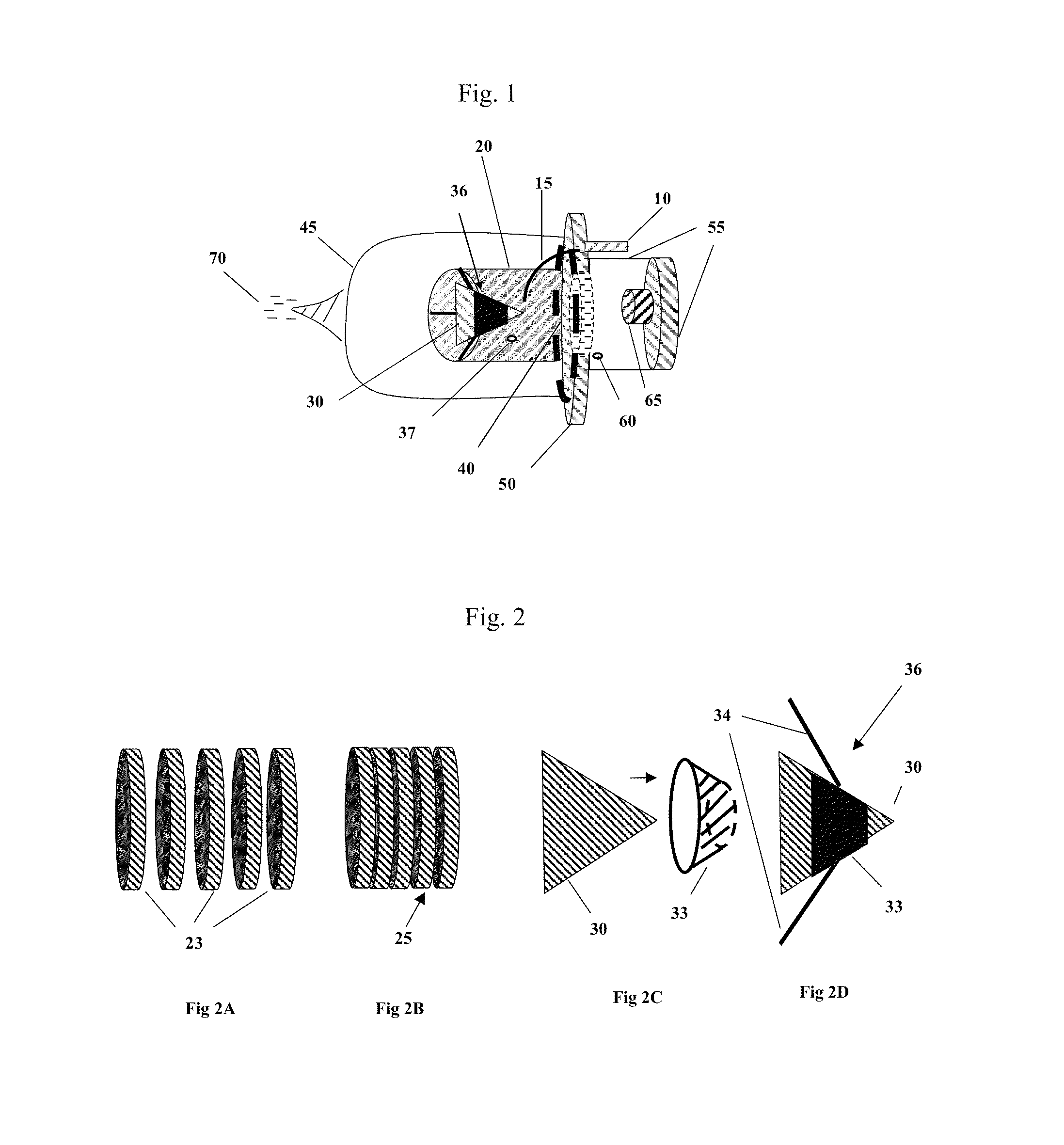
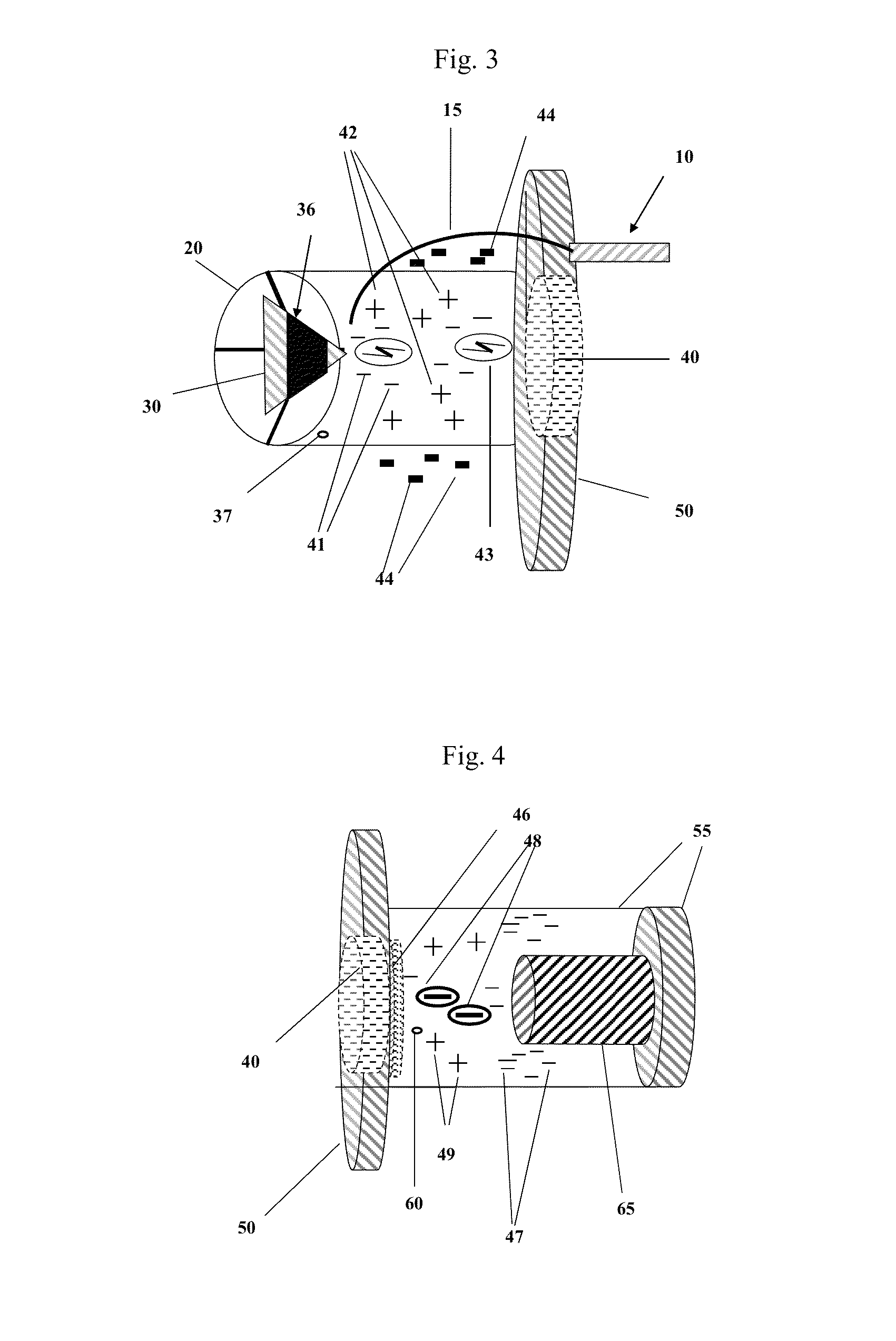
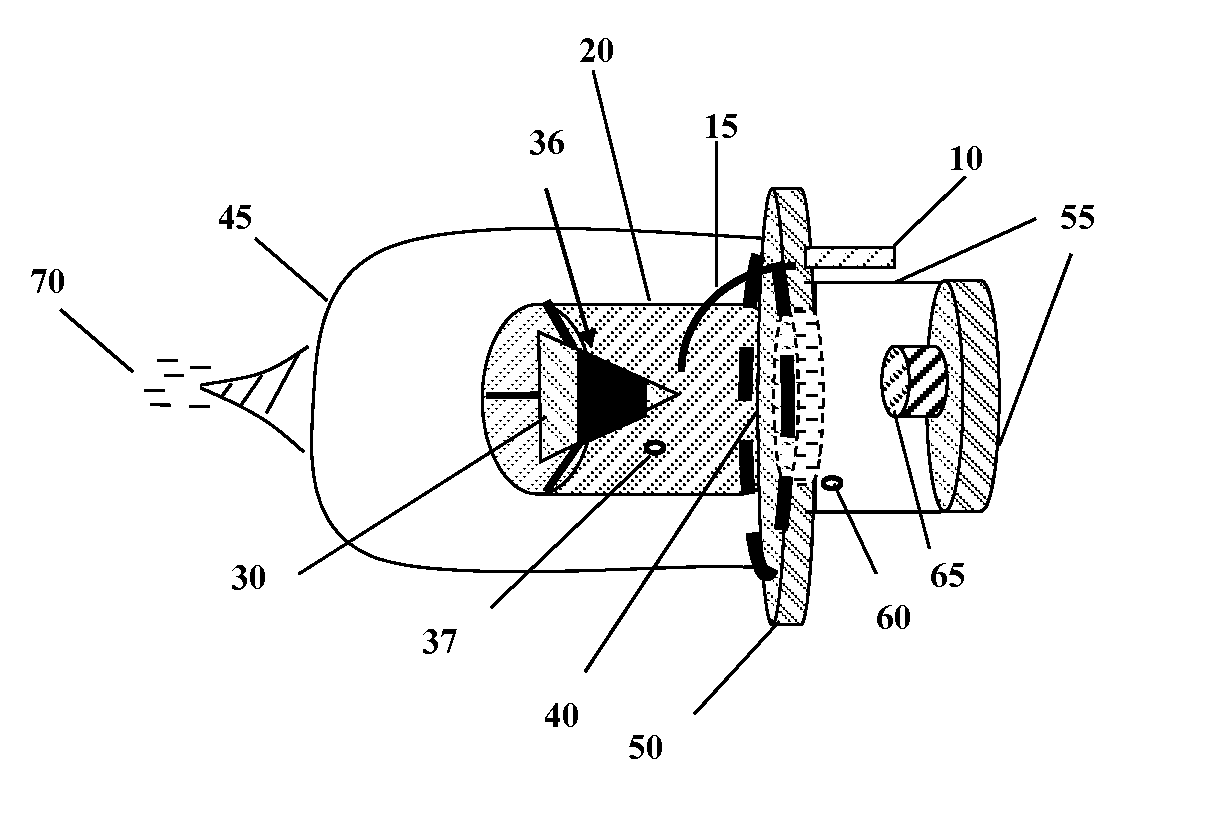
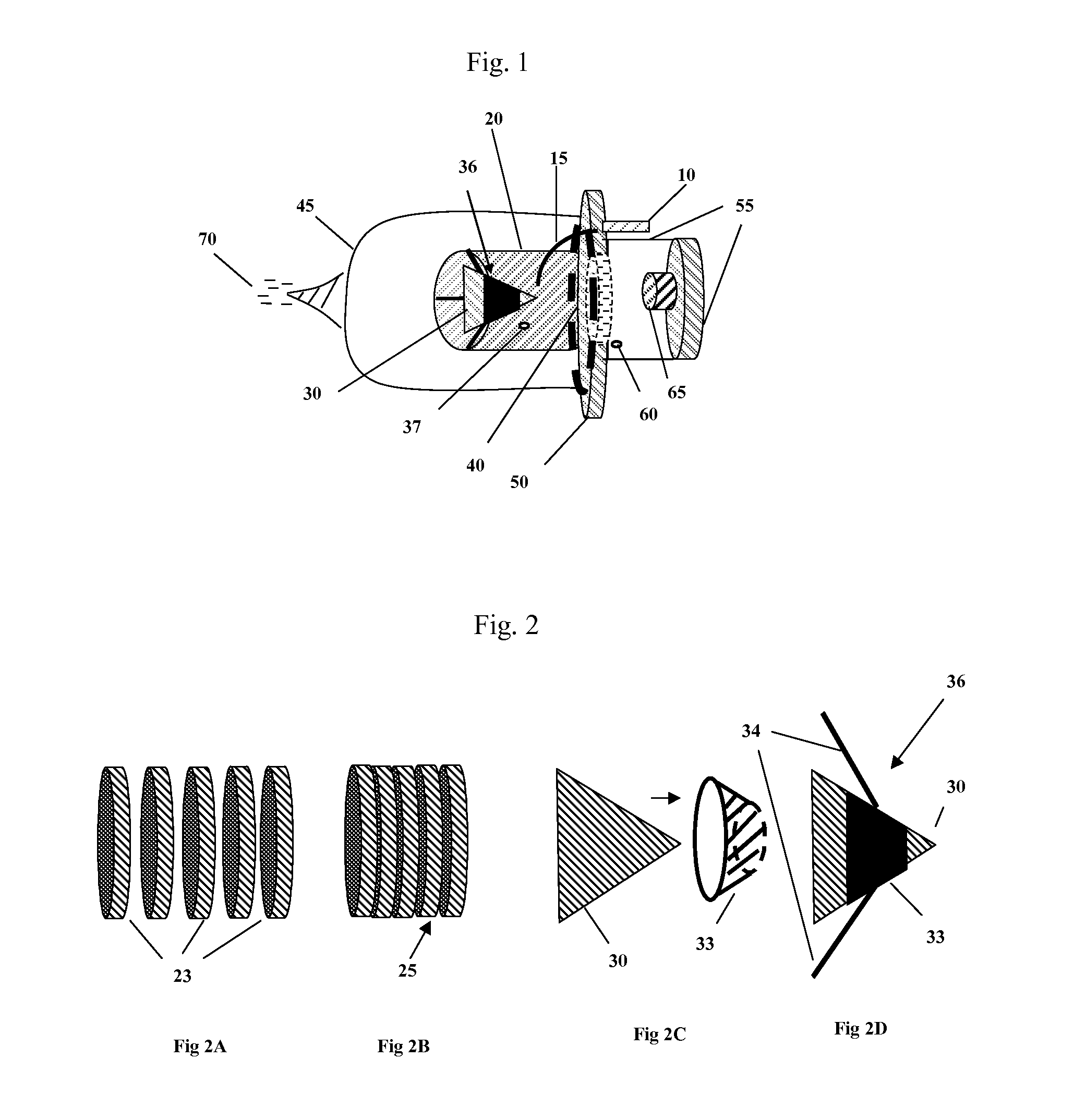
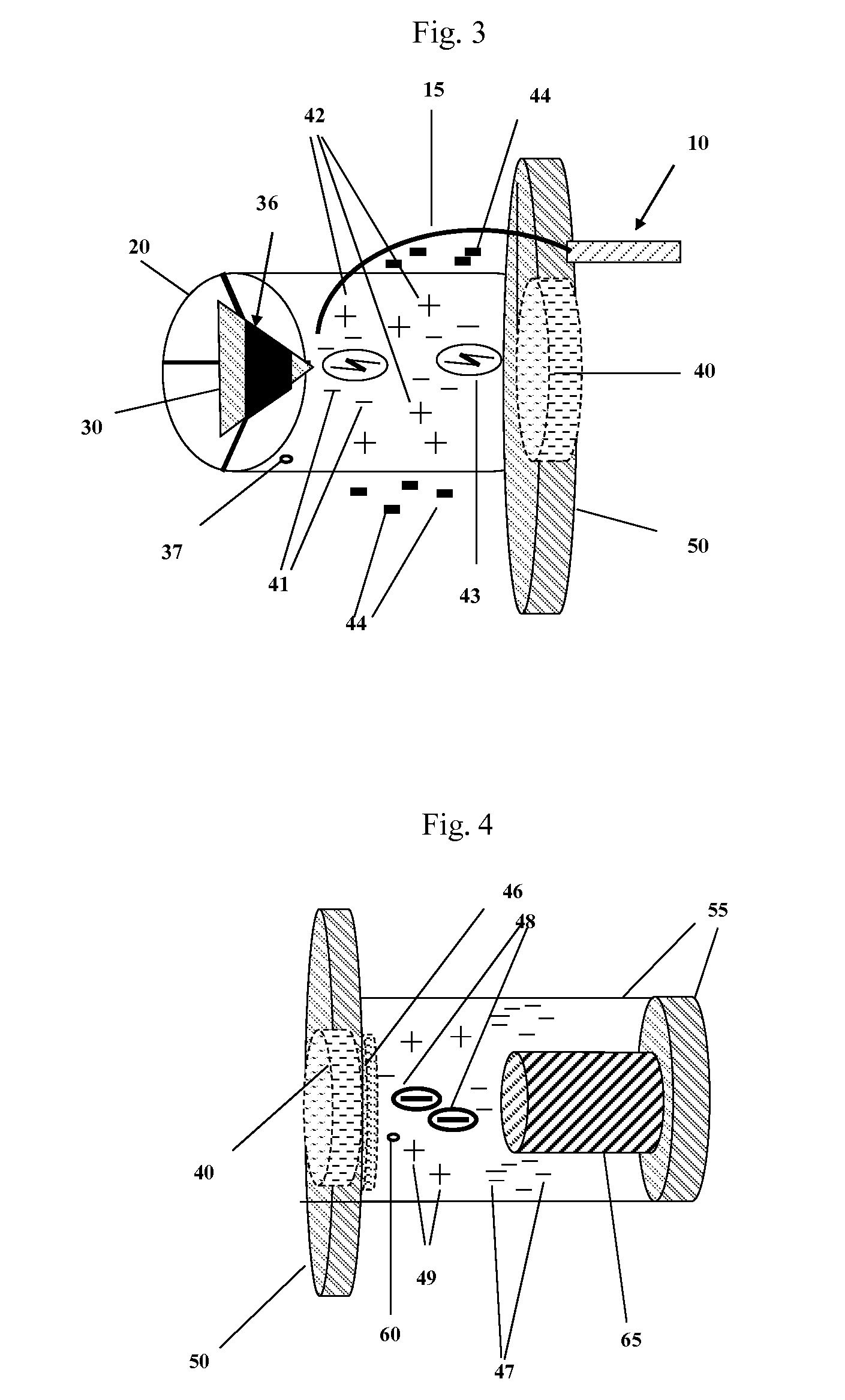
Thermal Pulse. The energy from the thermal pulse can initiate fires in dry, flammable, materials, such as; dry leaves, grass, old newspaper, thin dark flammable fabrics, etc. The incendiary effect of the thermal pulse is also substantially affected by the later arrival of the blast wave, which usually blows out any flames that have already been kindled.
Memory device with discrete layers of phase change memory material
InactiveUS6927410B2Reliably and more repeatedly programmableSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhase-change memoryInterface layer
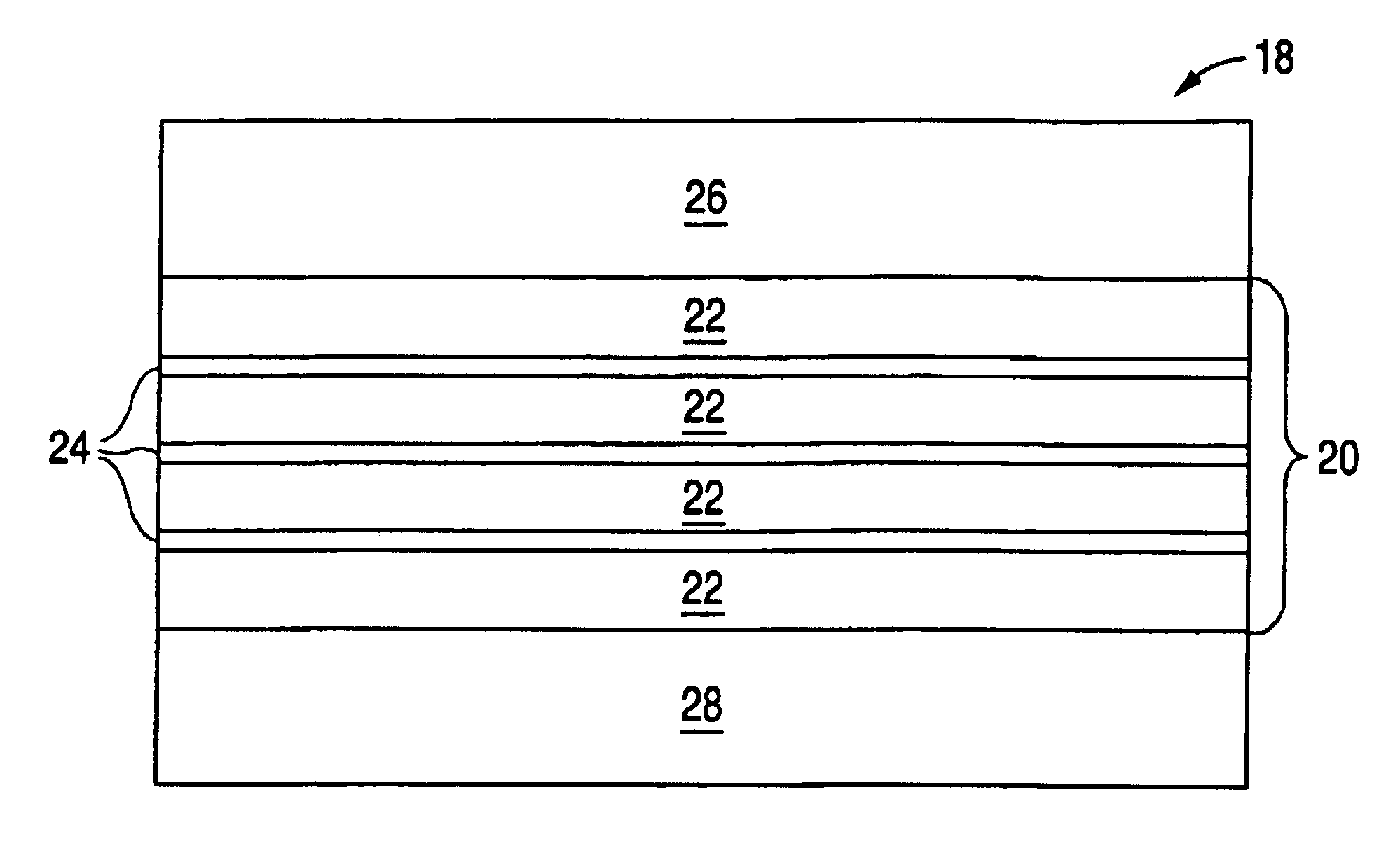
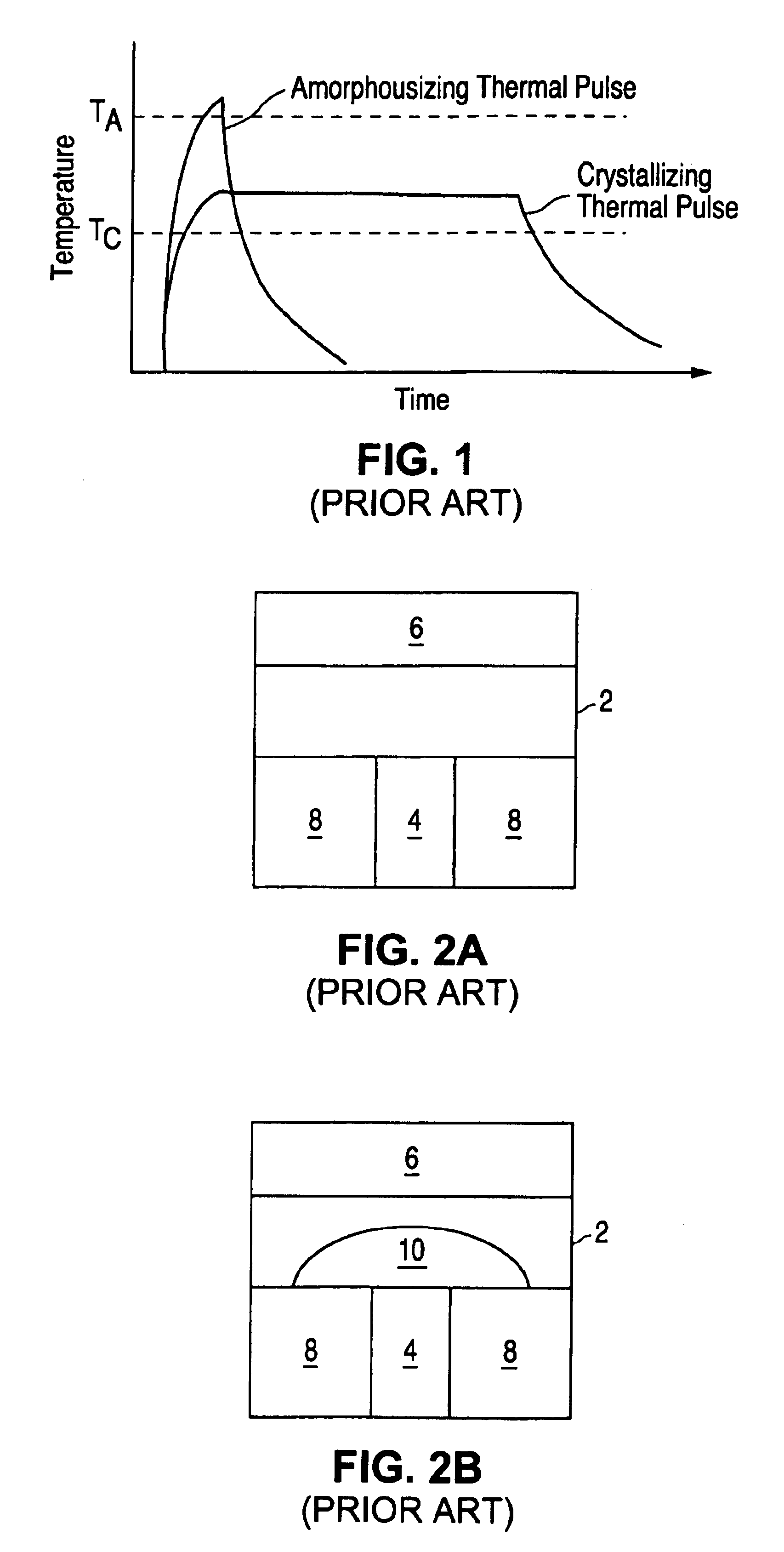
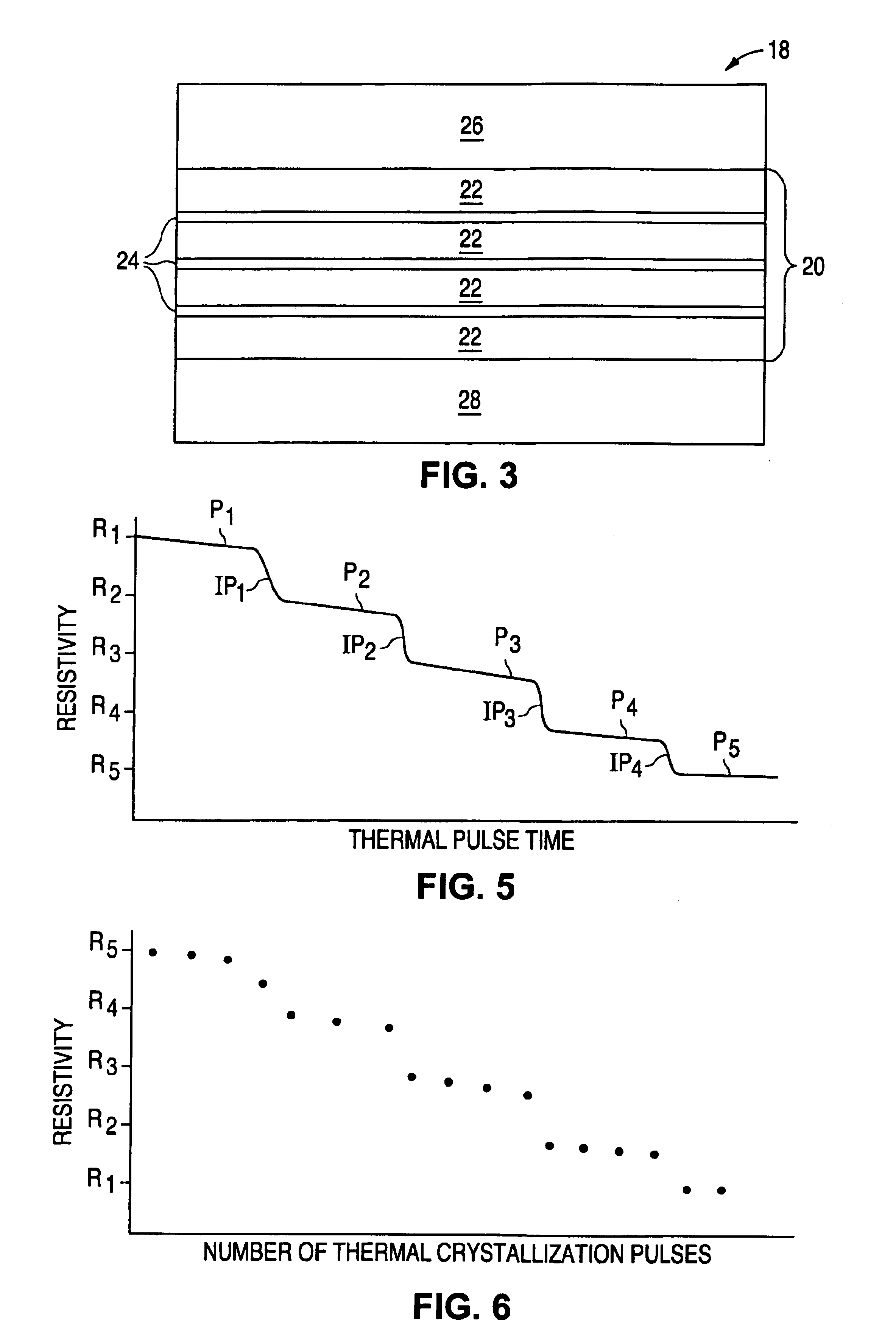
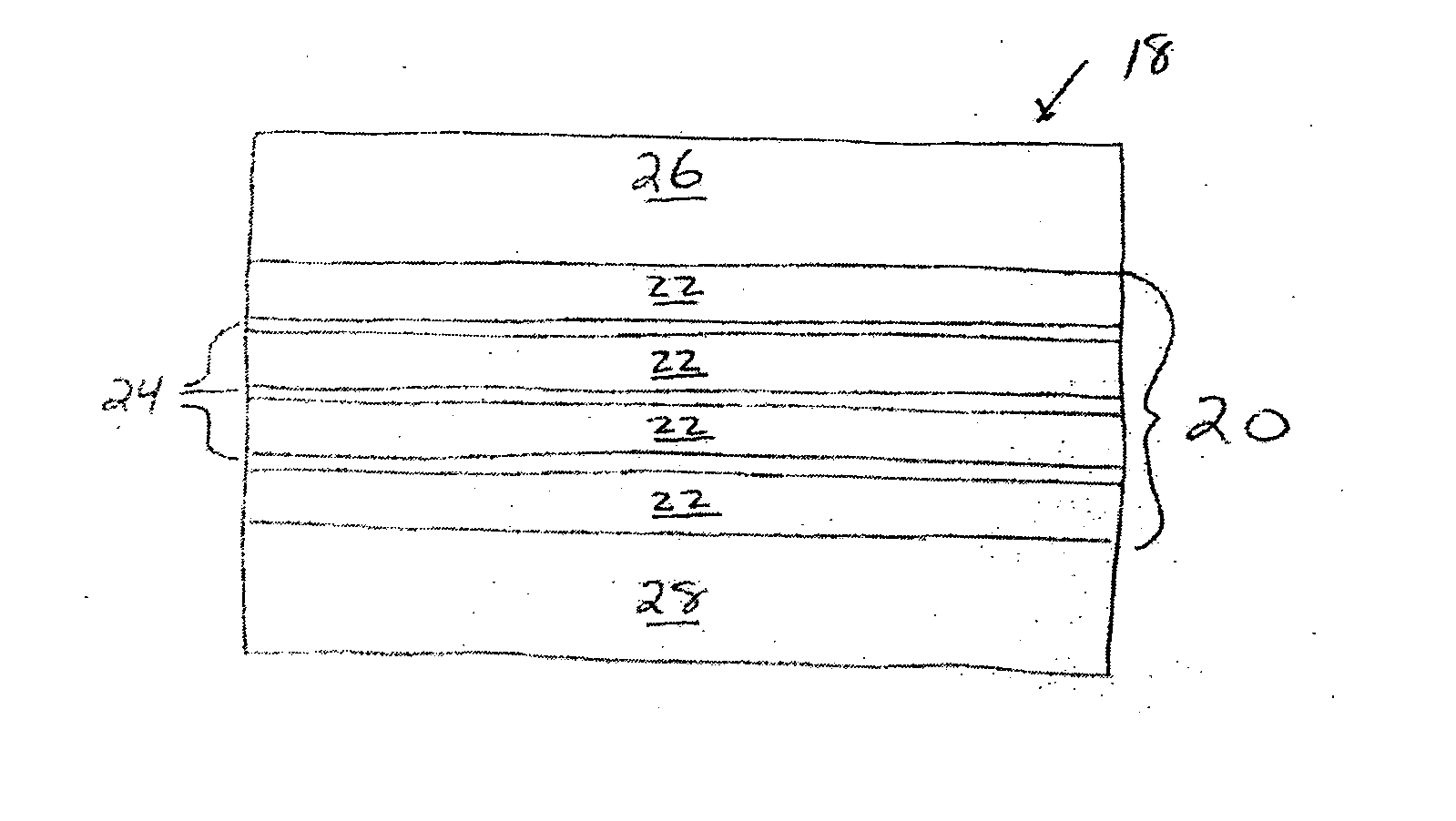
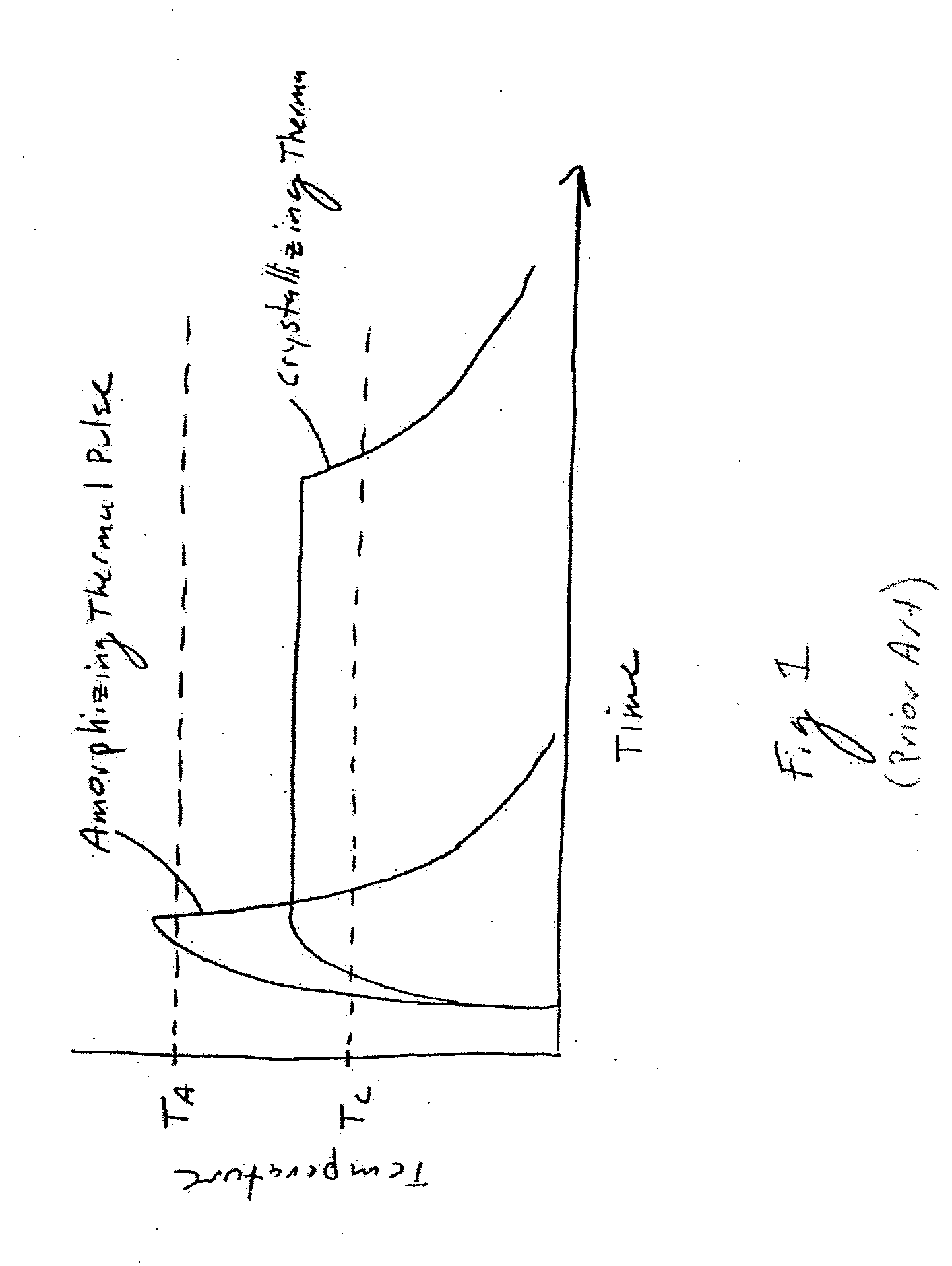
A phase changing memory device, and method of making the same, that includes programmable memory material disposed between a pair of electrodes. The programmable memory material includes discrete layers of phase change material, separated by conductive interface layers, that exhibits relatively stable resistivity values over discrete ranges of crystallizing and amorphousizing thermal pulses applied thereto, for multi-bit storage. The memory material and one of the electrodes can be disposed along spacer material surfaces to form an electrical current path that narrows in width as the current path approaches the other electrode, such that electrical current passing through the current path generates heat for heating the memory material disposed between the electrodes.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Memory device with discrete layers of phase change memory material
ActiveUS20050051901A1Reliably and more repeatedly programmableSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhase-change memoryInterface layer
A phase changing memory device, and method of making the same, that includes programmable memory material disposed between a pair of electrodes. The programmable memory material includes discrete layers of phase change material, separated by conductive interface layers, that exhibits relatively stable resistivity values over discrete ranges of crystallizing and amorphousizing thermal pulses applied thereto, for multi-bit storage. The memory material and one of the electrodes can be disposed along spacer material surfaces to form an electrical current path that narrows in width as the current path approaches the other electrode, such that electrical current passing through the current path generates heat for heating the memory material disposed between the electrodes.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
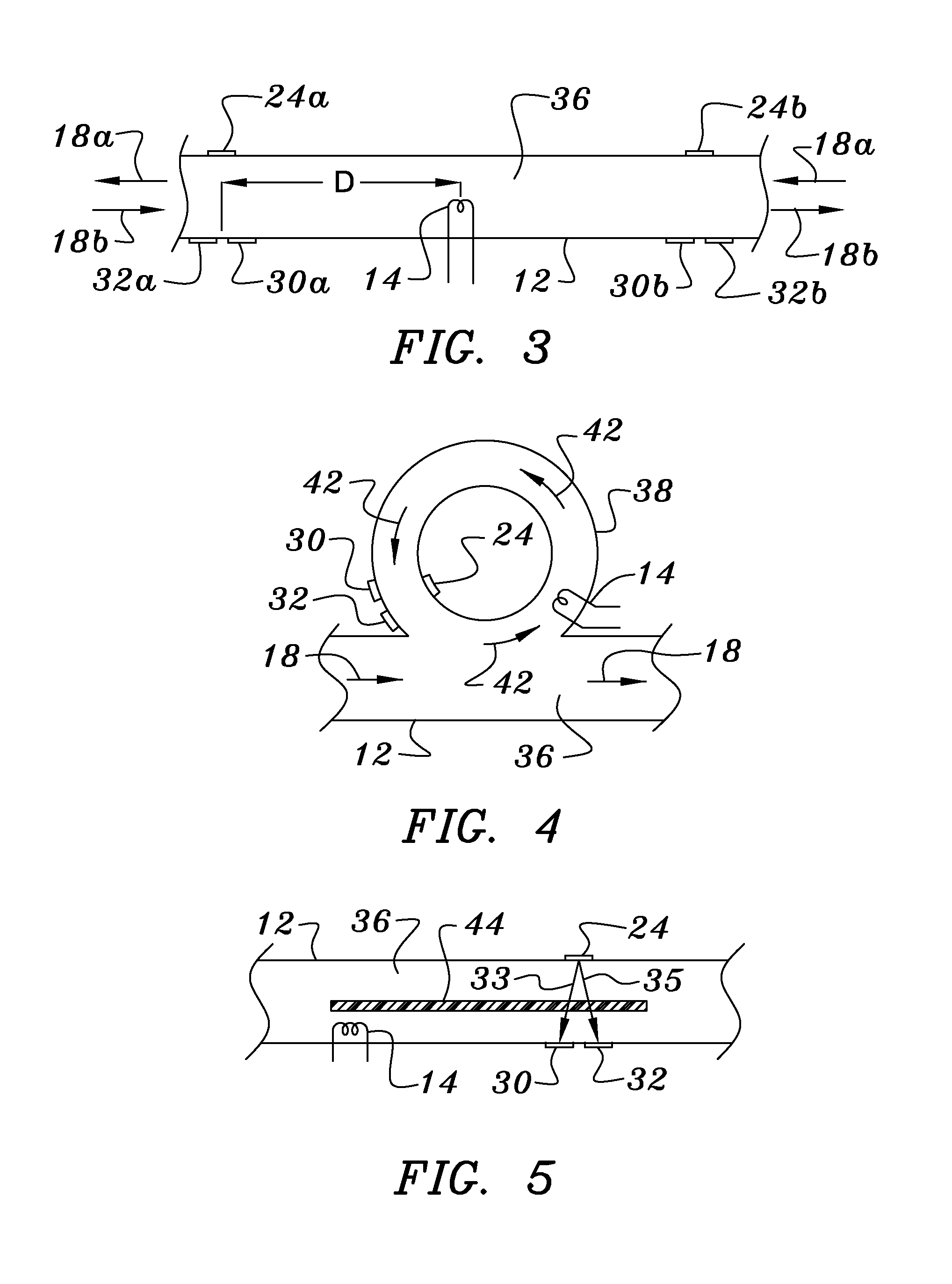
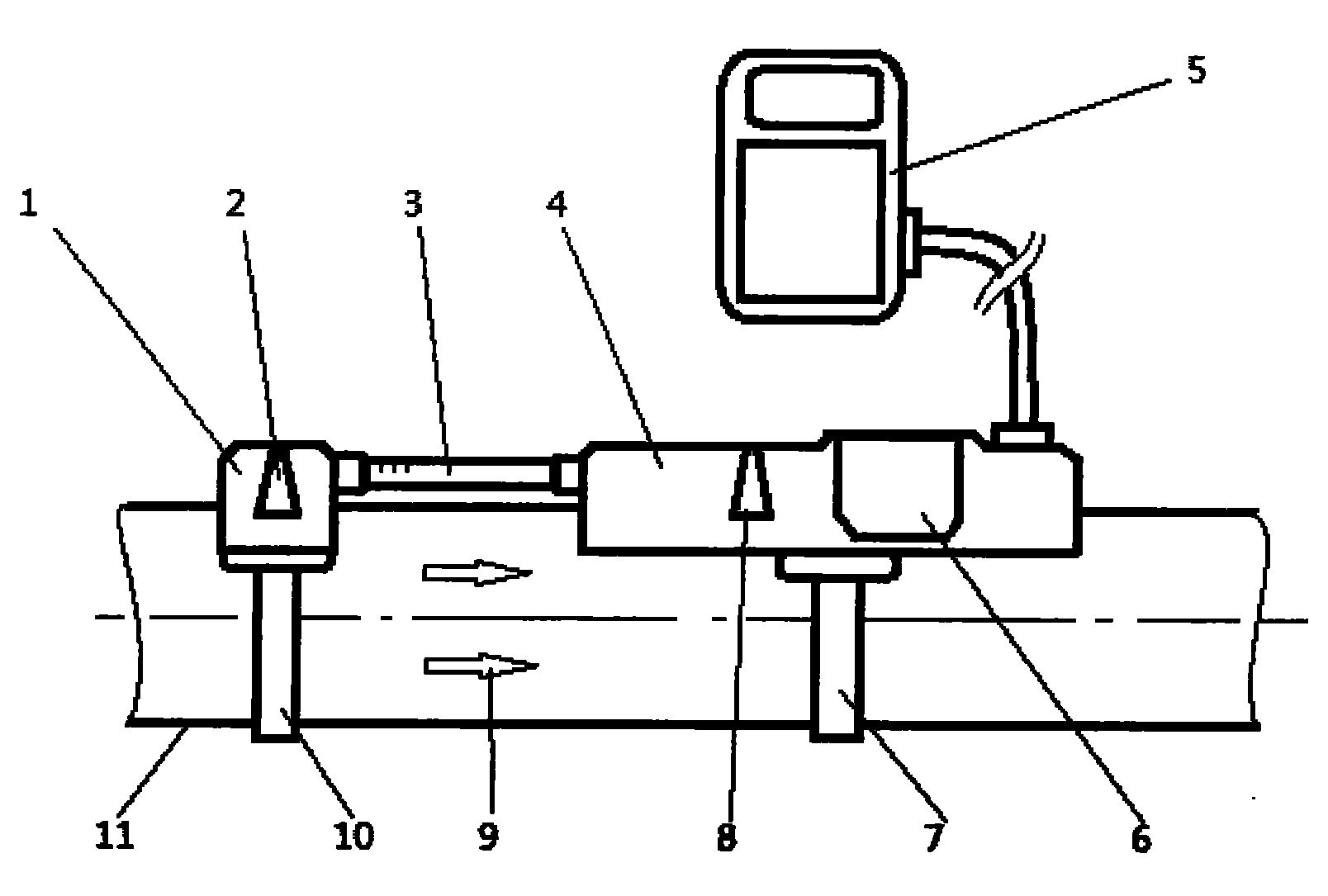
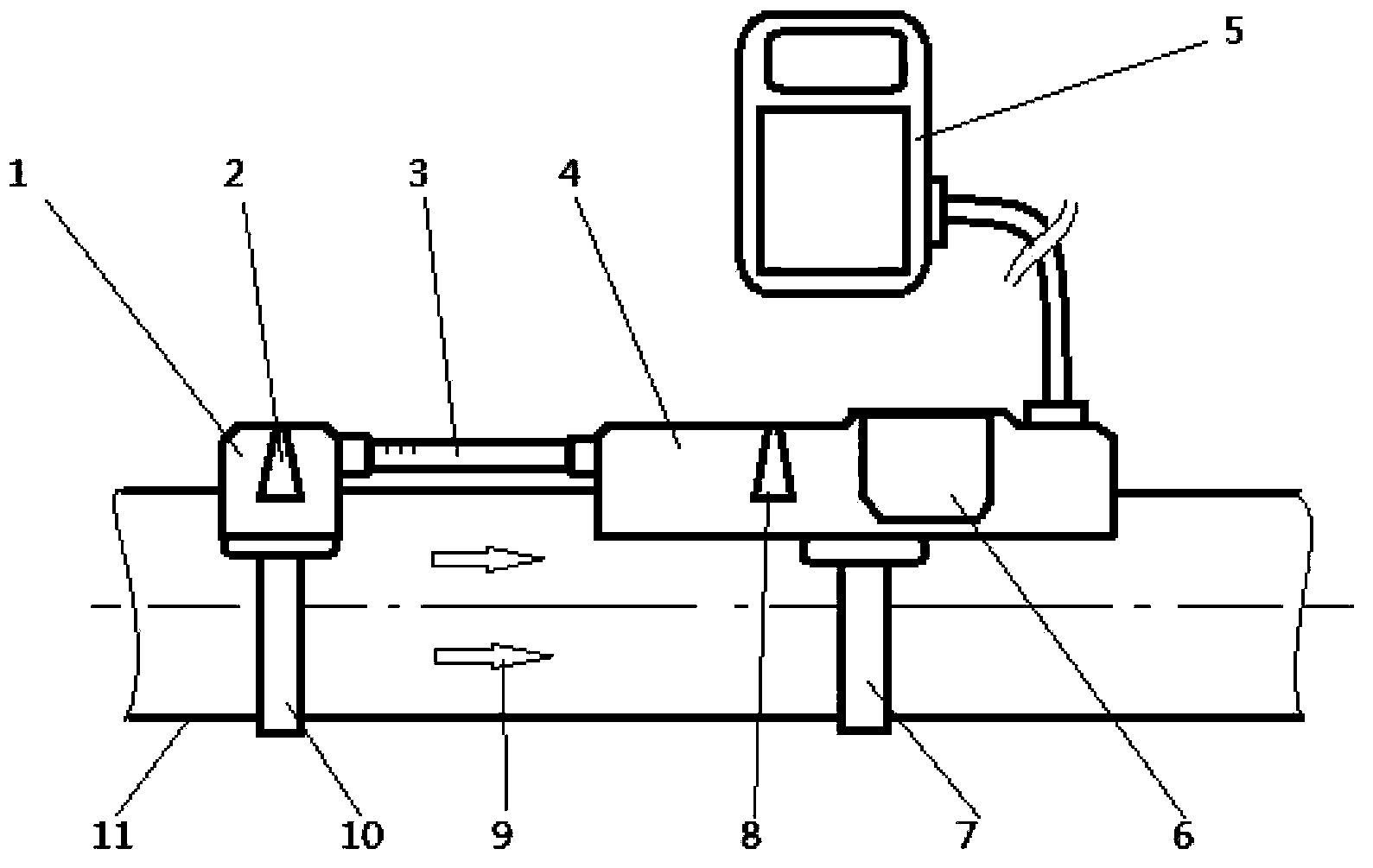
Thermal pulsed ultrasonic flow sensor
InactiveUS7270015B1Practical size limitationSmall sizeVolume/mass flow measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringAcoustic transmissionTransducer
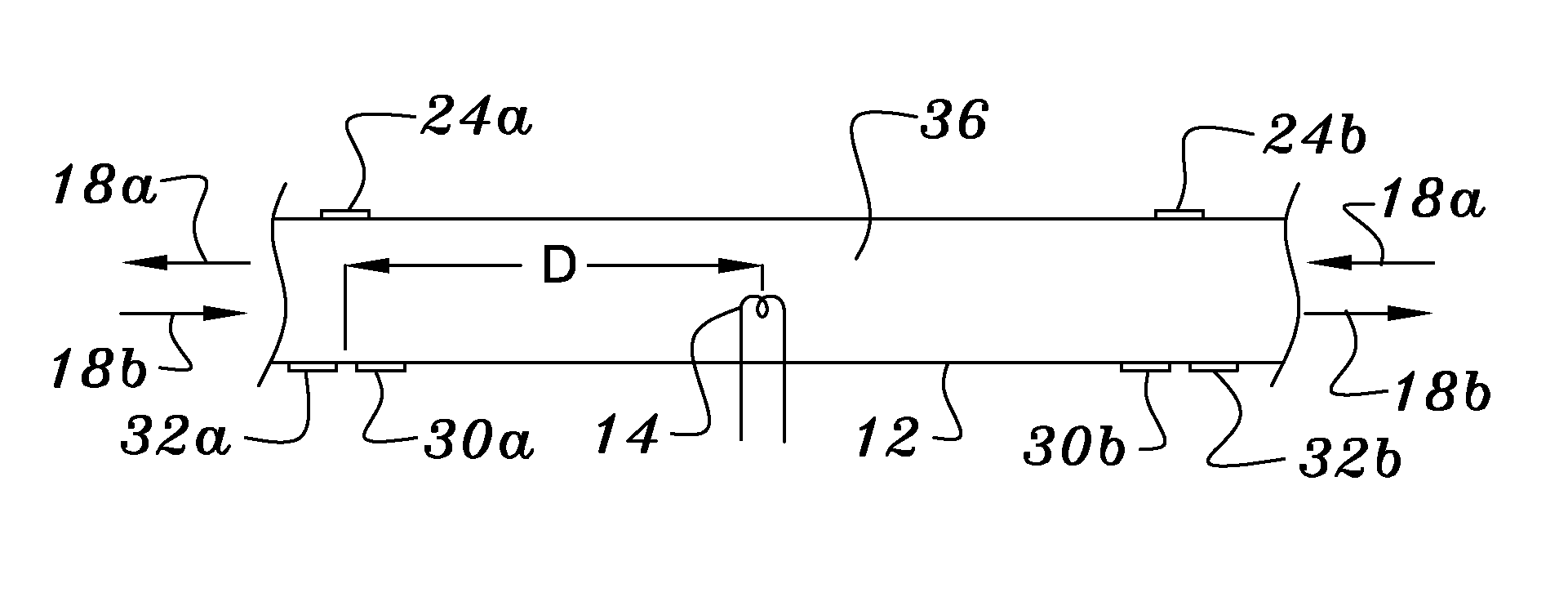
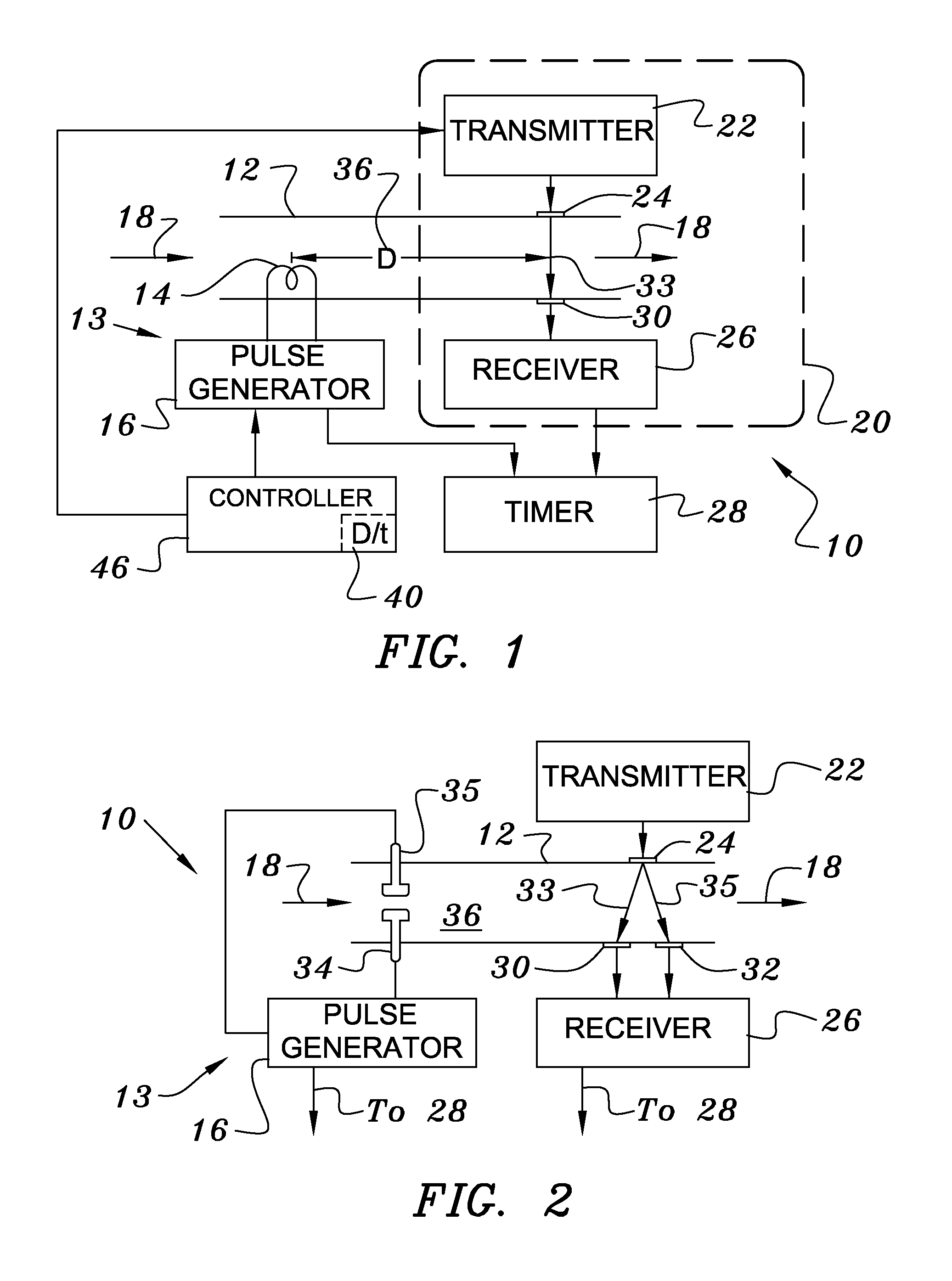
In thermal pulse flow measurements a relatively small bolus of flowing fluid is heated or cooled and the time required for the bolus to move downstream a known distance is measured. In many fluids, changing the temperature changes the acoustic transmission properties of the bolus from those of the rest of the fluid, so the bolus can be detected when it intersects an acoustic beam. The use of an acoustic beam or beams, which are usually defined between acoustic transmitting receiving transducers, typically provides a high frequency carrier which is modulated by the change in acoustic properties of the bolus when it passes between the two transducers. When compared to conventional thermal measurements, this acoustic approach provides faster response times and can thus be used for measuring higher flow rates.
Owner:ONICON INC
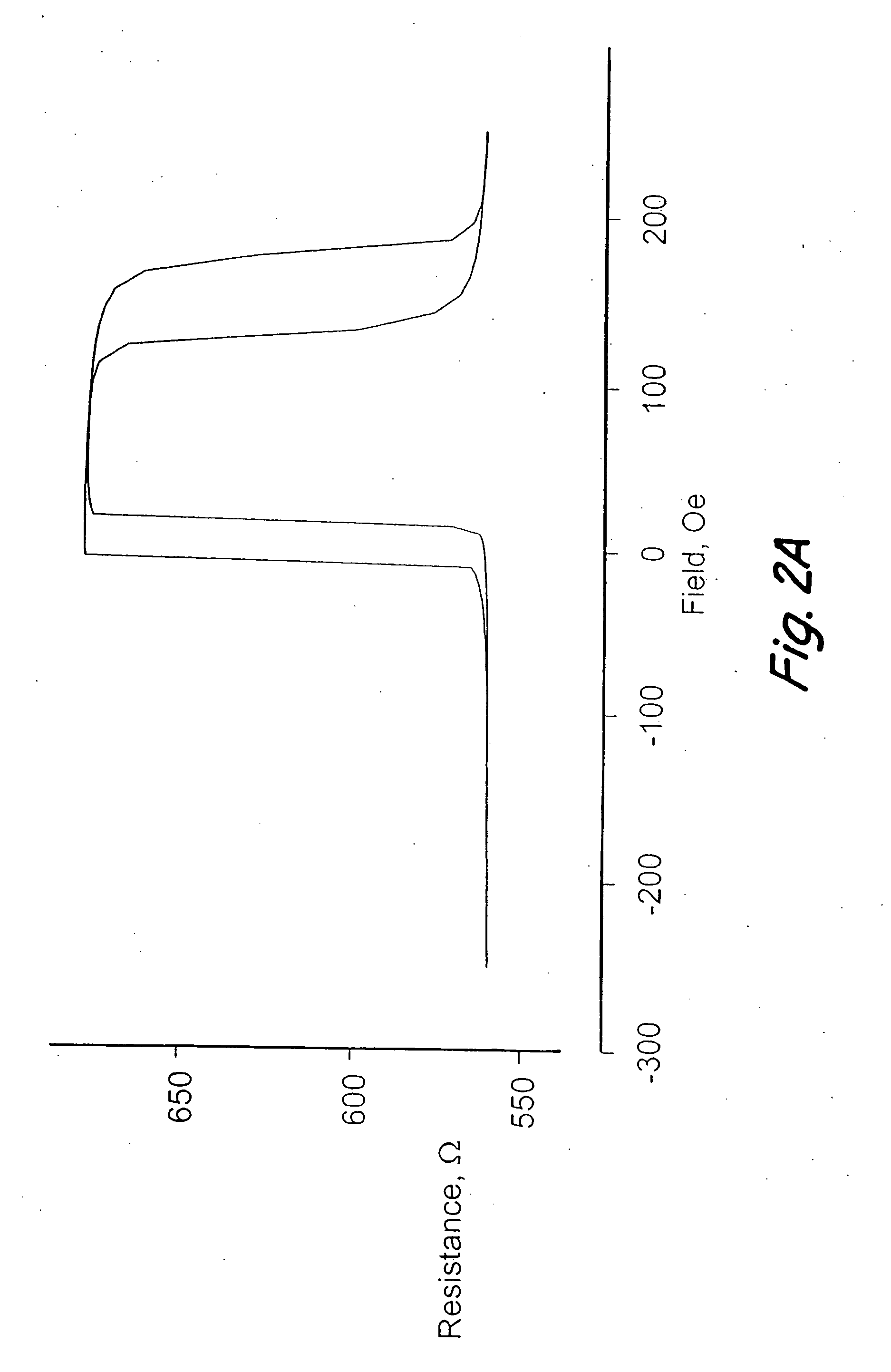
Magnetic memory layers thermal pulse transitions
InactiveUS20060083056A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryDigital storage
Owner:NVE CORP
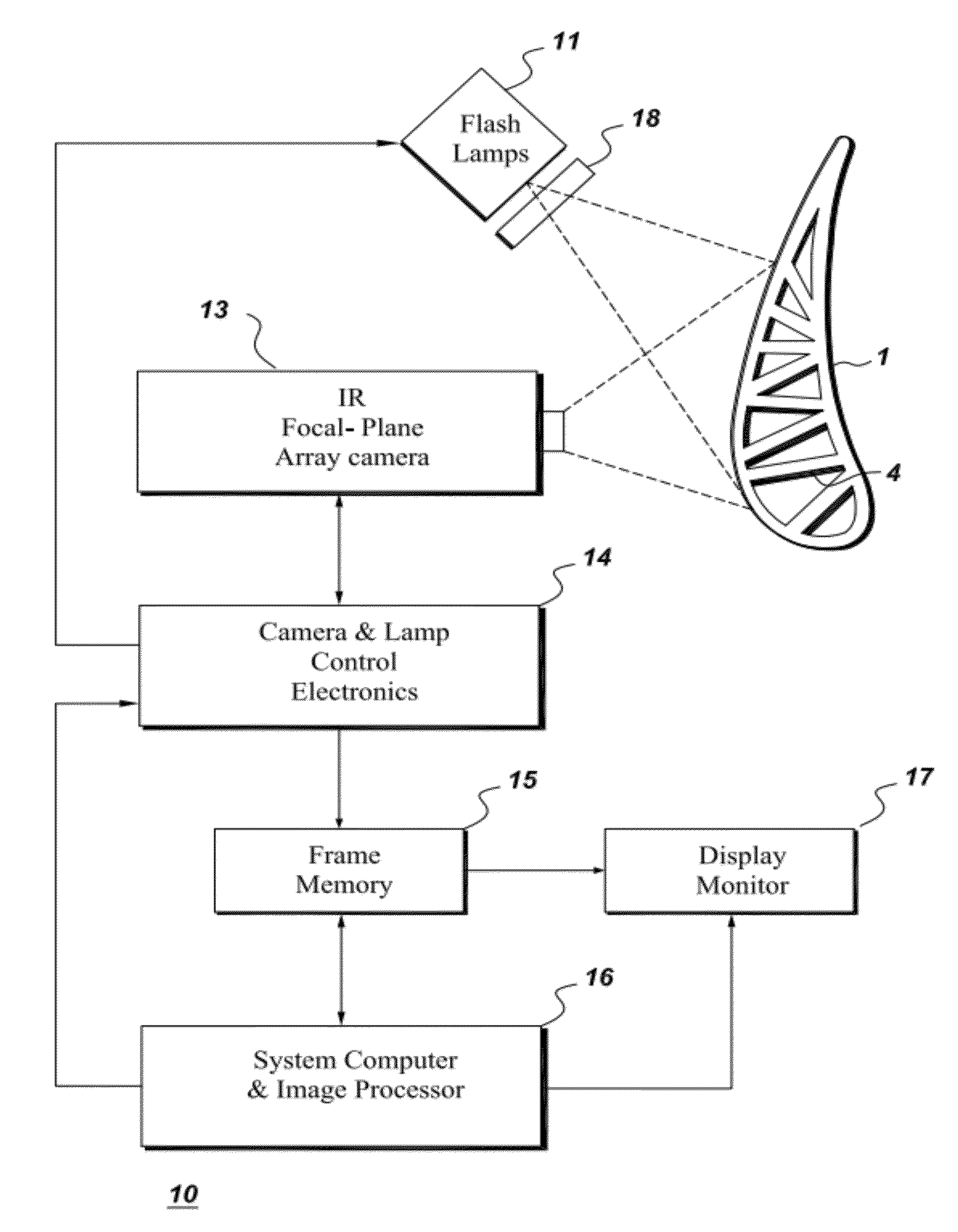
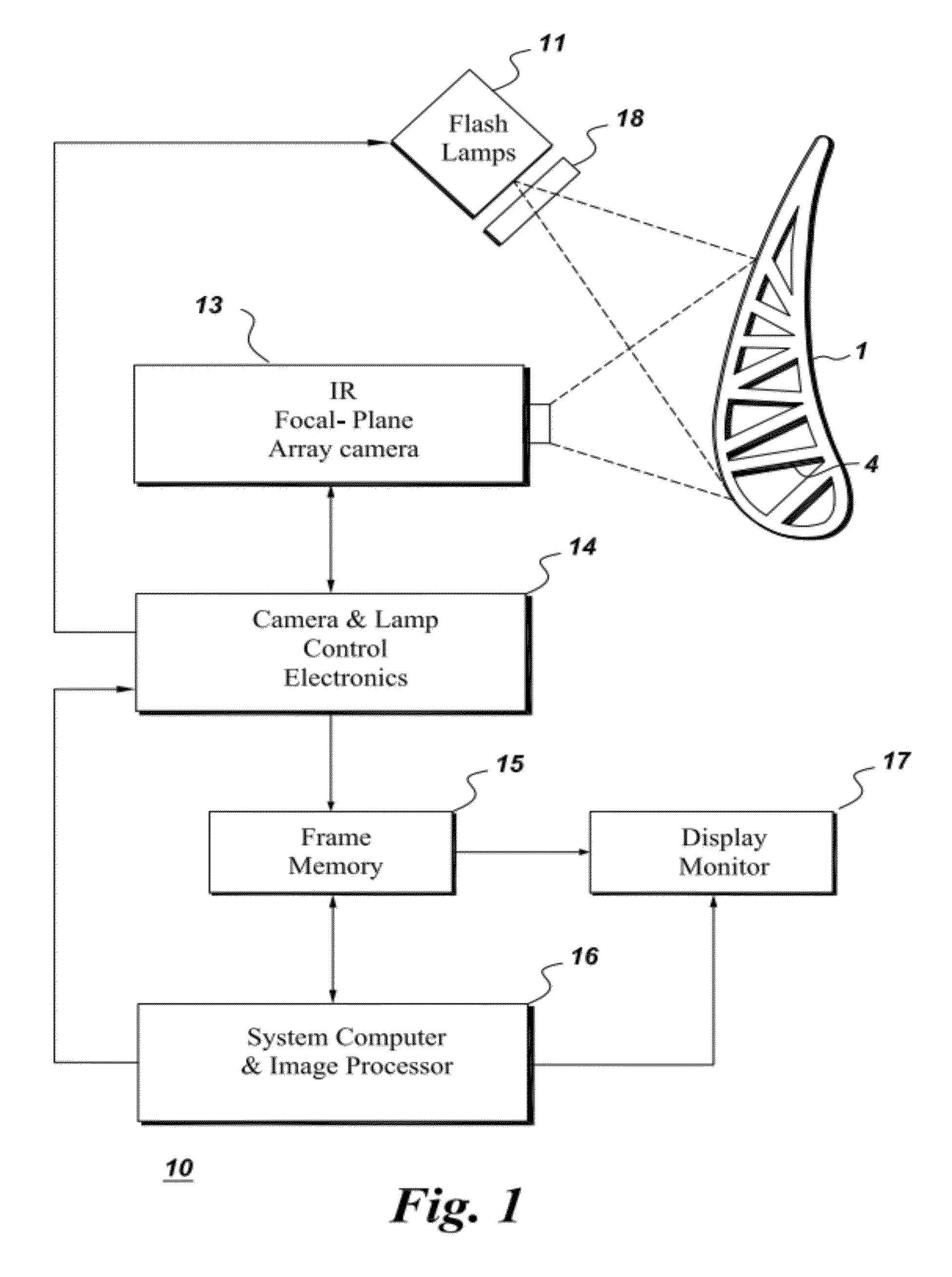
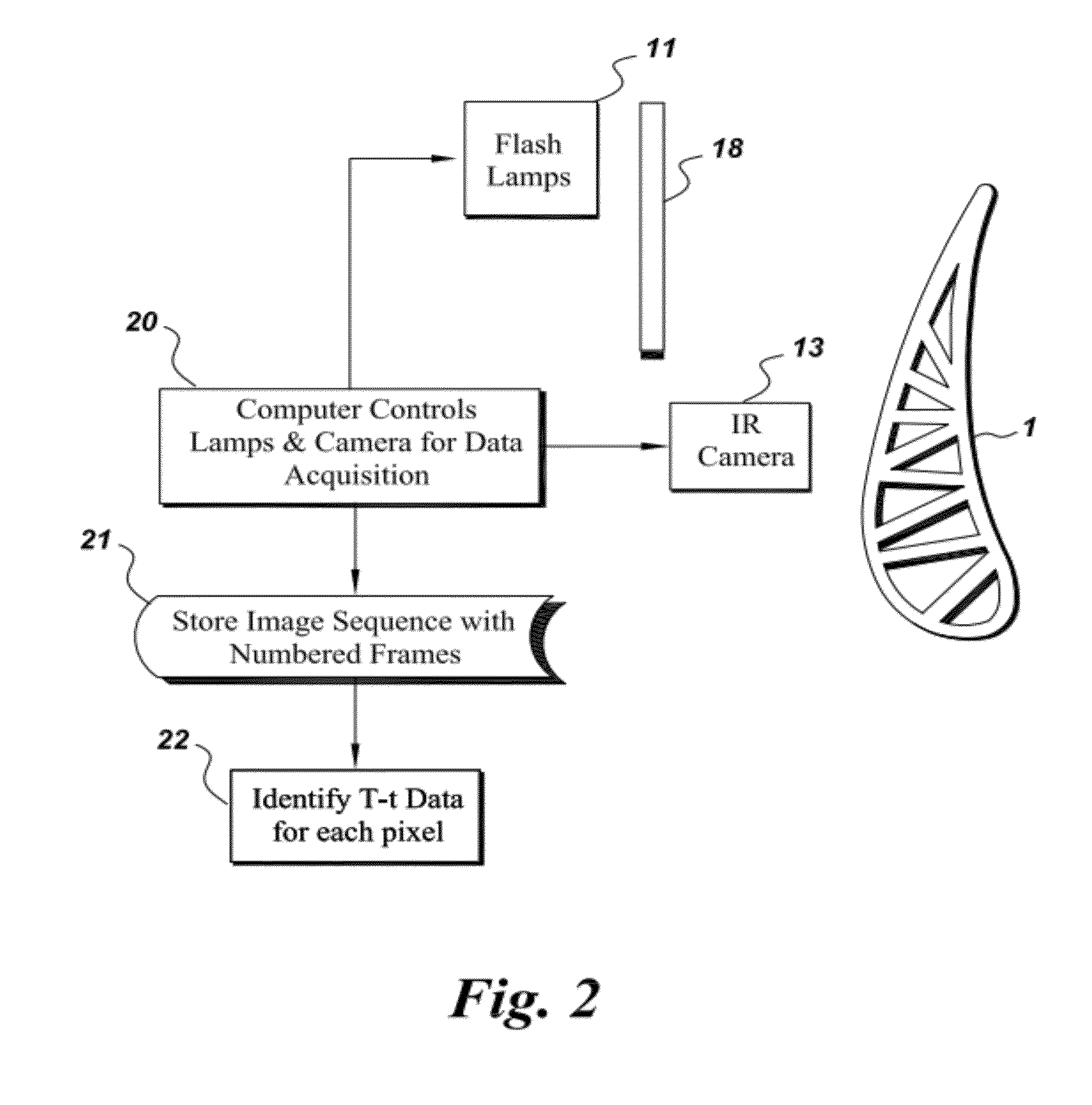
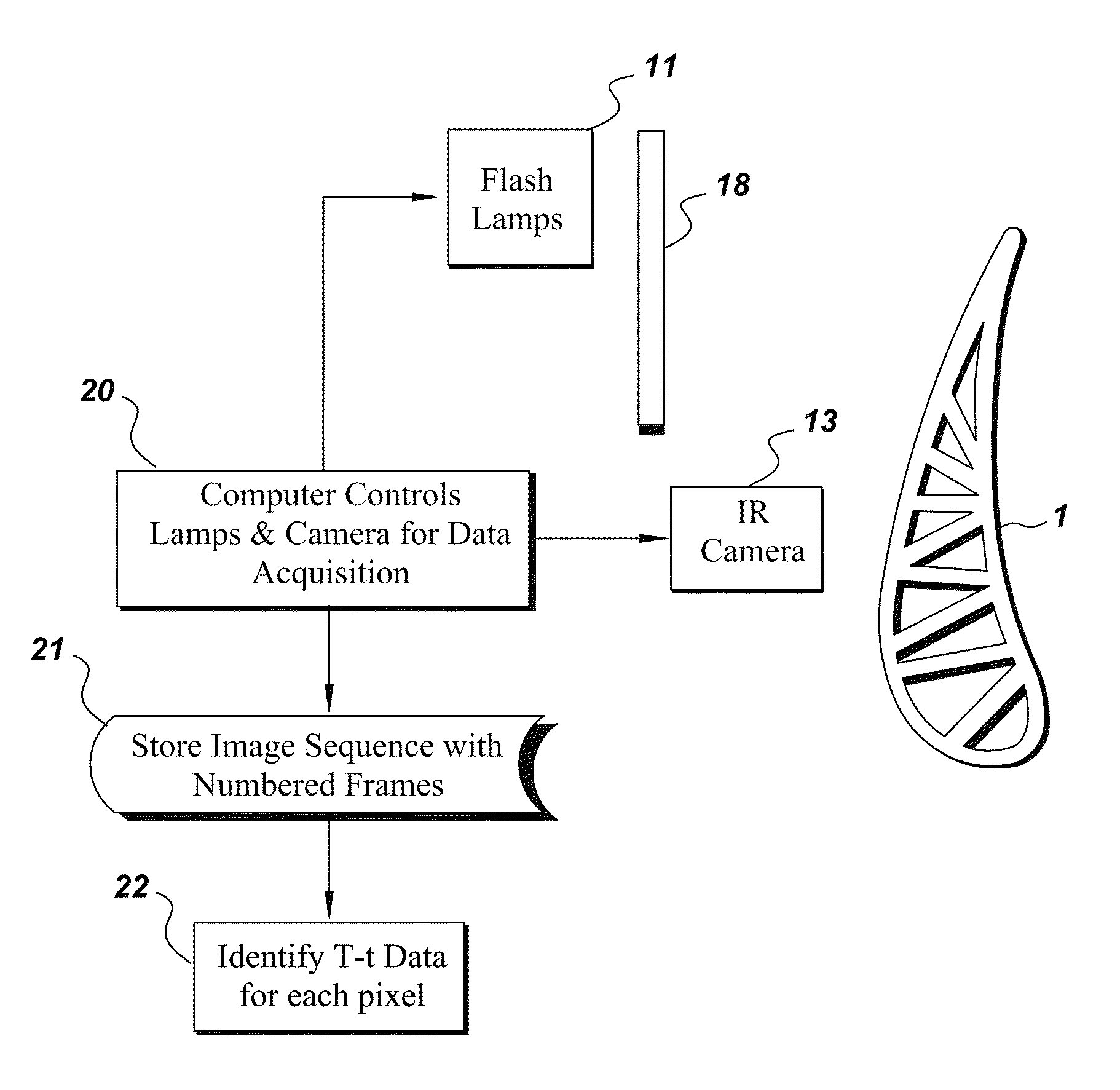
Thermal imaging method and appratus for evaluating coatings
InactiveUS20120050537A1Avoid high temperatureTelevision system detailsDigital computer detailsVariable thicknessCoated surface
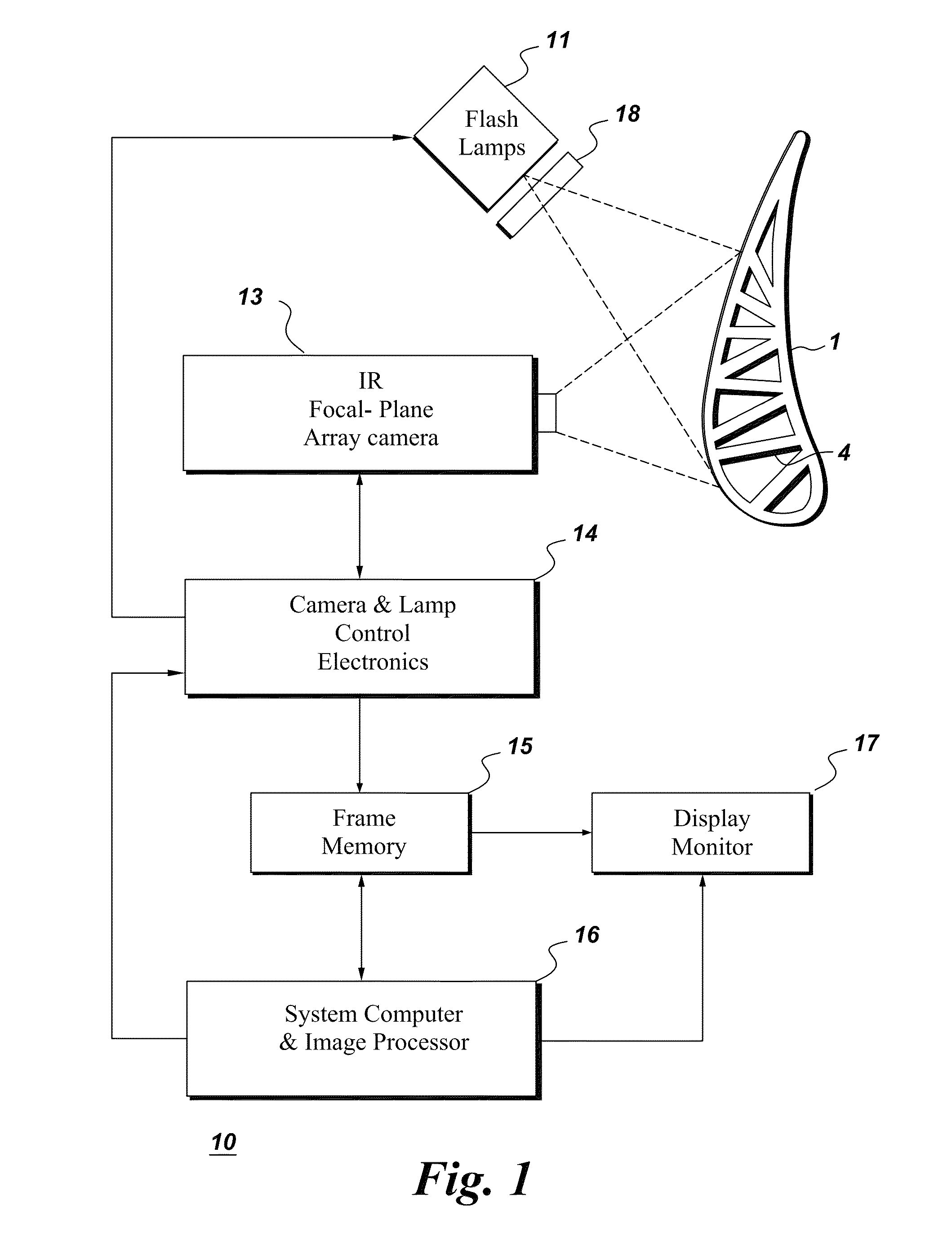
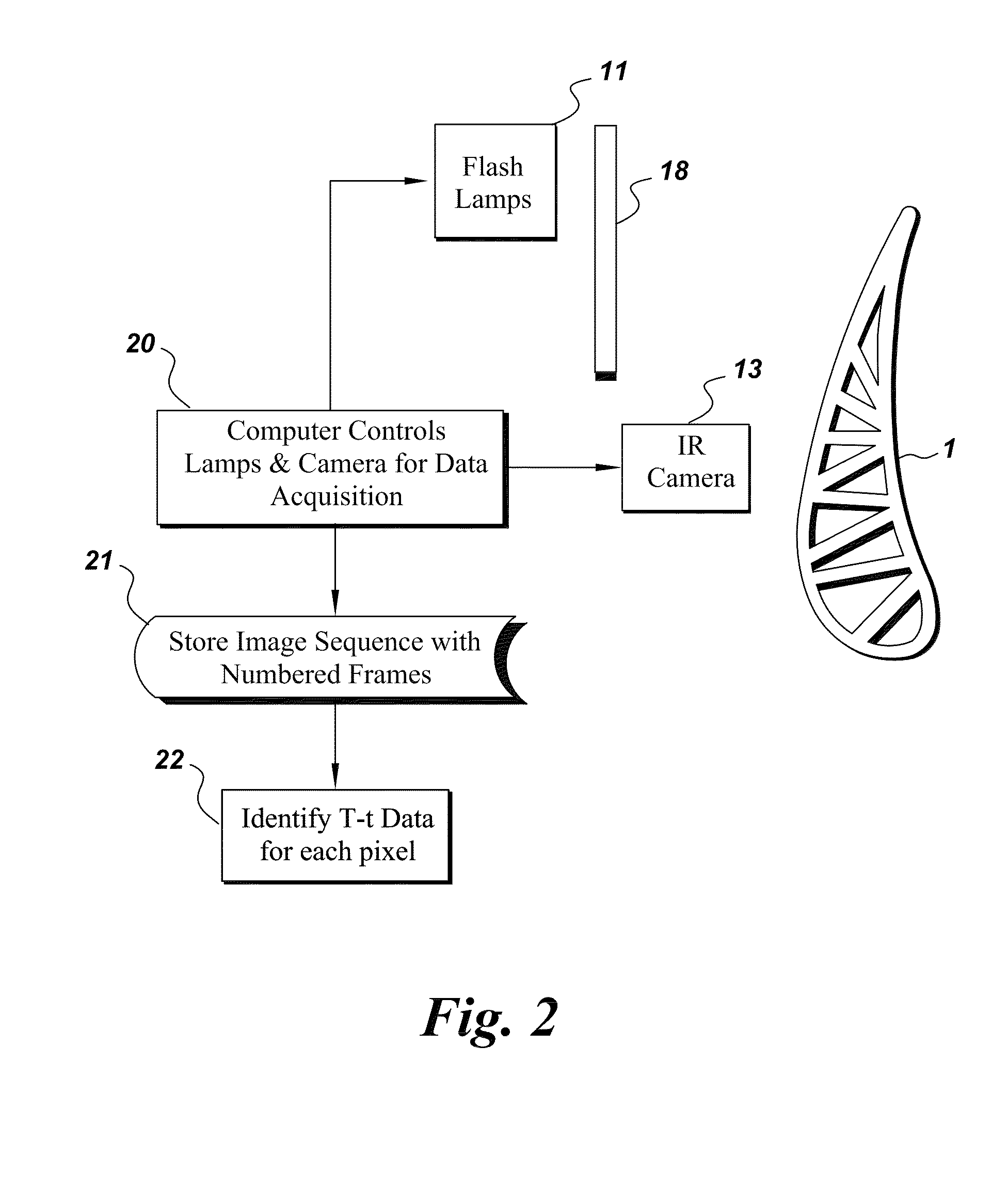
An apparatus is provided for determining variable thickness of a coating on a surface of a substrate using in part a flash-lamp source, capable of generating a thermal pulse at the coating surface, and a image capture and processing device capable of capture sequential image frames of the coating surface, whereas each sequential image frame corresponds to an elapsed time and comprises a pixel array, and wherein each pixel of the array corresponds to a location on the coating surface. A method of calculating coating thickness is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thermal imaging method and apparatus for evaluating coatings
InactiveUS8692887B2Television system detailsDigital computer detailsVariable thicknessCoated surface
An apparatus is provided for determining variable thickness of a coating on a surface of a substrate using in part a flash-lamp source, capable of generating a thermal pulse at the coating surface, and a image capture and processing device capable of capture sequential image frames of the coating surface, whereas each sequential image frame corresponds to an elapsed time and comprises a pixel array, and wherein each pixel of the array corresponds to a location on the coating surface. A method of calculating coating thickness is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
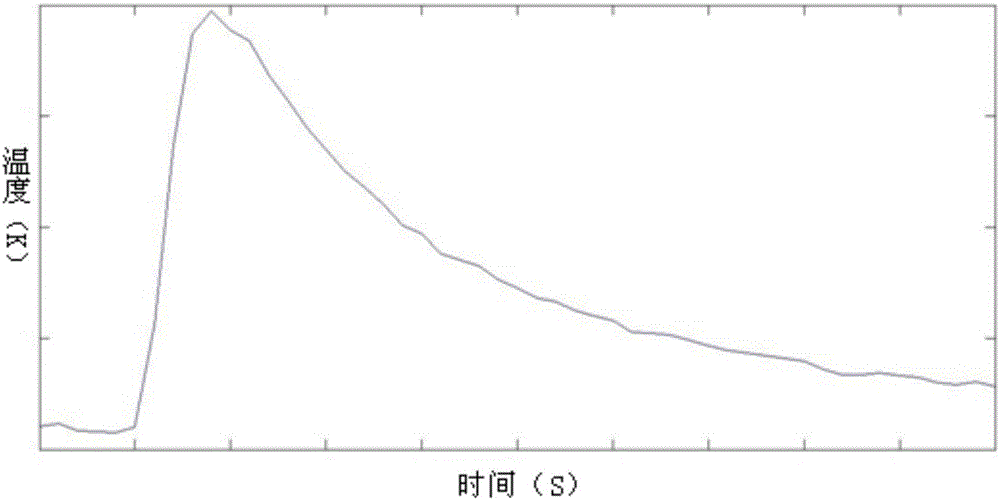
Thermal pulse sap flow or water flux density measuring apparatus capable of correcting space and measuring method
InactiveCN103913481AReduce measurement errorSimple structureMaterial heat developmentVolume/mass flow measurementObservational errorMeasurement device
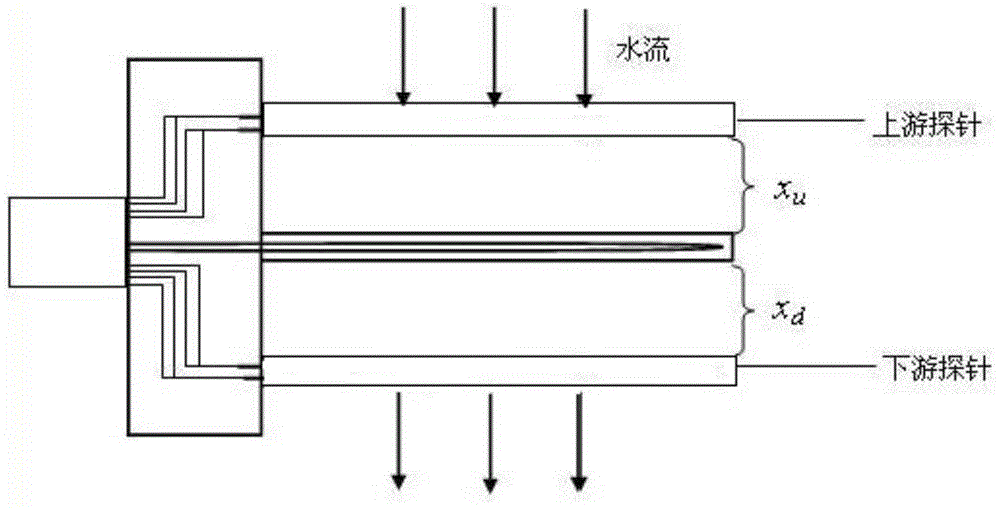
The invention reveals a thermal pulse sap flow or water flux density measuring apparatus capable of correcting space and a measuring method. The measuring apparatus comprises a base, temperature probes and a heating probe, wherein the temperature probes and the heating probe are fixed on the base, a first temperature measurement element and a second temperature measurement element are respectively arranged in each temperature probe along the axis direction of the temperature probe, the two temperature measurement elements are both connected with a data acquisition device, and a heating wire is arranged in the heating probe and connected with a heating device. According to the measuring apparatus and the measuring method provided by the invention, each temperature probe employs at least two temperature measurement elements, so measurement errors of sap flow in plants or water flux density in soil caused by bending deformation of the temperature probes or heating probes due to external causes in practical application are reduced. Moreover, the apparatus has the advantages of a simple structure, low cost, convenience in usage and rapid and accurate measurement.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nanoparticles and systems and methods for synthesizing nanoparticles through thermal shock
ActiveUS20180369771A1Increase temperatureHeat treatmentsMaterial nanotechnologyThermal energyThermal shock
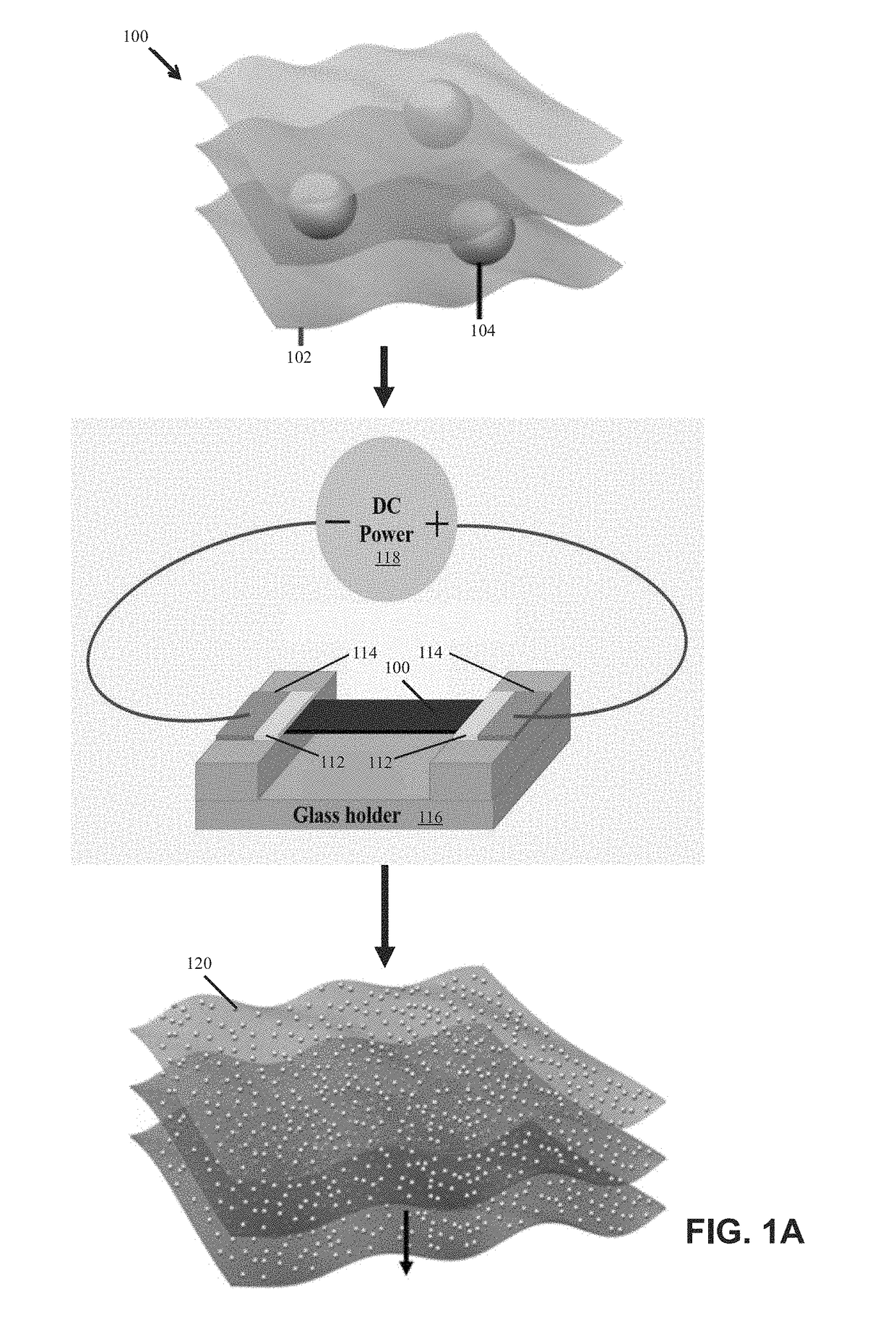
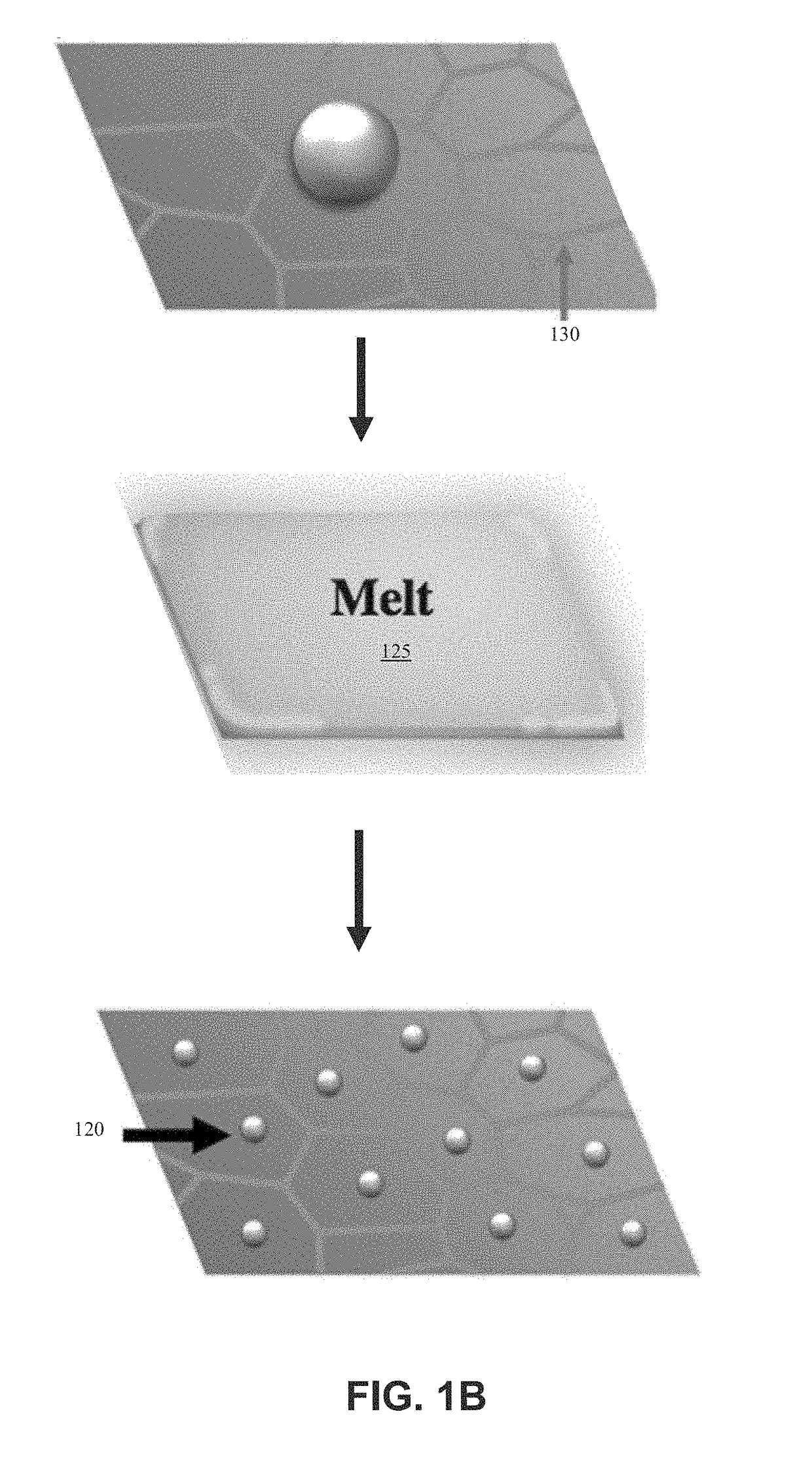
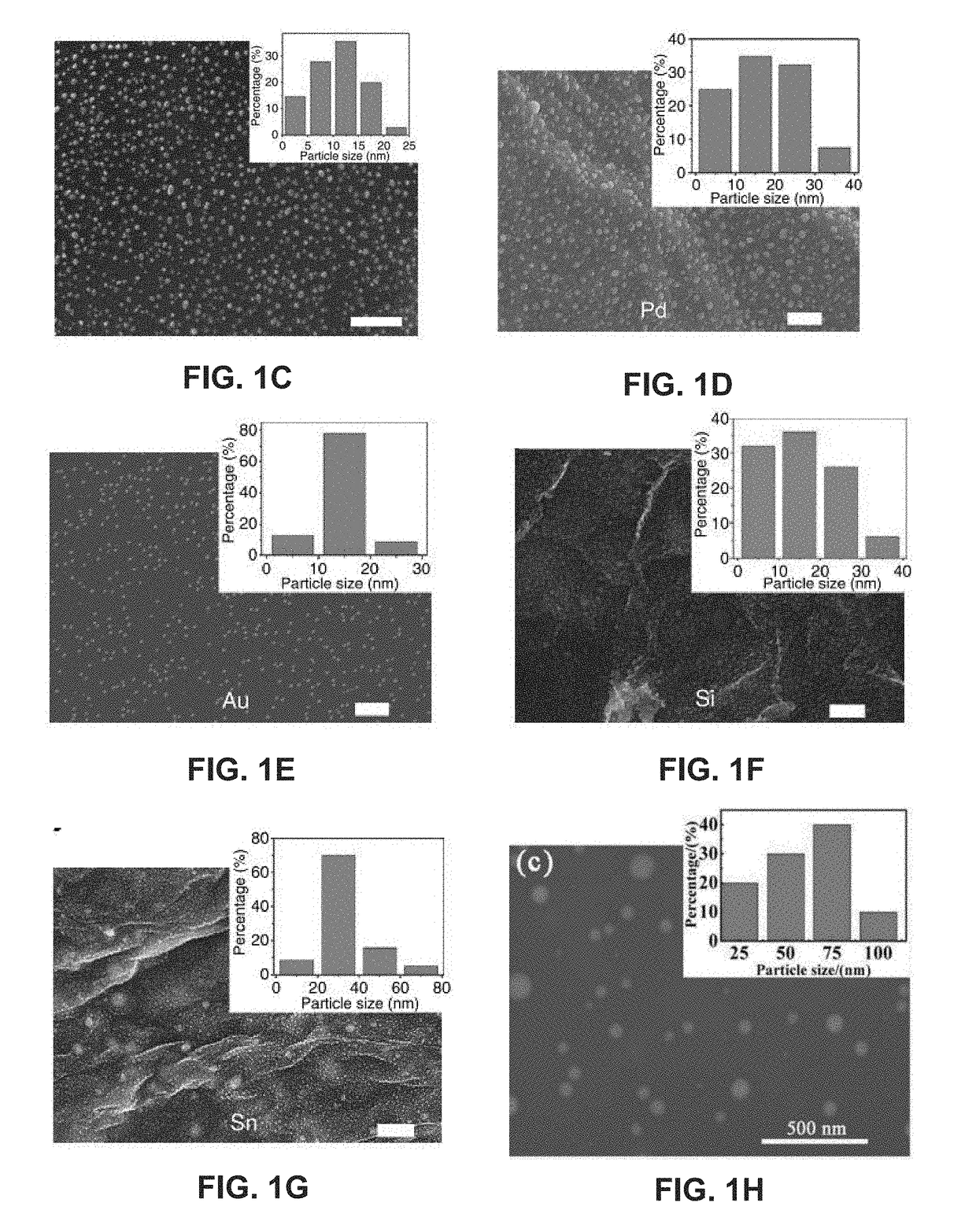
Systems and methods of synthesizing nanoparticles on substrates using rapid, high temperature thermal shock. A method involves depositing micro-sized particles or salt precursors on a substrate, and applying a rapid, high temperature thermal pulse or shock to the micro-sized particles or the salt precursors and the substrate to cause the micro-sized particles or the salt precursors to become nanoparticles on the substrate. A system may include a rotatable member that receives a roll of a substrate sheet having micro-sized particles or salt precursors; a motor that rotates the rotatable member so as to unroll consecutive portions of the substrate sheet from the roll; and a thermal energy source that applies a short, high temperature thermal shock to consecutive portions of the substrate sheet that are unrolled from the roll by rotating the first rotatable member. Some systems and methods produce nanoparticles on existing substrate. The nanoparticles may be metallic, ceramic, inorganic, semiconductor, or compound nanoparticles. The substrate may be a carbon-based substrate, a conducting substrate, or a non-conducting substrate. The high temperature thermal shock process may be enabled by electrical Joule heating, microwave heating, thermal radiative heating, plasma heating, or laser heating.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method for determining soil moisture on basis of thermal pulse
InactiveCN101598690AAvoid damageWeighing by removing componentMaterial thermal conductivityDiffusionSoil science
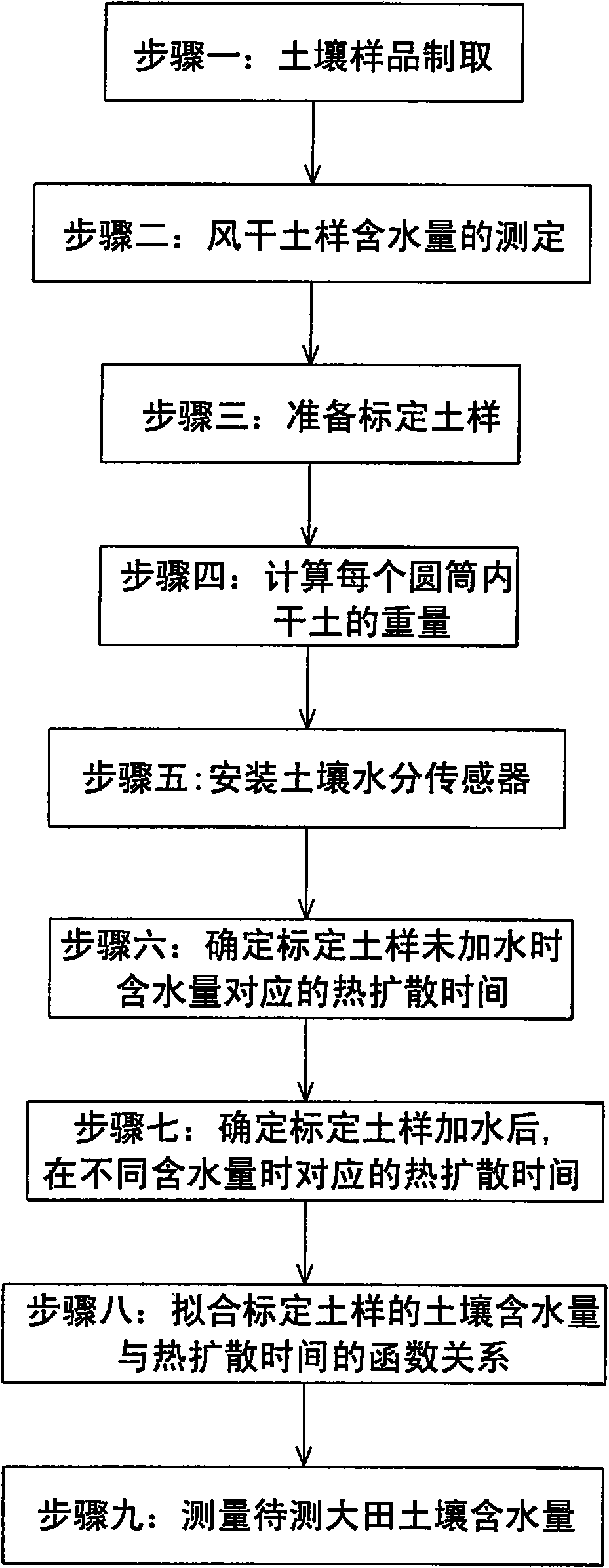
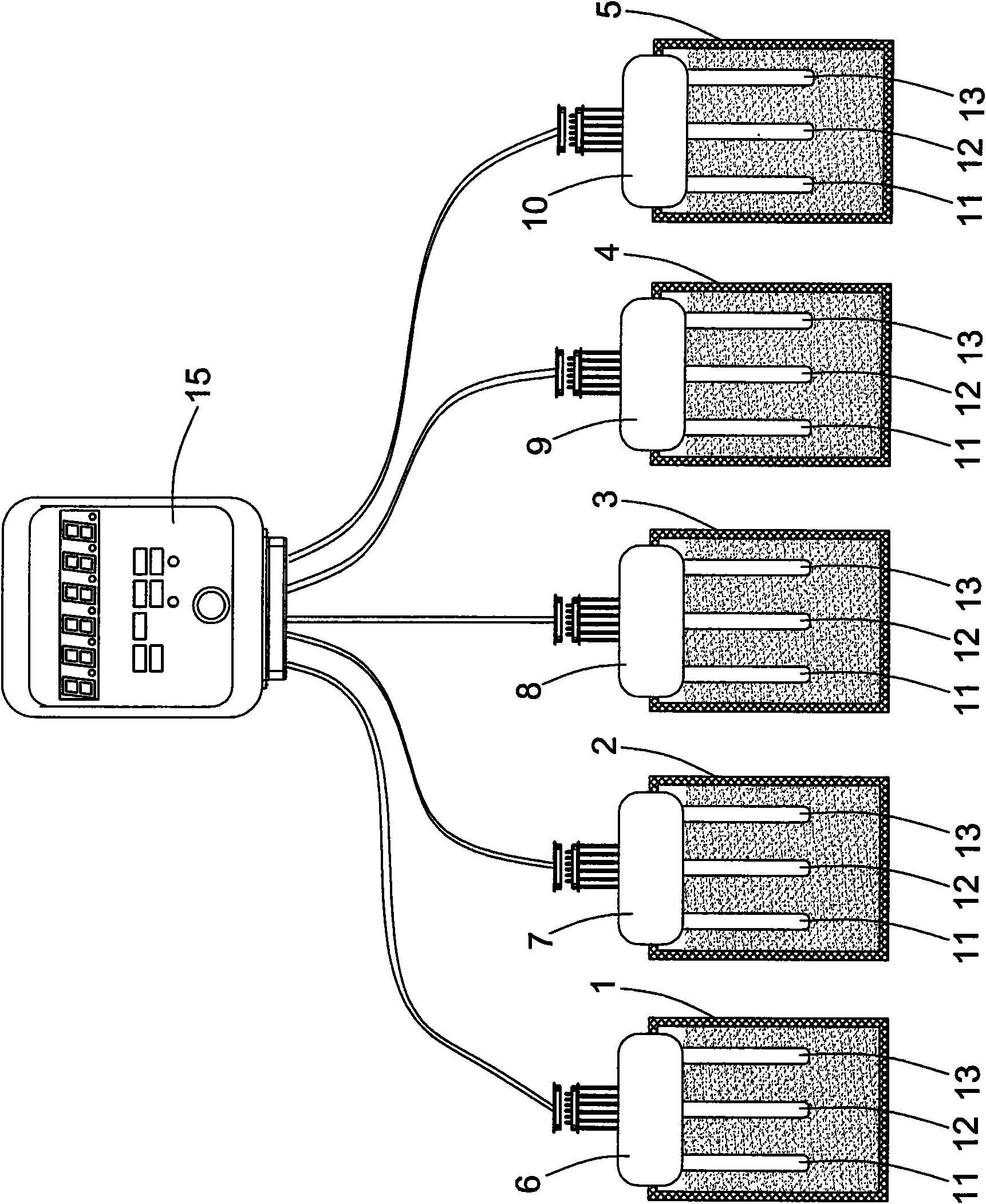
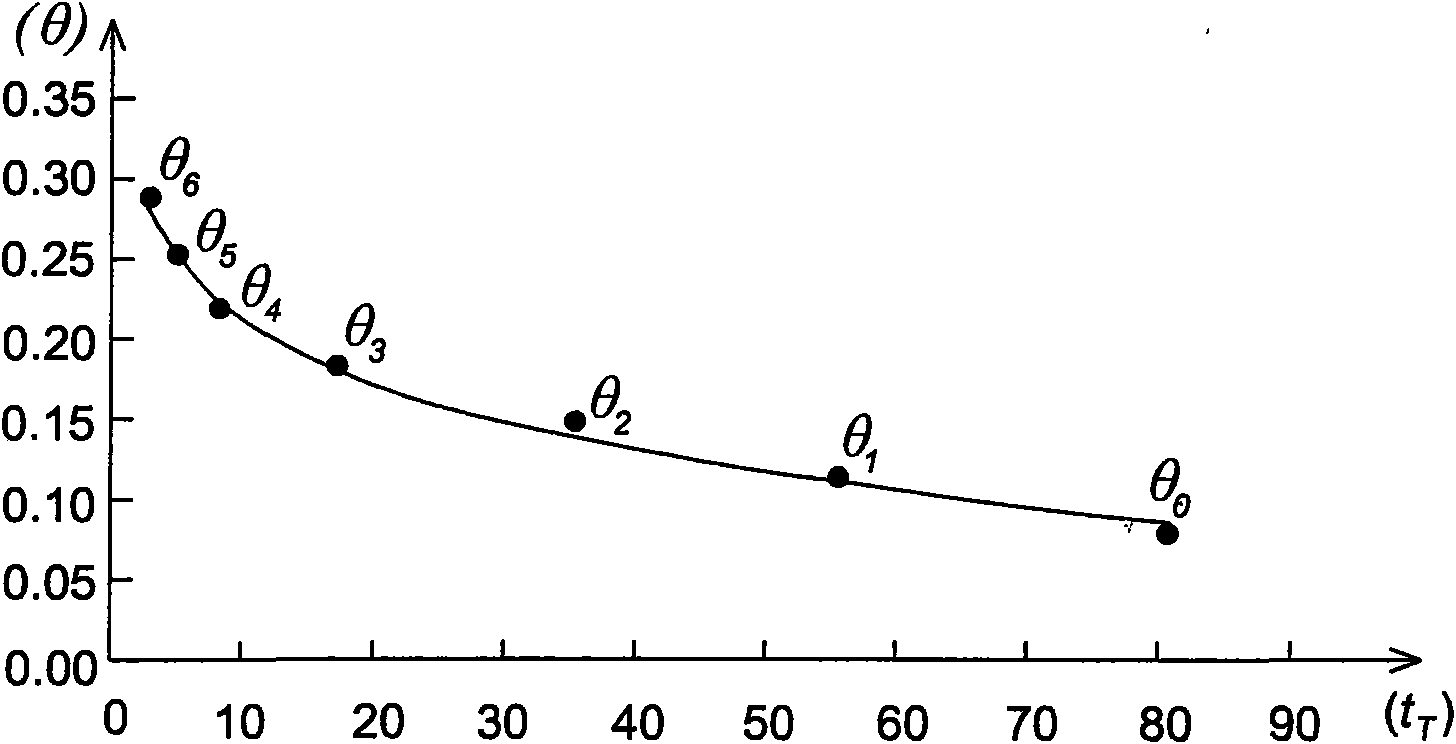
The invention discloses a method for determining soil moisture on the basis of thermal pulse. The method comprises the following steps: Step 1, preparing a soil sample; Step 2, determining the moisture content of the air-dried soil sample; Step 3, preparing a calibration soil sample; Step 4, calculating the weight of dry soil in each cylinder; Step 5, mounting a soil moisture sensor; Step 6, confirming the thermal diffusion time corresponding to the moisture content of the calibration soil sample which is not watered; Step 7, confirming the thermal diffusion time corresponding to different moisture contents of the watered calibration soil sample; Step 8, fitting the function relation between the moisture content of the calibration soil sample and the thermal diffusion time; Step 9, determining the soil moisture of the field to be determined. The method of the invention for determining the soil moisture on the basis of thermal pulse has the advantages of simple principle, high accuracy, easy operation and small destroy; the method with the function of continuous multipoint positioning or mobile determination is not subject to the internal media of the soil, therefore, the application range is wide; the method is free from electromagnetic radiation, thereby causing no harm to human bodies.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Magnetic memory layers thermal pulse transitions
ActiveUS7023723B2Stay magneticMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesDigital storageMagnetic memory
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a bit structures therein a magnetic material film in which a magnetic property thereof is maintained below a critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained, and may also have a plurality of word line structures each with heating sections located across from the magnetic material film in a corresponding one of the bit structures. These bit structures are sufficiently thermally isolated to allow selected currents in the adjacent word lines or in the bit structure, or both, to selectively heat the bit structure to approach the critical temperature. Such bit structures may have three magnetic material layers each with its own critical temperature for maintaining versus not maintaining a magnetic property thereof.
Owner:NVE CORP
Testing apparatus and method for vertical osmotic coefficient of streambed shallow-layer sediment
InactiveCN103234884AReduce distractionsZero pollutionPermeability/surface area analysisTest efficiencyThermal insulation
The invention discloses a testing apparatus for a vertical osmotic coefficient of a streambed shallow-layer sediment. The apparatus comprises a thermal insulation sleeve, a metal bar and temperature sensors and pressure sensors positioned in the thermal insulation sleeve and the metal bar. Vertical temperature distribution of a sediment in the vertical sleeve and hydraulic pressure values of two ends of the sediment can be measured under the action of thermal pulse, and the vertical osmotic coefficient of a soil column can be calculated through a relation formula for the osmotic coefficient and spatial and temporal distribution of temperature. The invention further discloses a testing method for the vertical osmotic coefficient of the streambed shallow-layer sediment. According to the invention, the apparatus has a simple structure and high testing efficiency and poses small interference on a spatial structure of particles of a to-be-tested streambed sediment; and the testing method is a novel environment-friendly economic testing method for the vertical osmotic coefficient of a streambed sediment and has good application prospects.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Rock thermophysics on-site test method under non-constant power condition
InactiveCN101430317ALow stability requirementsReduce testing costsEarth material testingMaterial thermal analysisConstant powerMathematical model
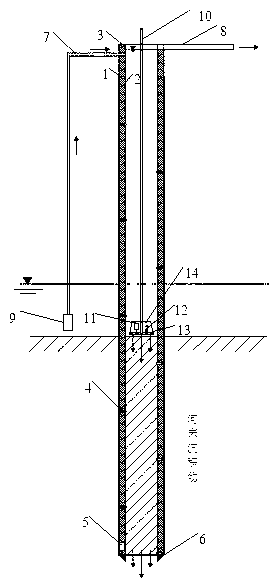
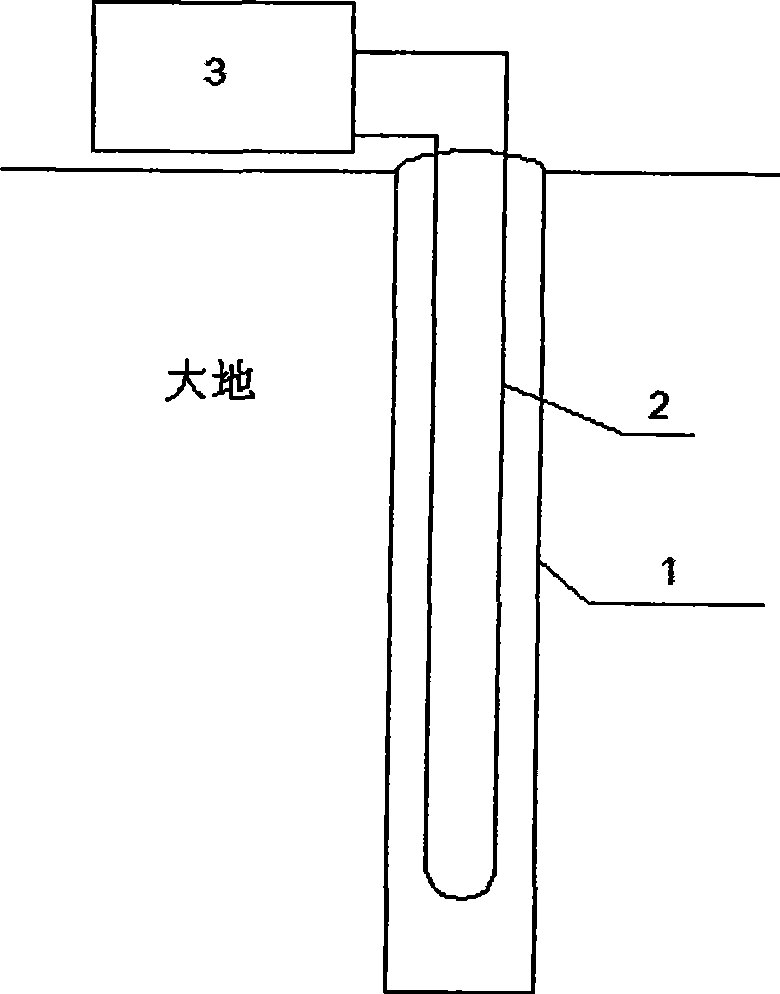
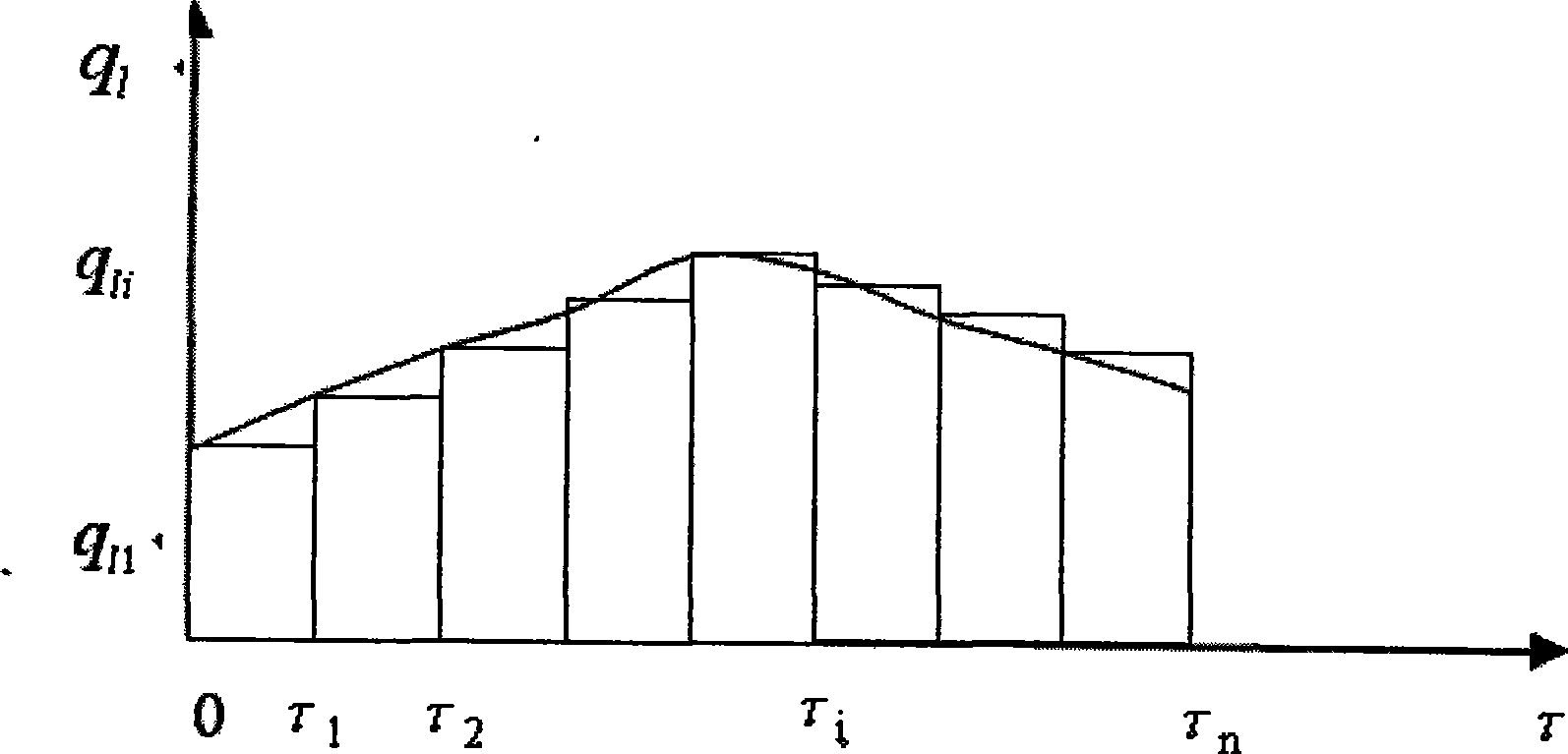
The invention discloses an onsite thermal property testing method under the condition of a non-constant power. The trend of a heating power or cooling power changing with time is analyzed under the condition of power instability such as the interruption of a power supply and large fluctuation of voltage, and by dividing the non-constant power into a plurality of sections in terms of time, wherein, the power of each section is comparatively constant (the power can be considered as zero when heating or cooling are interrupted); the heat-transfer process of buried pipes is considered to undergo a plurality of step heating flux actions which are further disintegrated into a superposition of a plurality of thermal pulses; linear superposition principle is adopted for analyzing and a mathematical model is established; and ground thermal property parameters can be obtained by integrating the mathematical model with a parameter estimation method and other methods.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
T-max plant stem flow measuring method and device thereof
InactiveCN101793538ASolving the Difficulties of Measuring Low Velocity Stem FlowVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsHeat fluxLow speed
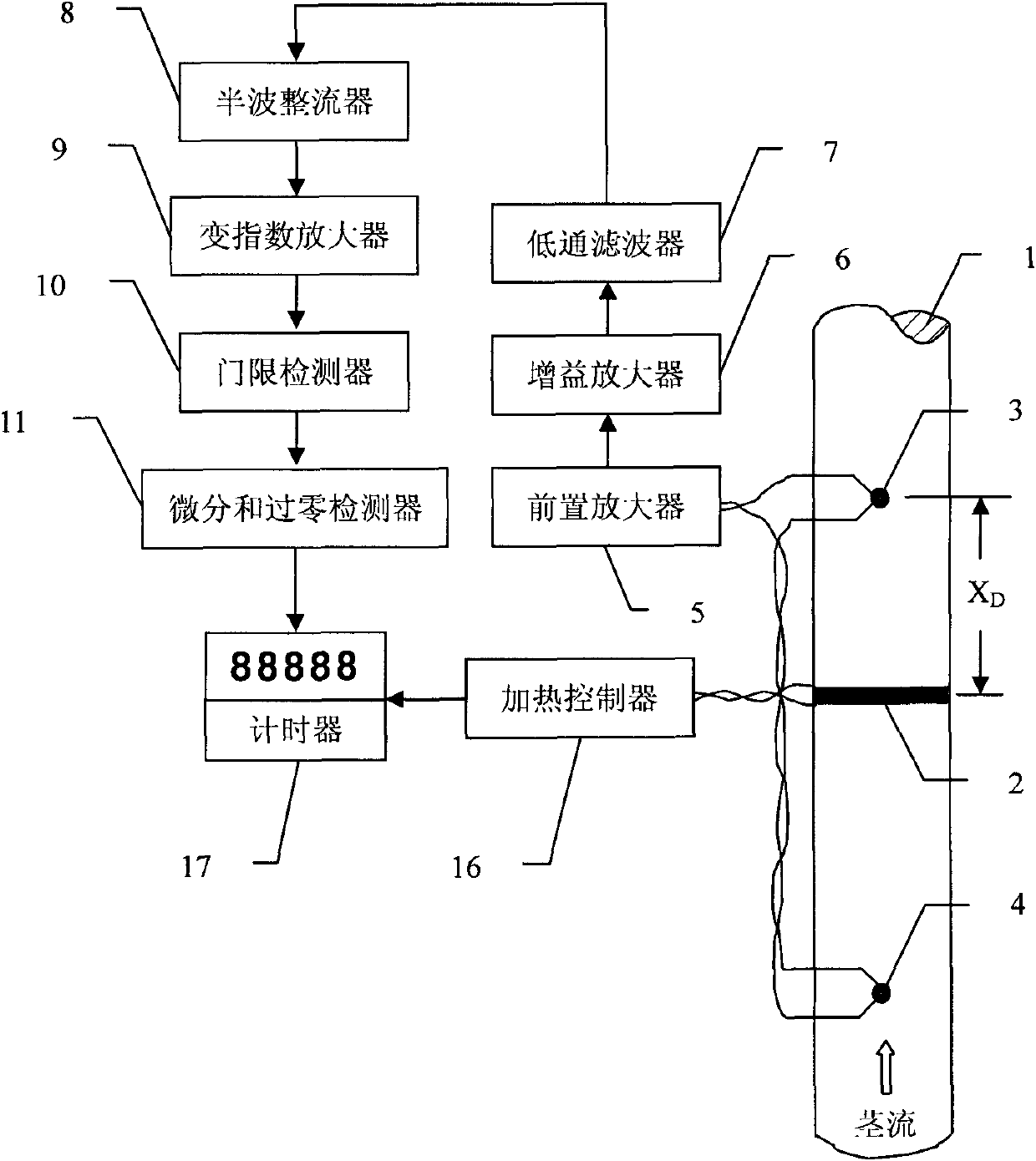
The invention relates to a T-max plant stem flow measuring method and a device thereof. A heater is arranged on a plant stem; a detection temperature sensor is arranged at a position with a distance of XD from the heater at the downstream of the stem flow on the stem; a compensation temperature sensor is arranged on the stem, which is not influenced by the thermal pulse, at the upstream or downstream of the stem flow; the detection temperature sensor and the compensation temperature sensor form a temperature difference detector; a heating controller is reset and starts a timer after controlling the heater arranged on the plant stem to emit the thermal pulse for heating the plant stem; a temperature difference signal acquired by the temperature difference detector finds a peak point of the temperature different signal out by preamplification, gain amplification, lowpass filtering, half-wave rectification, alteration index amplification, threshold detection, differentiation and zero-crossing detection; and the timer is turned off at the peak point; and a time recorded by the timer is substituted in the stem flow computing formula of the T-max method so that the capacity of measuring the low-speed stem flow by using the T-max method is greatly improved. The T-max plant stem flow measuring method and the device thereof have the advantages of low cost, high precision, high reliability, little heat flux, wide measurement range and convenient use.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Pulsed plasma generator
A pulsed electrostatic / electric field generator apparatus providing a source of large quantity, free slow-speed high energy free electrons, or high energy positive ions, contained in an electrostatic / electric field capacity exceeding 1 Joule. The pulsed electrostatic / electric field generator apparatus encapsulates an enclosed non-equilibrium, non-thermal pulsed power plasma. A key subcomponent of this apparatus incorporates an innovative unipolar piezoelectric capacitor creating high voltage nanosecond rise time pulses in a multistage high energy step-up pulsed plasma generation sequence of steps. The resulting multi-Joule electrostatic / electric field is then tapped to provide a source of current and / or potential for use by external loads.
Owner:ROSENER KIRK
Method for synthesizing metal oxide particles
InactiveUS20140273147A1Without burdensome complexityCost efficient and simpleFermentationMetalMaterials science
The invention is directed to a method for producing metal oxide particles, the method comprising subjecting non-oxide metal-containing particles to an oxidation step that converts the non-oxide metal-containing particles to said metal oxide particles. The invention is also directed to the resulting metal oxide compositions. In particular embodiments, non-oxide precursor particles are produced by microbial means, and the produced non-oxide precursor particles subjected to oxidation conditions under elevated temperature conditions (e.g., by a thermal pulse) to produce metal oxide particles or a metal oxide film.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
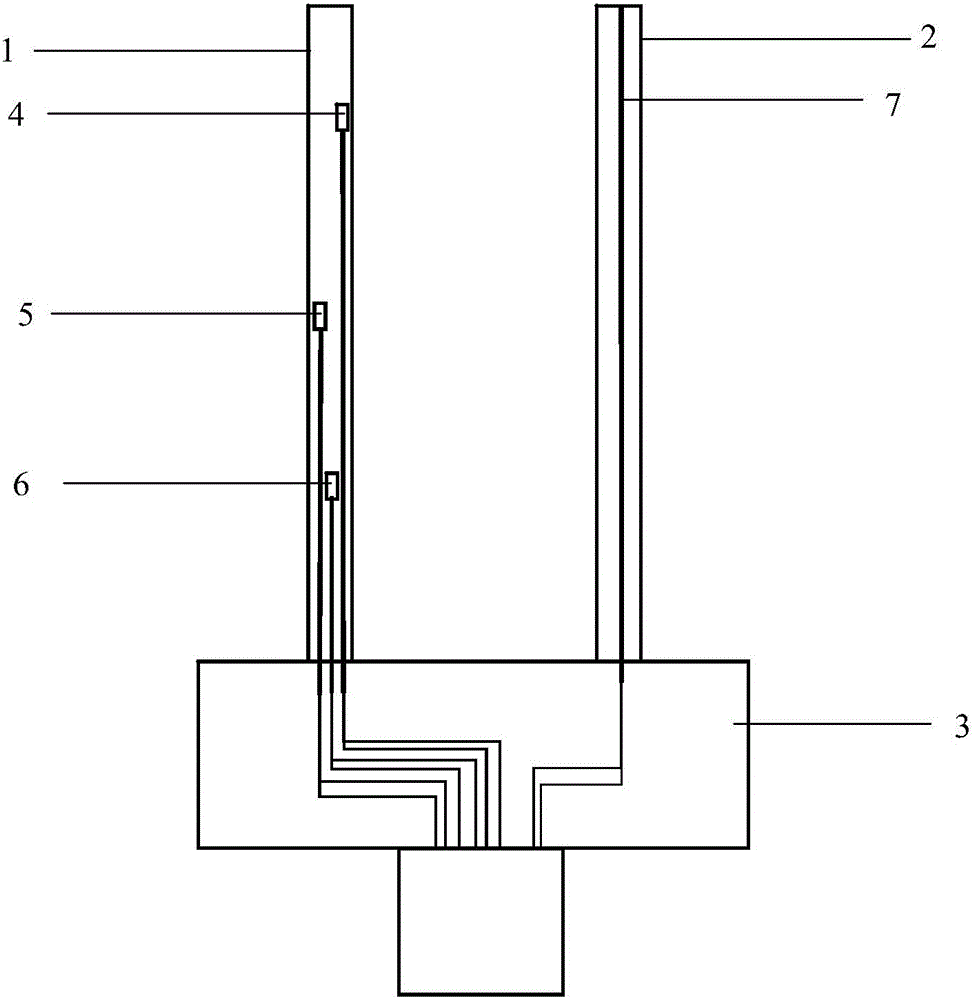
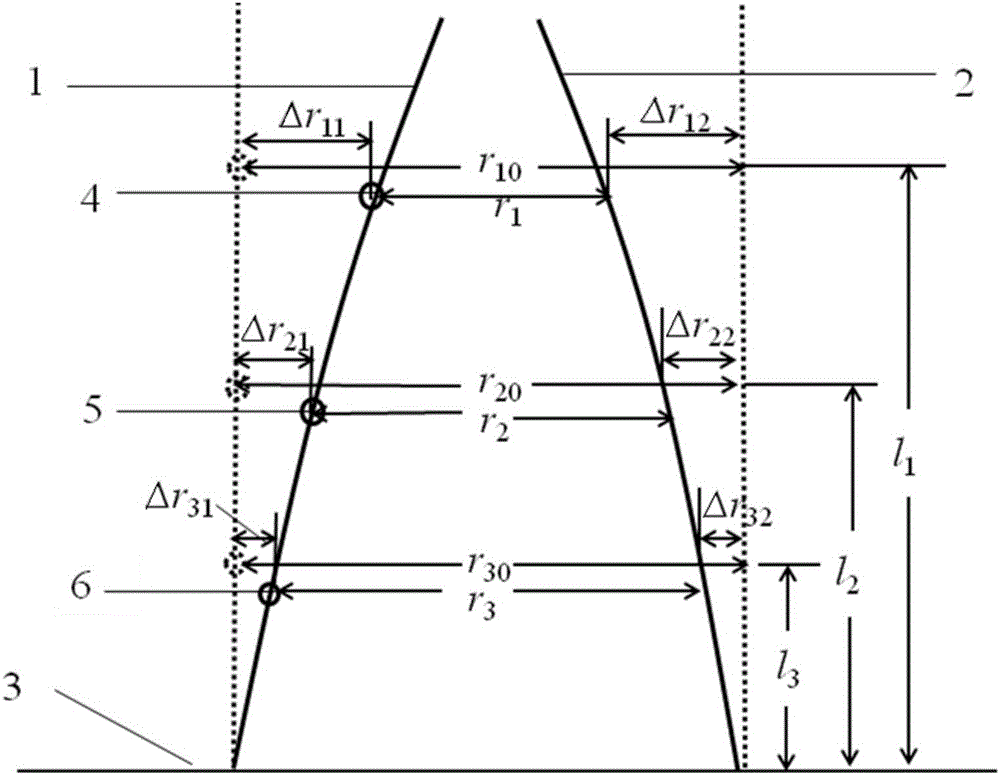
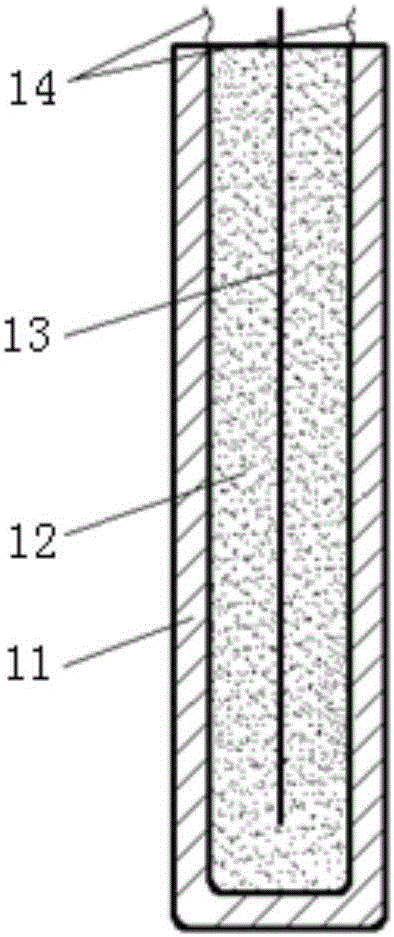
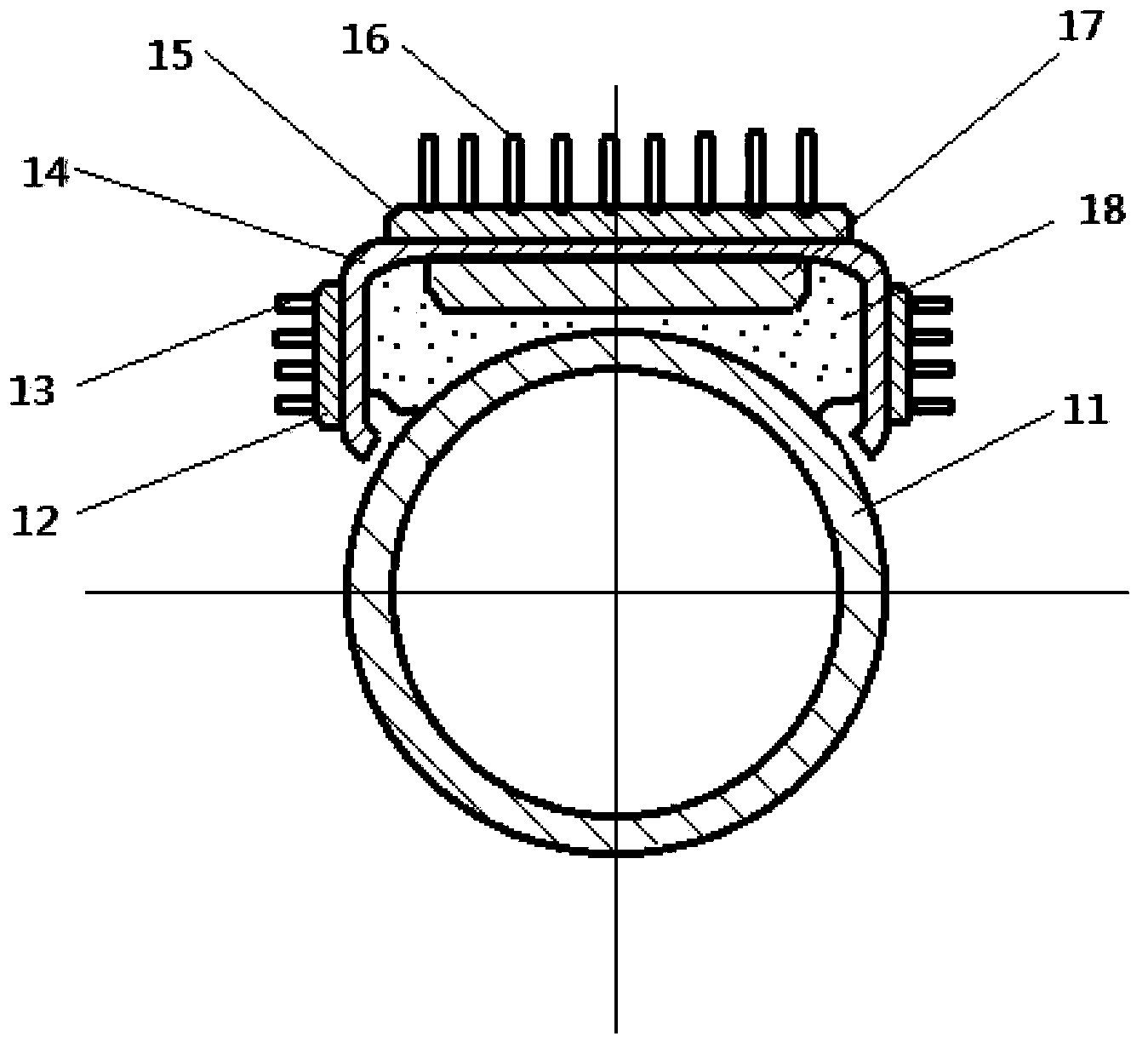
Double-probe thermal pulse thermal characteristic measuring system capable of calibrating probe interval in situ and method
ActiveCN105717156AReduce measurement errorHigh precisionMaterial heat developmentTemperature responseThermodynamics
The invention discloses a double-probe thermal pulse thermal characteristic measuring system capable of calibrating the probe interval in situ by itself and a method based on the system. By means of the system and the method, thermal characteristic parameter measurement errors caused by changes of the probe interval can be reduced. The system comprises a heating probe, a base, a heating device, a data processing device and at least one temperature probe, wherein the base is used for fixing the heating probe and the temperature probes; a heating wire is arranged in the heating probe, the ratio of the length to the inner diameter of the heating probe is larger than a preset numerical value, and the heating probe conducts heating through the heating device; at least three temperature measuring elements are arranged in each temperature probe in the axial direction; the data processing device is connected with temperature measuring elements and used for obtaining temperature response data collected by the temperature measuring elements after the heating probe and the temperature probes are inserted into a substance to be measured, obtaining the actual interval between each temperature measuring element and the heating probe according to the temperature response data and obtaining thermal characteristic parameters of the substance to be measured through fitting according to the actual interval.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
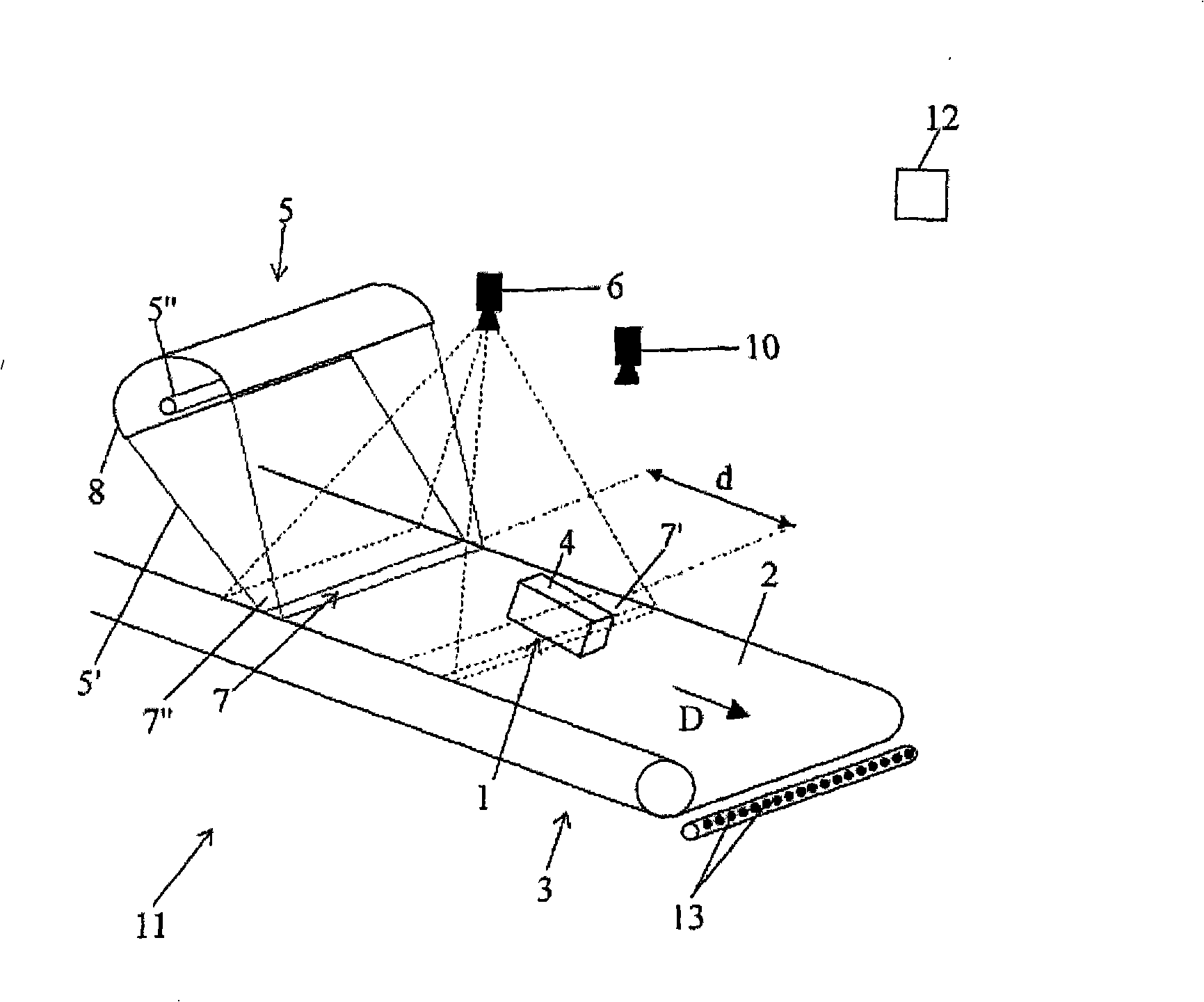
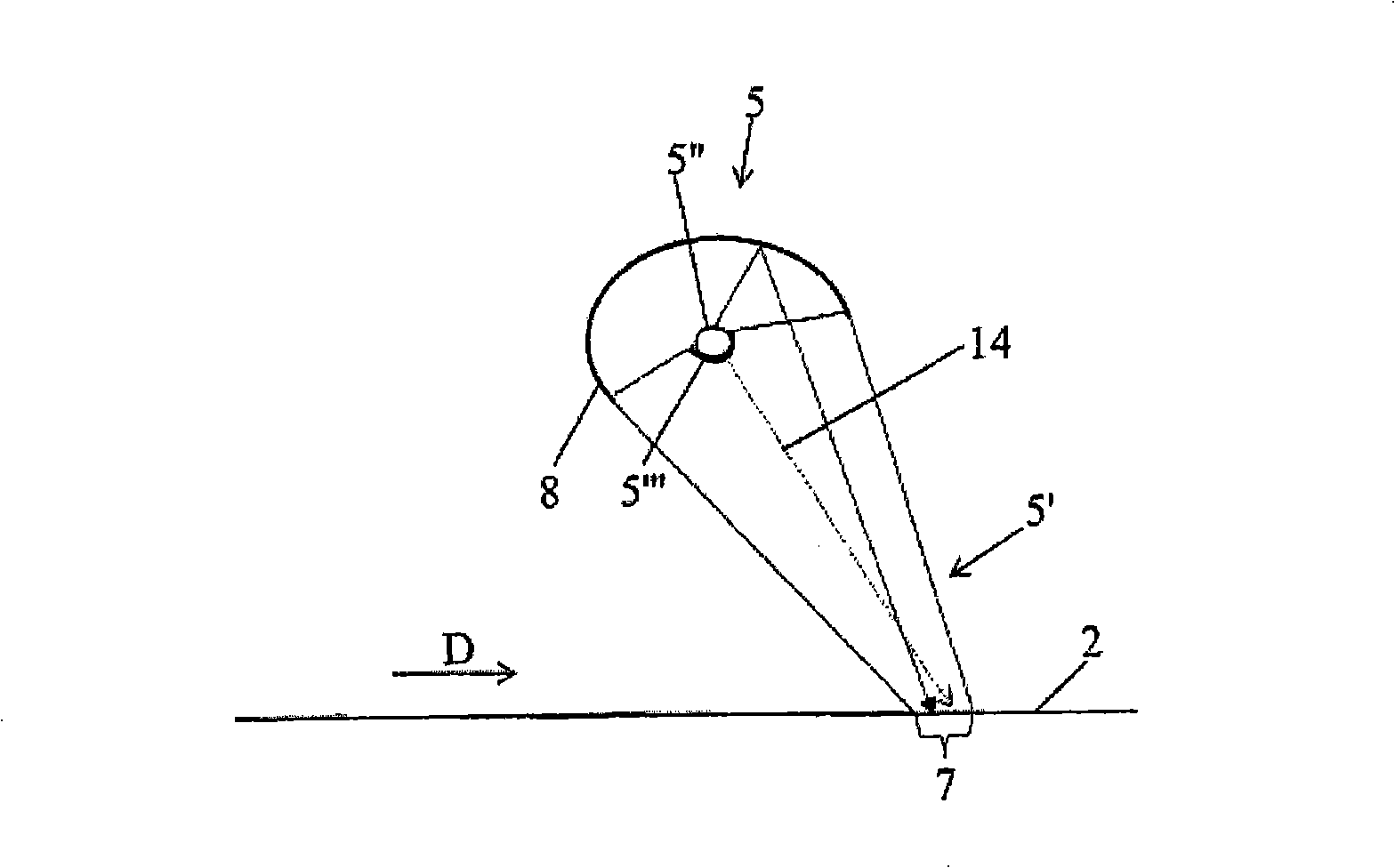
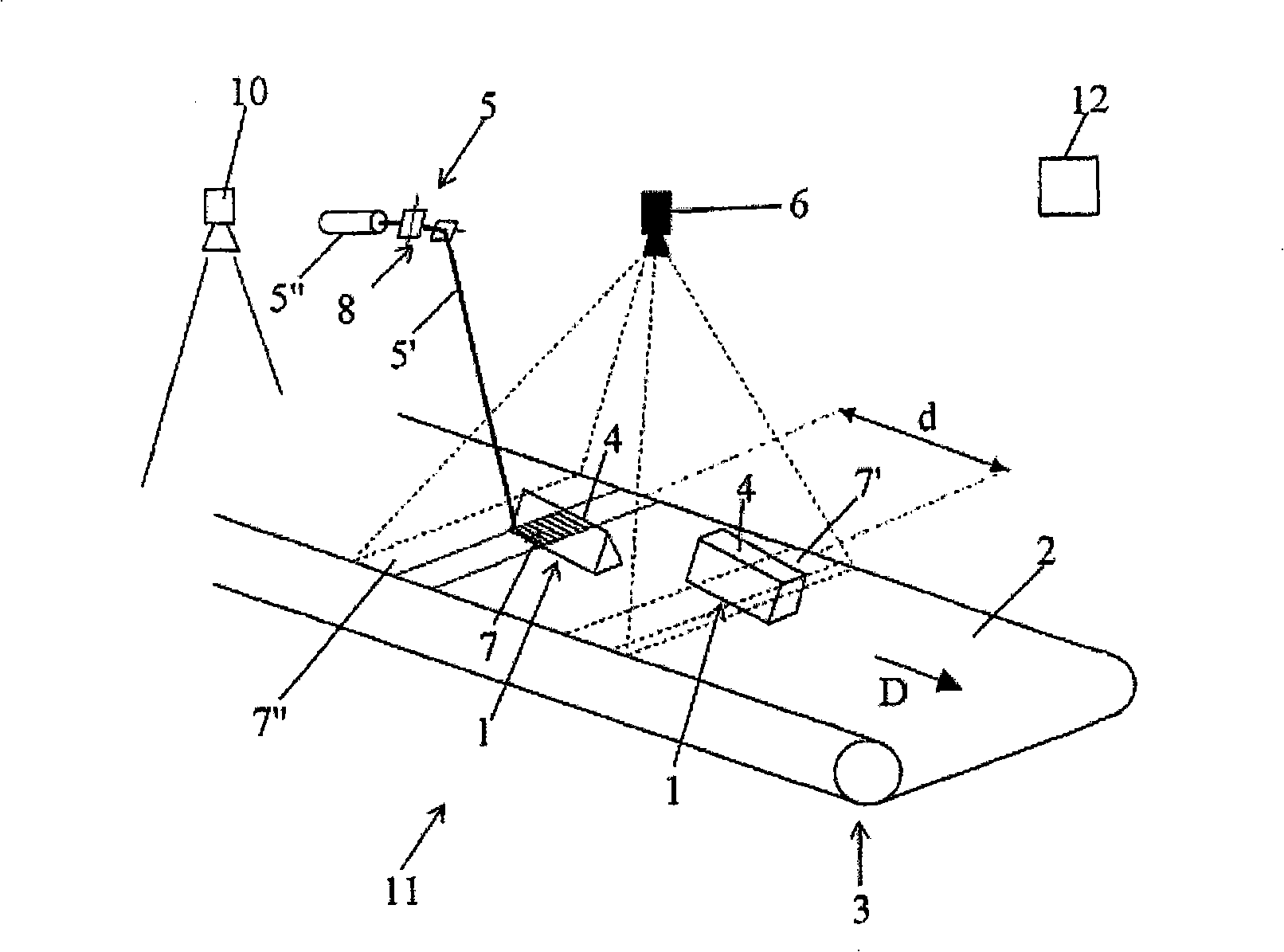
Method and machine for automatically inspecting and sorting objects according to their thickness
The subject of the present invention is a method and a machine for automatically inspecting and sorting non-metallic objects. The method is characterized in that it essentially consists in temporarily subjecting a surface or outer layer (4) of objects (1) travelling as a monolayer stream to the thermal radiation from at least one heating means (5) some distance away, so as to deliver, to each of these travelling objects (1), a non-impairing thermal pulse which is identical for all the objects in terms of thermal energy applied per unit area in the plane of conveying (2), then in taking at least one thermal image of each of the objects by means of at least one linear or matrix thermal detector (6), for example a thermal camera, after a specified amount of time has elapsed following application of the thermal pulse, then in classifying or categorizing each travelling object (1) according to the data contained in its thermal image(s), in delivering a control or actuation signal for each object and, finally, in separating the travelling objects (1) according to their class or category and / or according to the corresponding control or actuation signal delivered.
Owner:佩朗精品工艺股份有限公司
Device and method for measuring soil water flow velocity on basis of thermal pulse method
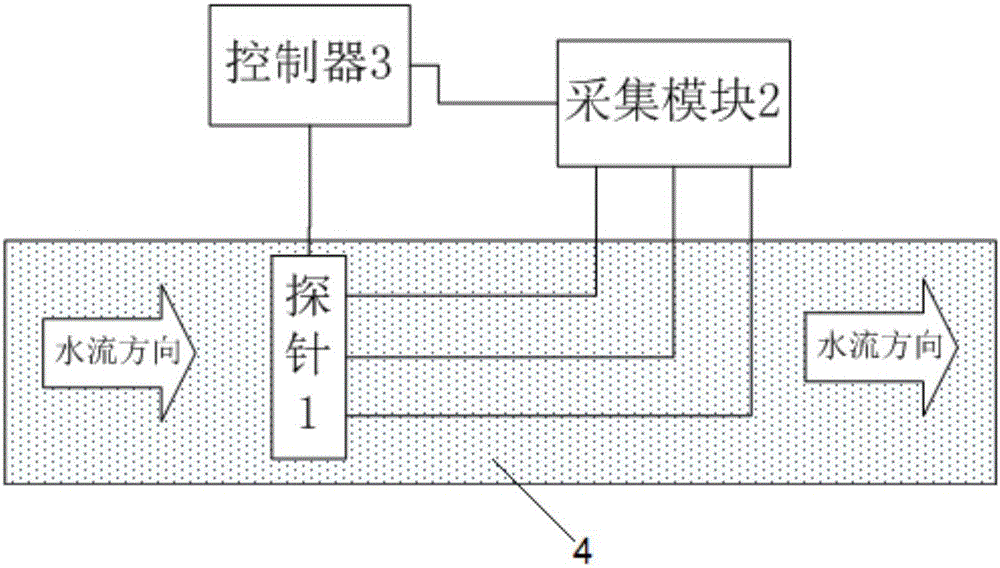
ActiveCN106199061ANo bendingMeet assembly needsFluid speed measurement using thermal variablesElectrical resistance and conductanceHeating time
The invention relates to a device and method for measuring the soil water flow velocity on the basis of a thermal pulse method. The device comprises a probe, a collection module and a controller; the probe is perpendicularly inserted into soil completely, closely makes contact with the soil and comprises a thermal conducting metal steel shell, a heating resistance wire and thermocouple bare wires, a through hole is formed in the center of the top of the thermal conducting metal steel shell, the heating resistance wire penetrates through the through hole to be fixedly inserted into the probe, the thermocouple bare wires for measuring surface temperature signals of the thermal conducting metal steel shell are uniformly distributed at the periphery of the heating resistance wire, the output ends of the thermocouple bare wires are connected with an input port of the collection module through signal transmission lines separately, and the controller is connected with the heating resistance wire and the collection module separately and used for controlling the heating time of the heating resistance wire to enable heat to be capable of being transmitted into the soil in the mode of an instantaneous pulse and controlling the collection module to conduct data collection. The device and method are precise in measurement and stable in thermal transmission and can be widely applied to soil water flow velocity measurement.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
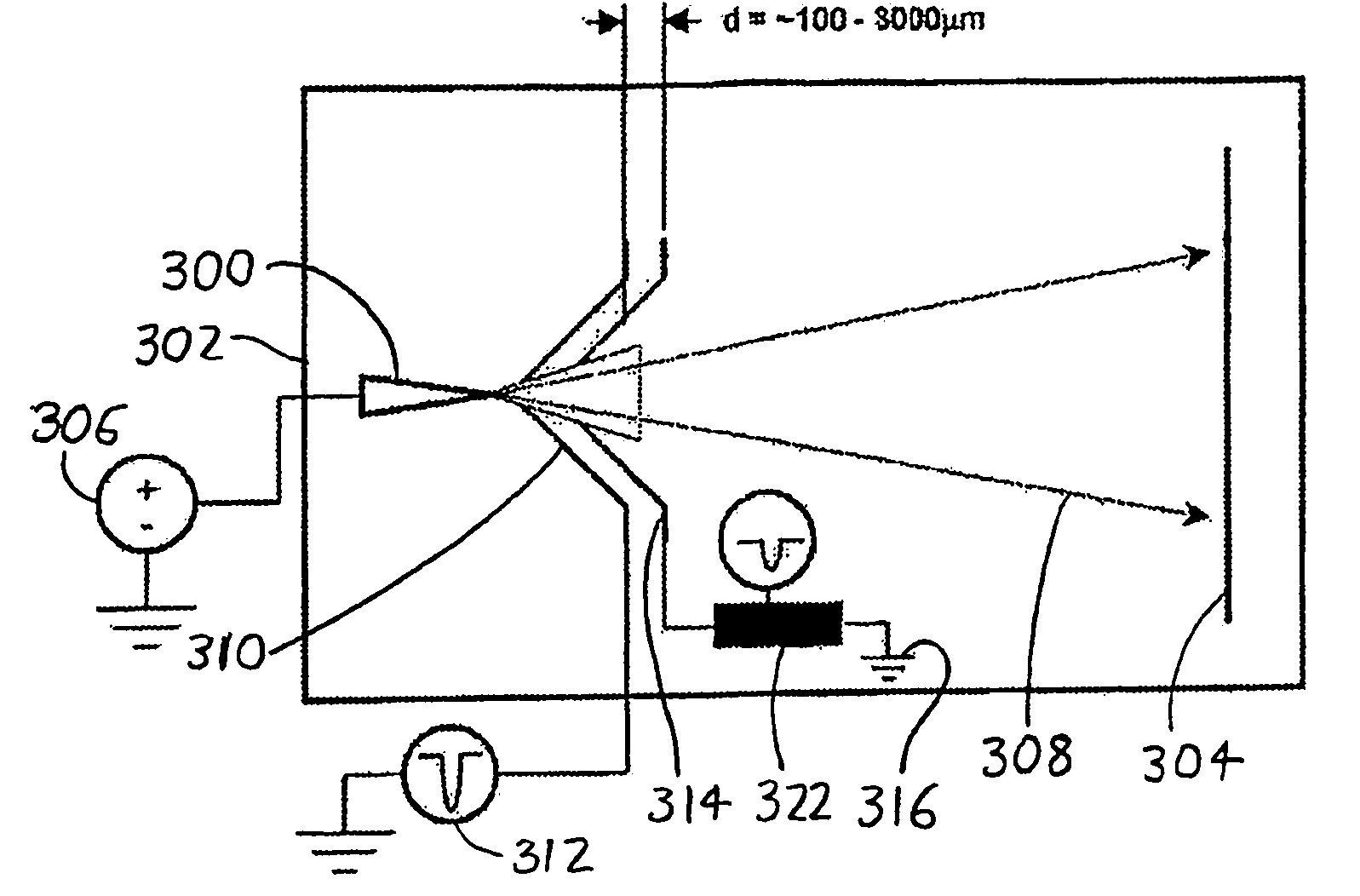
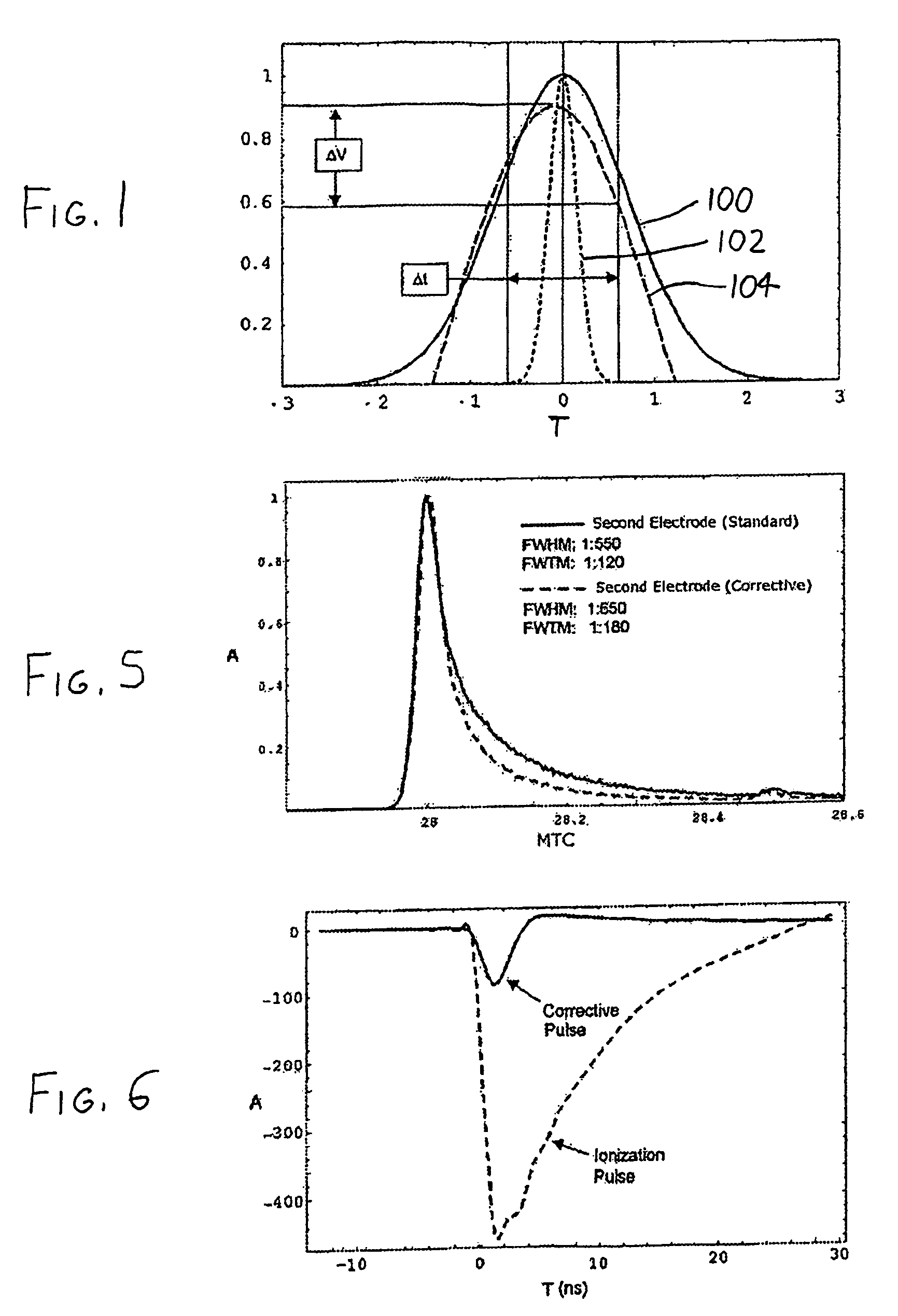
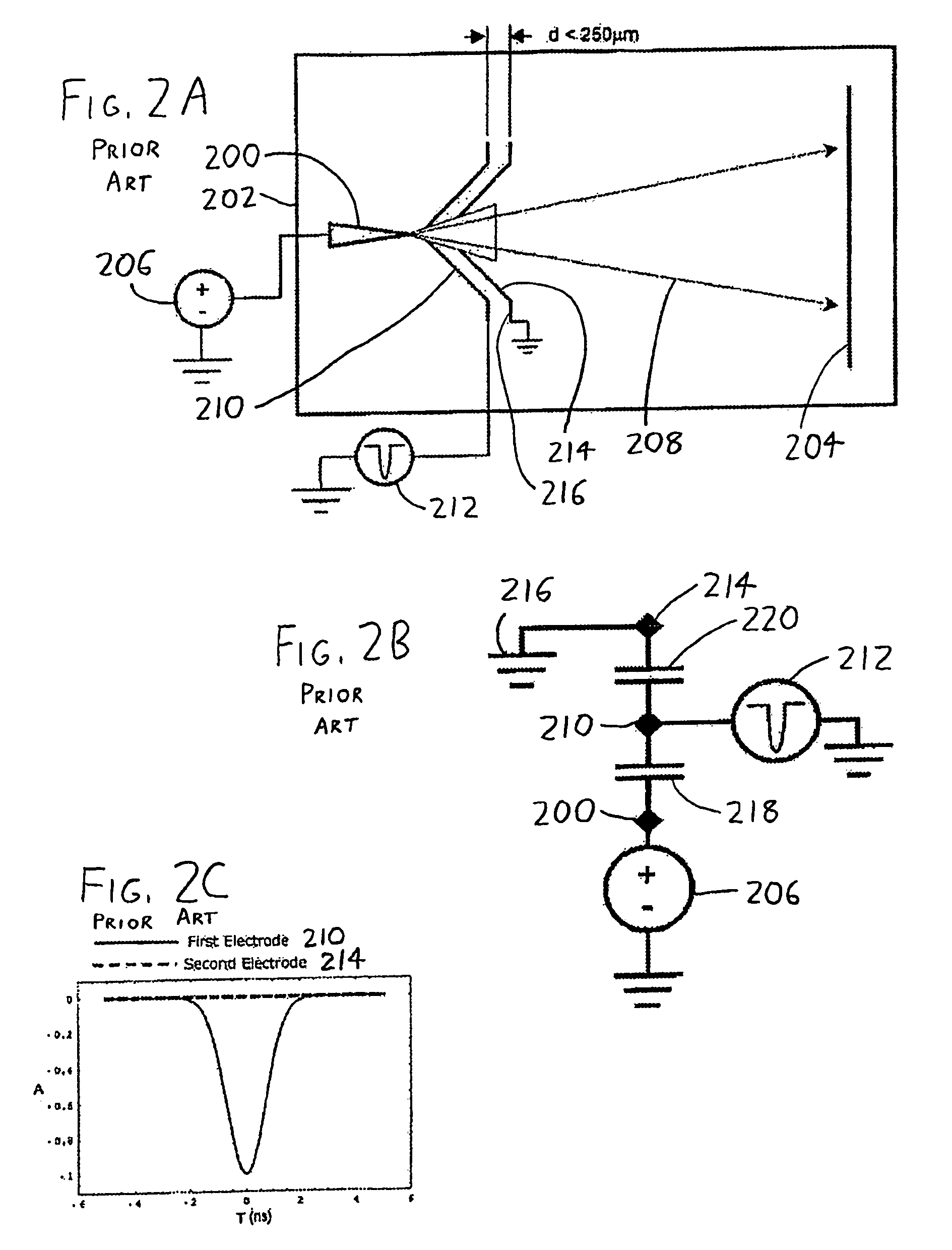
Methods and devices for atom probe mass resolution enhancement
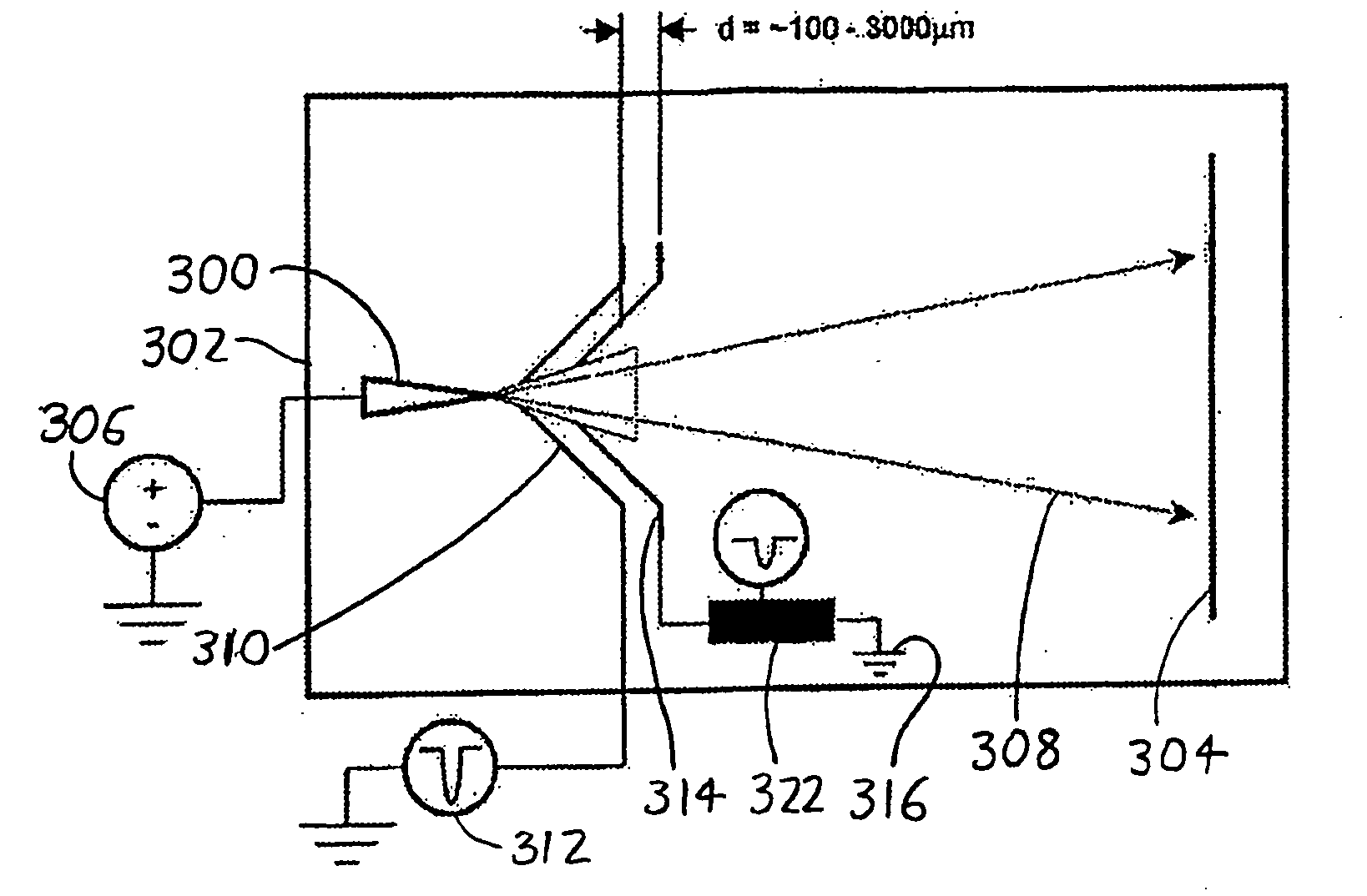
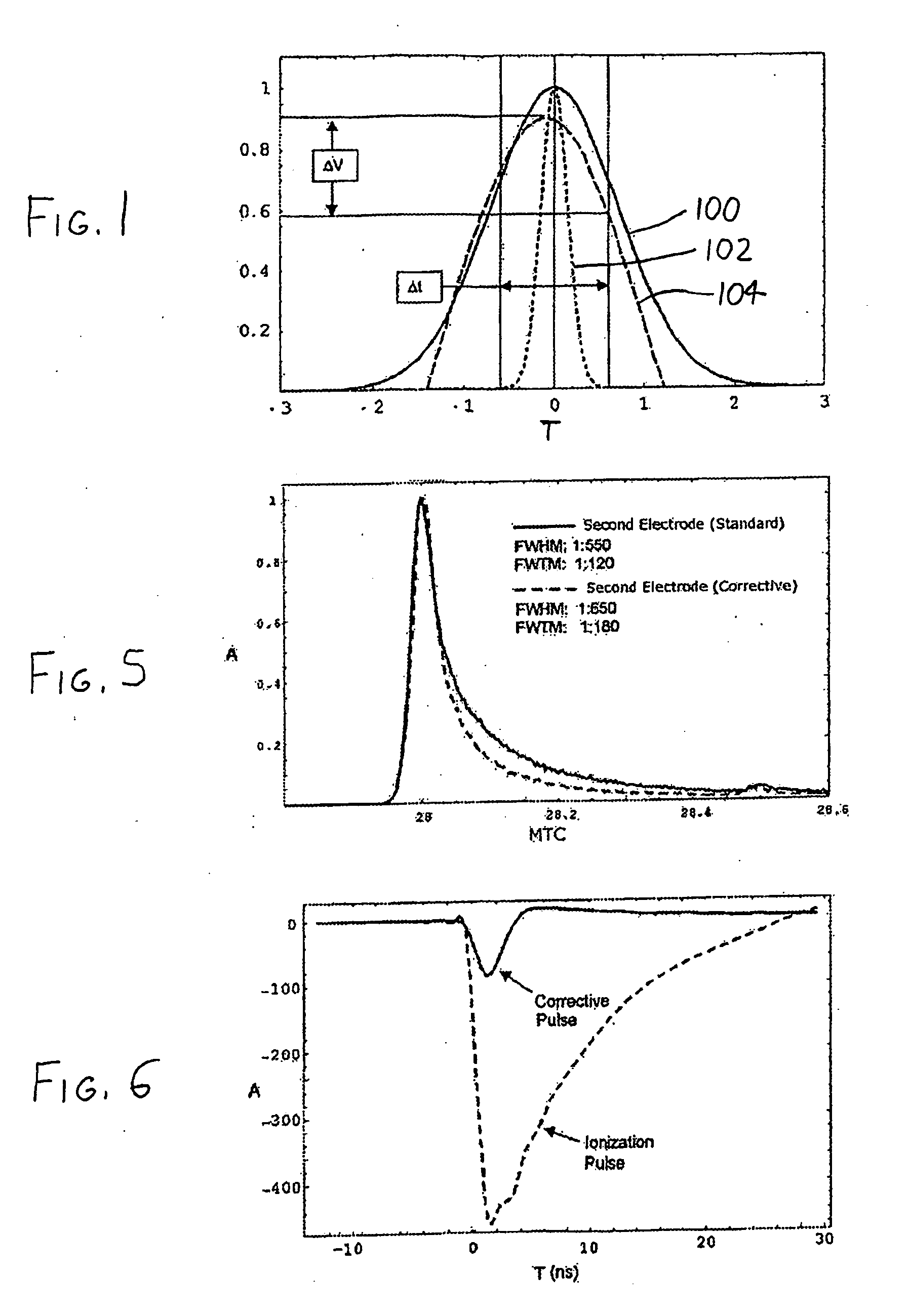
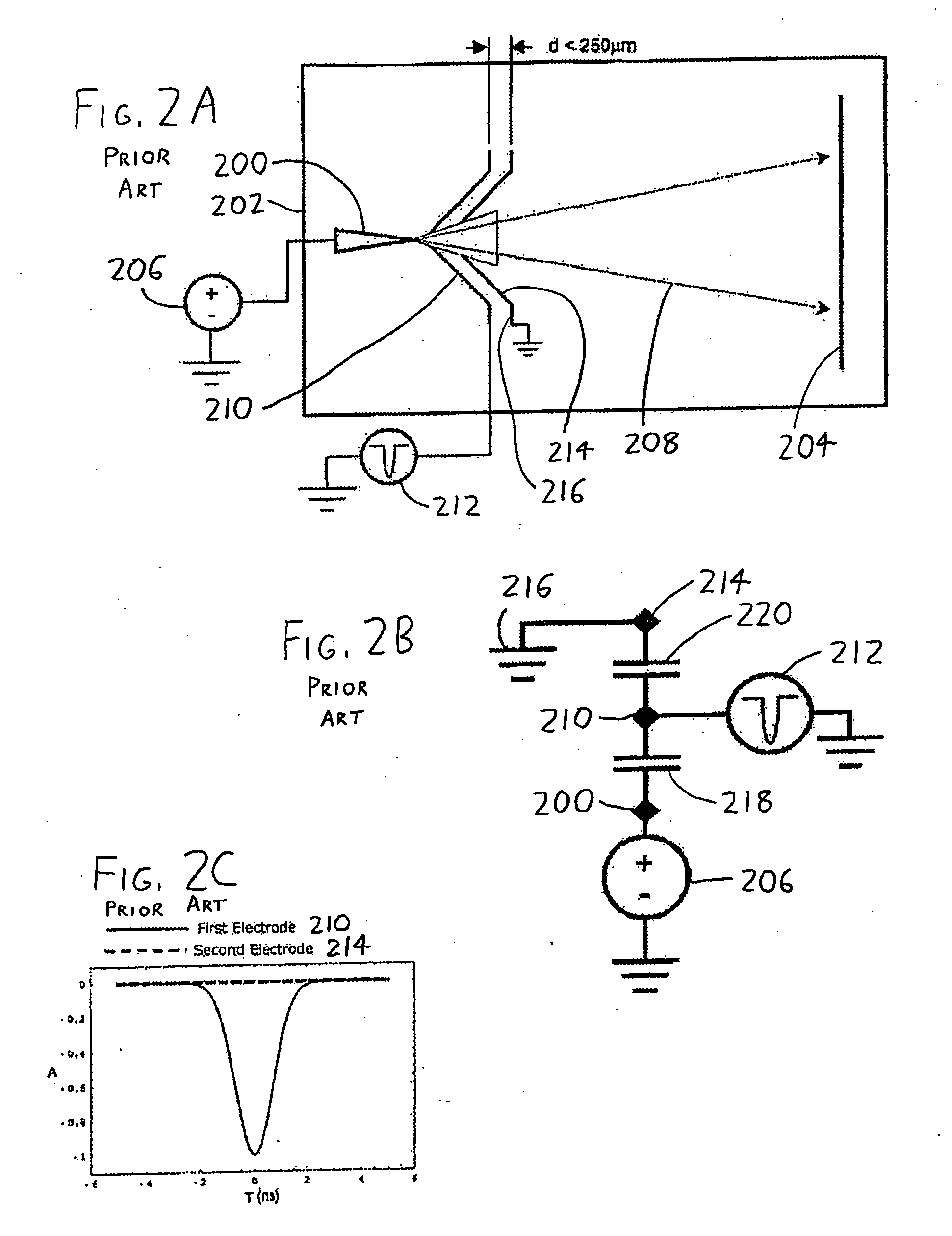
InactiveUS7772552B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesElectricityVoltage pulse
In an atom probe or other mass spectrometer wherein a specimen is subjected to ionizing pulses (voltage pulses, thermal pulses, etc.) which induce field evaporation of ions from the specimen, the evaporated ions are then subjected to corrective pulses which are synchronized with the ionizing pulses. These corrective pulses have a magnitude and timing sufficient to reduce the velocity distribution of the evaporated ions, thereby resulting in increased mass resolution for the atom probe / mass spectrometer. In a preferred arrangement, ionizing pulses are supplied to the specimen from a first counter electrode adjacent the specimen. The corrective pulses are then supplied from a second counter electrode which is coupled to the first via a passive or active network, with the network controlling the form (timing, amplitude, and shape) of the corrective pulses.
Owner:CAMECA INSTR
Double-sided in-situ measurement system and method for charge distribution in thin dielectric film
PendingCN110244138AReduce the problem of resolution dropImprove spatial resolutionElectrostatic field measurementsCapacitanceResistor
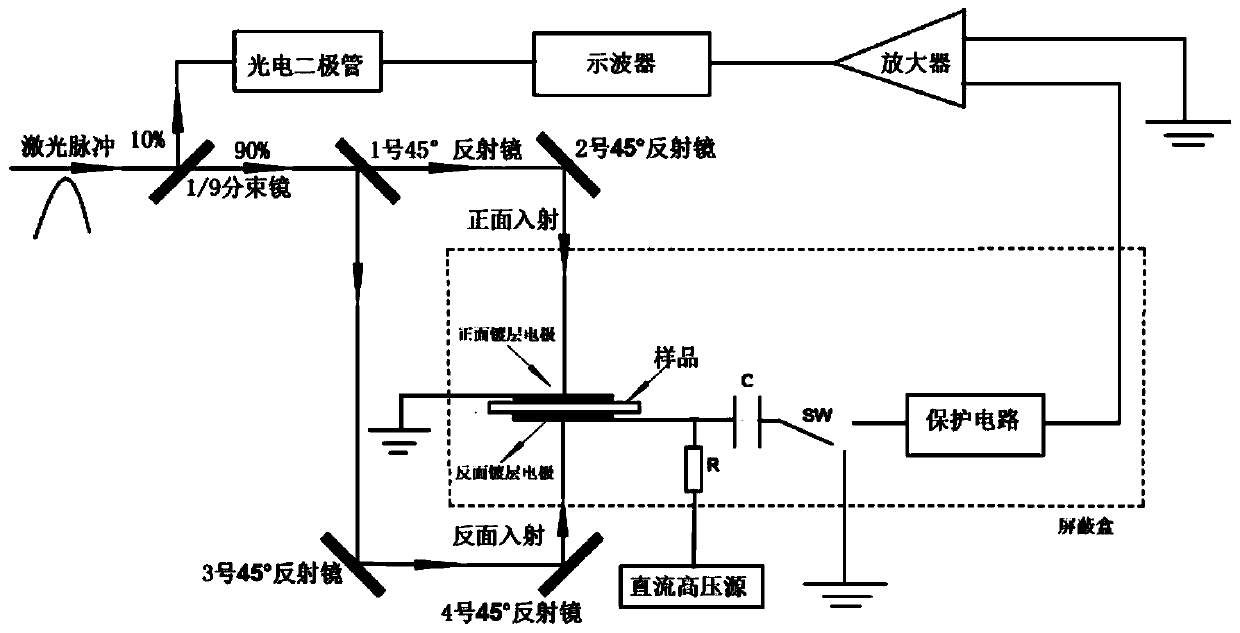
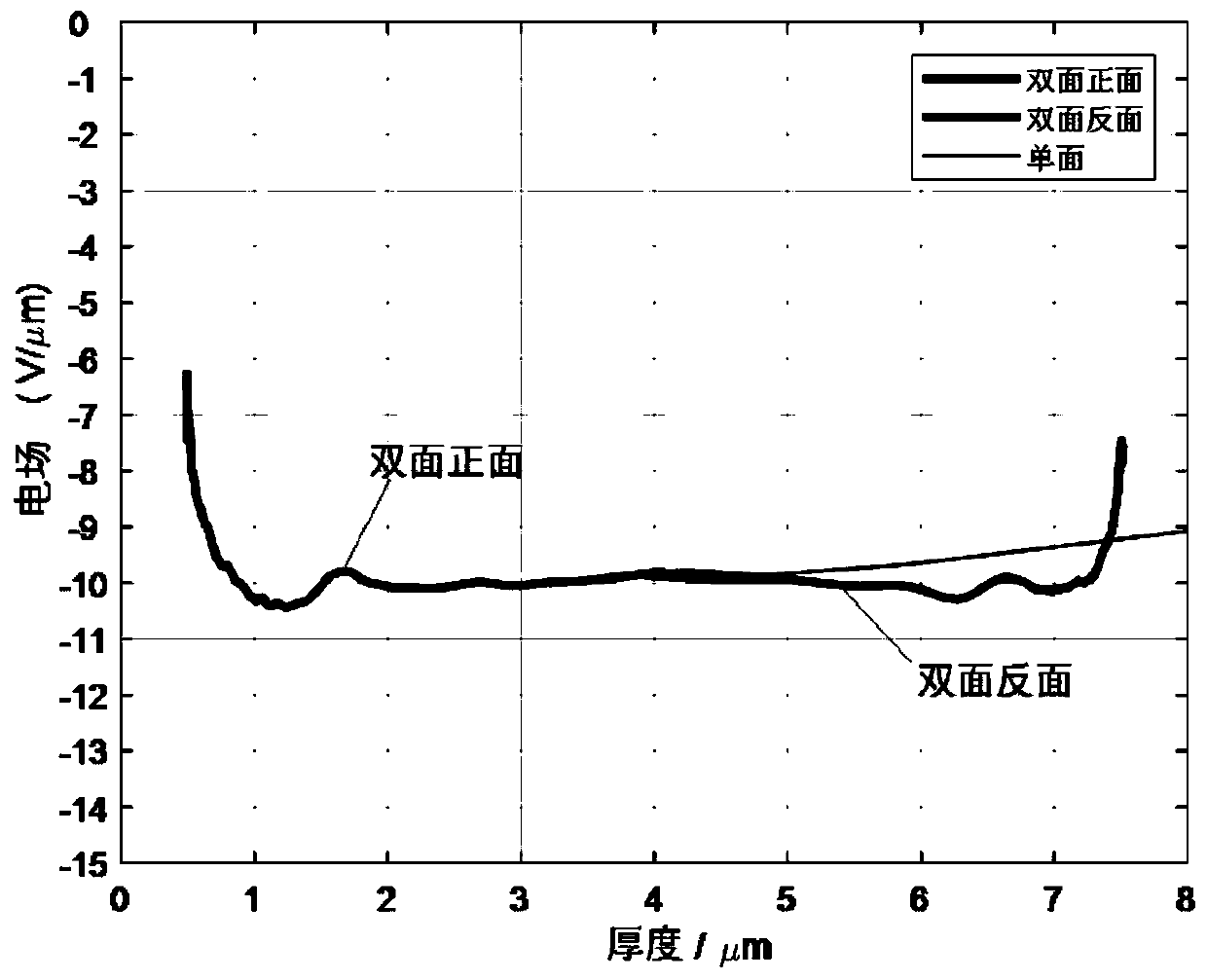
The invention relates to a double-sided in-situ measurement system and method for charge distribution in a thin dielectric film, and the system comprises a sample to be tested, a pulse laser, a photoelectric trigger circuit, a double-sided measuring optical path, a pressurizing circuit and a measuring circuit, wherein the laser generated by the pulse laser is divided into two paths, which respectively enter the photoelectric trigger circuit and the double-sided measuring optical path; the double-sided measuring optical path respectively injects the laser into a front plating electrode and a reverse plating electrode in two directions; the pressurizing circuit comprises a DC high voltage source that is applied to the reverse plating electrode of the thin dielectric film through a current limiting resistor, the reverse plating electrode is also connected to the movable end of a single-pole double-throw switch through a coupling capacitor, two fixed ends are respectively connected to the ground and a protection circuit, the protection circuit is connected to the measuring circuit, and the front plating electrode is grounded. Compared with the prior art, the invention greatly reduces the problem of the reduced resolution of the thermal pulse method in the direction of incidence of light, and improves the spatial resolution of the measurement as a whole.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Non-intrusive flow measuring device for industrial gas pipeline
ActiveCN102128654AFree from destructionAvoid lostVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsAviationEngineering
The invention discloses a non-intrusive flow measuring device for an industrial gas pipeline, which is used in the fields of industrial production, energy metering, aerospace and the like to realize the non-intrusive measurement of the air flow in the pipeline and realize the energy-saving, quick and convenient flow monitoring. Mainly based on a thermal type principle, the device adopts a measurement technique based on temperature change and time difference as well as corresponding analysis methods to create innovation in and make improvement on the thermal type flow measuring devices available on the market to improve the application performance and range of these devices. Therefore, the device has an unprecedented development prospect in related fields. The hardware part of the device mainly comprises a thermal pulse generator, a temperature sensor, a temperature controller and a signal acquiring and processing machine. The flow rate is reflected by the influences of the air flow in the pipeline on the time of the transmission of the thermal pulse by the pipe wall, and thus, the non-intrusive measurement is realized. The data process program in the signal acquiring and processing machine can effectively solve the problems such as environmental interferences, so that correct and accurate measurement is realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
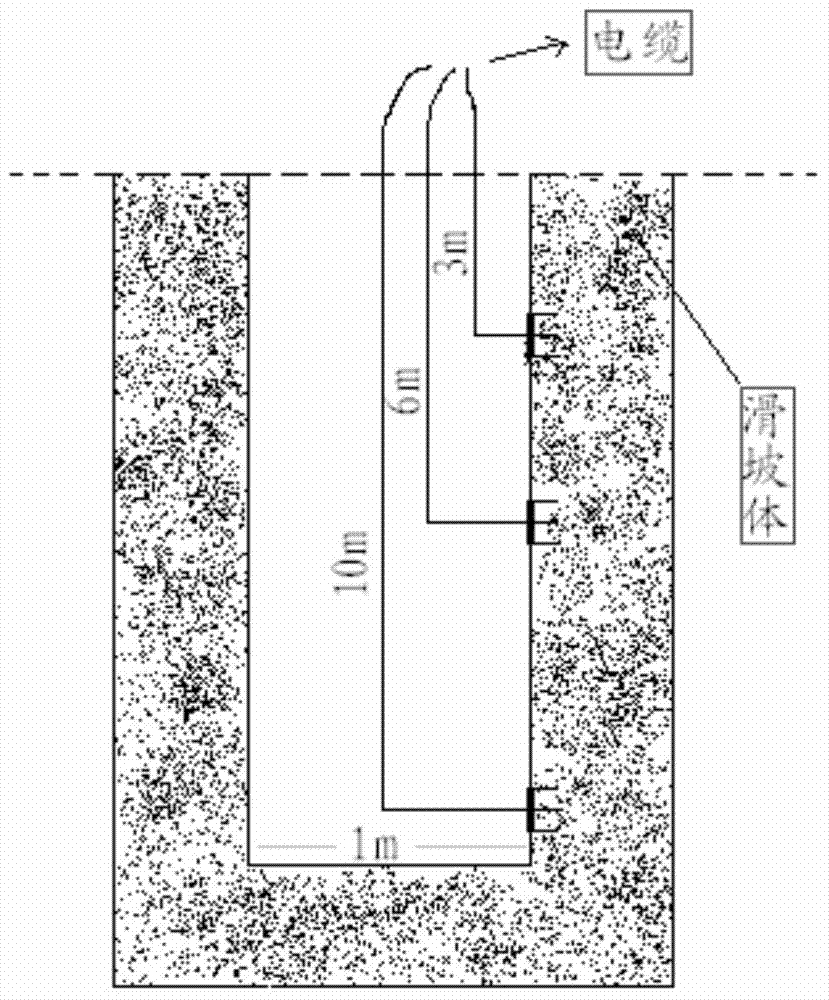
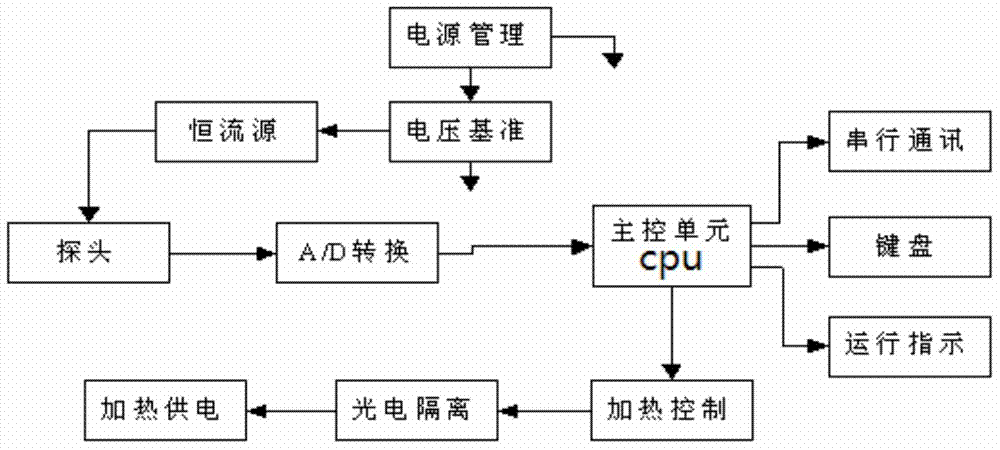
In-situ detection method of stratal hydrothermal parameters
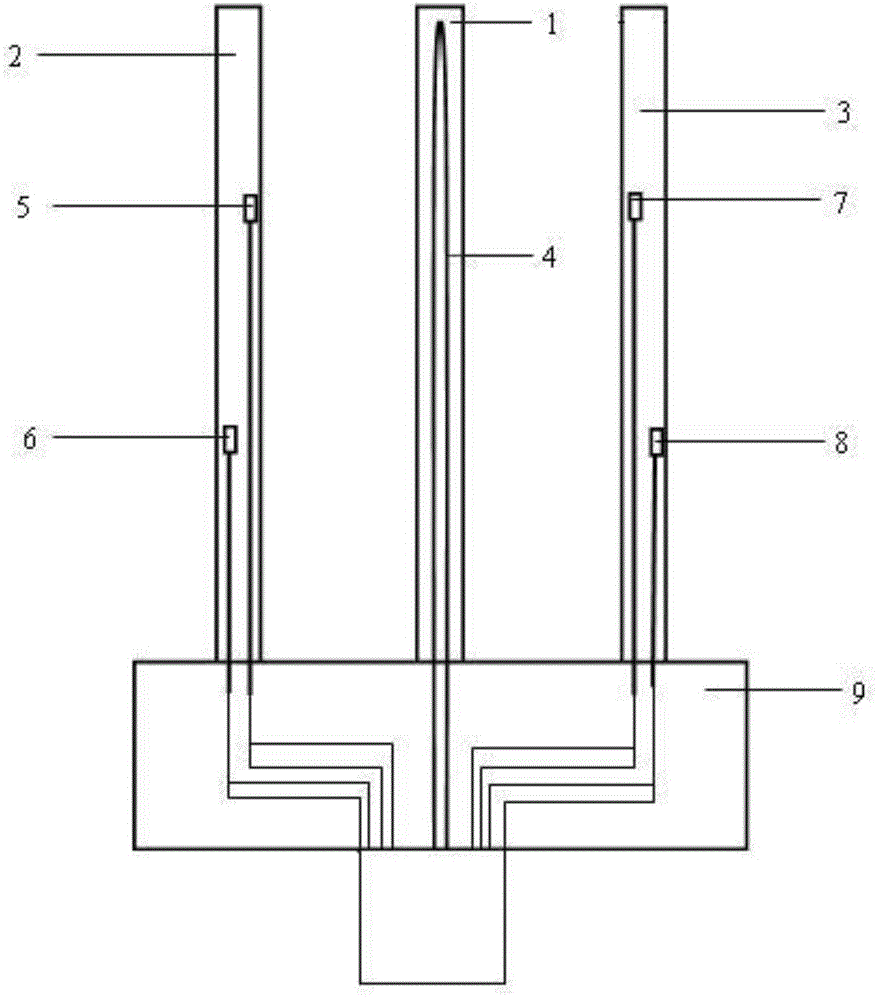
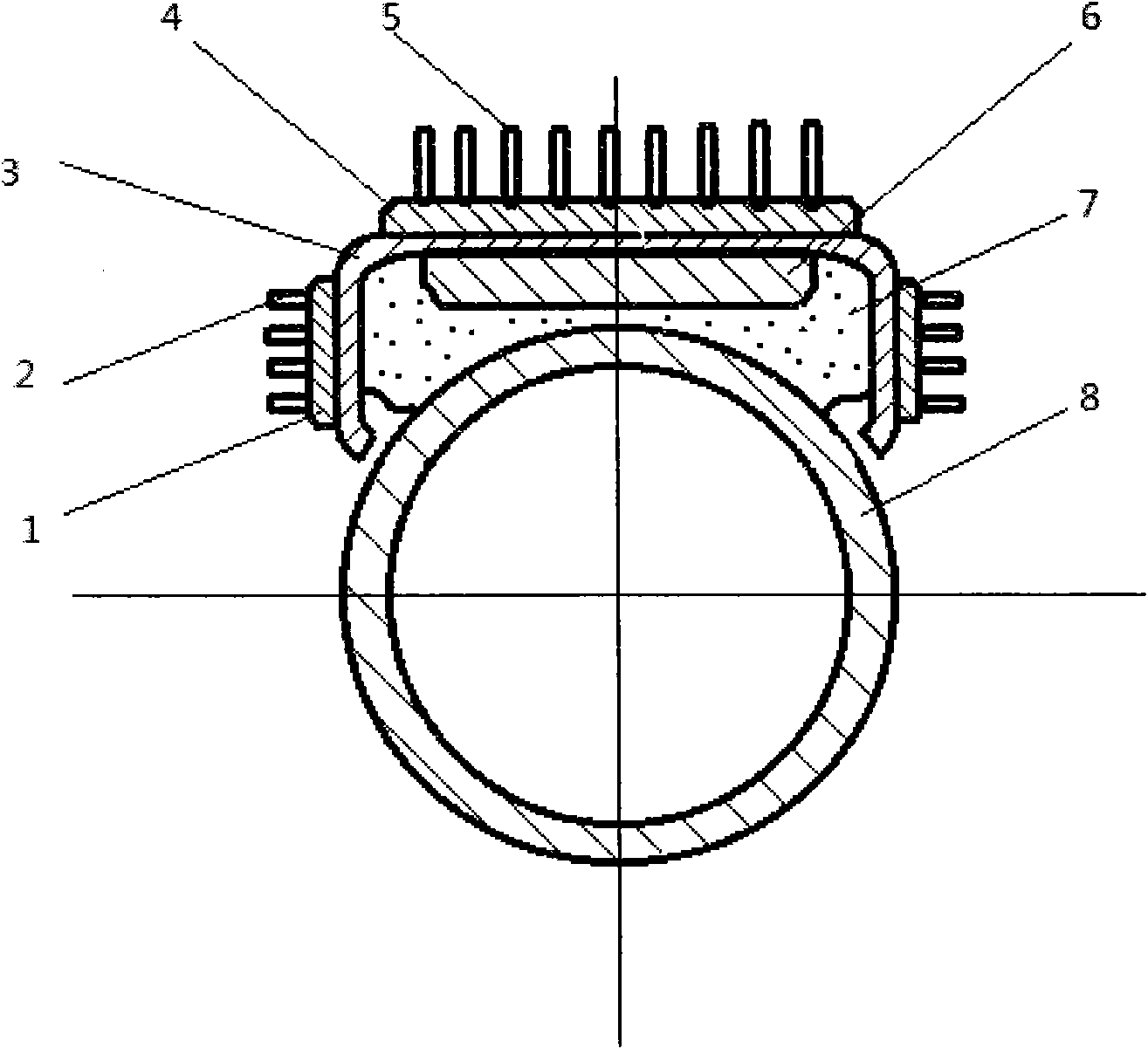
InactiveCN104502404ARealize layered in situ measurementMany measurement parametersMaterial heat developmentThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsTemperature differenceEmpirical formula
The invention discloses an in-situ detection method of stratal hydrothermal parameters. The in-situ detection method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: measuring temperature of stratums at various monitored points by using a three-pin compound probe, controlling a middle probe of the three-pin compound probe to emit thermal pulse by a CPU of a detection apparatus, simultaneously, collecting the temperature value of a lower probe of the three-pin compound probe and the corresponding time, collecting all temperature value data measured by the lower probe within 80s after emitting thermal pulse, intercepting data within 20s-75s, and calculating the heat conductivity of the stratum by utilizing an embedded heat conductivity processing program by the CPU; obtaining the water content of the stratums at various monitored points by utilizing an empirical formula between the water content and the heat conductivity; and measuring temperature difference to obtain the temperature difference value delta T at the upper and lower probes of the three-pin compound probe, and processing by using data fitting inversion software so as to obtain a permeability velocity value of stratum water parameters at the monitored points. The in-situ detection method disclosed by the invention is high in measurement precision, high in practicability and low in monitoring cost.
Owner:CENT FOR HYDROGEOLOGY & ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY CGS
Pulsed Plasma Generator
A pulsed electrostatic / electric field generator apparatus providing a source of large quantity, free slow-speed high energy free electrons, or high energy positive ions, contained in an electrostatic / electric field capacity exceeding 1 Joule. The pulsed electrostatic / electric field generator apparatus encapsulates an enclosed non-equilibrium, non-thermal pulsed power plasma. A key subcomponent of this apparatus incorporates an innovative unipolar piezoelectric capacitor creating high voltage nanosecond rise time pulses in a multistage high energy step-up pulsed plasma generation sequence of steps. The resulting multi-Joule electrostatic / electric field is then tapped to provide a source of current and / or potential for use by external loads.
Owner:ROSENER KIRK
Display substrate and driving method thereof and display device
ActiveCN106501985APrevent freezingInhibition thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal energyLight energy
The embodiment of the invention provides a display substrate and a driving method thereof and a display device and relates to the technical field of display. The display substrate is used for solving the problem of increase of the thickness of a display device caused by a heating plate. The display substrate comprises a display area and a non-display area. The display substrate further comprises a trigger electrode arranged on the display area and a heat source layer. The trigger electrode is in contact with the heat source layer and is used for receiving thermal pulse signals and performing thermal trigger on the heat source layer. The heat source layer is used for absorbing light energy, performing photothermal conversion under thermal trigger of the trigger electrode, and converting the stored light energy into thermal energy for release. The display substrate is used for manufacturing the display device.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Methods and devices for atom probe mass resolution enhancement
InactiveUS20090050797A1Reduce velocity distributionReducing ΔvMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesElectricityVoltage pulse
In an atom probe or other mass spectrometer wherein a specimen is subjected to ionizing pulses (voltage pulses, thermal pulses, etc.) which induce field evaporation of ions from the specimen, the evaporated ions are then subjected to corrective pulses which are synchronized with the ionizing pulses. These corrective pulses have a magnitude and timing sufficient to reduce the velocity distribution of the evaporated ions, thereby resulting in increased mass resolution for the atom probe / mass spectrometer. In a preferred arrangement, ionizing pulses are supplied to the specimen from a first counter electrode adjacent the specimen. The corrective pulses are then supplied from a second counter electrode which is coupled to the first via a passive or active network, with the network controlling the form (timing, amplitude, and shape) of the corrective pulses.
Owner:CAMECA INSTR
A method and device for electro-spark bronze plating on the surface of aircraft metal parts
ActiveCN113068437BImprove surface propertiesExtend your lifeMetallic material coating processesEvaporationEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for electro-spark bronze plating on the surface of aircraft metal parts. The electrodes of the device vibrate by means of a vibrator to periodically connect and disconnect the circuit, and instantaneously form sparks of instantaneous thermal pulse discharge on the surface of the metal workpiece. , so that the contact part of the electrode material is melted, boiled and evaporated. This method uses different power, vibration frequency, and amplitude for electro-spark bronze plating. The end surface of the electrode material contacts the workpiece surface and swings to both sides to make a uniform movement back and forth, so that the surface layer of the workpiece alloying. The invention solves the problem that the traditional electric spark strengthening has a large thermal impact on the workpiece substrate and the hardness drops significantly, and at the same time it cannot meet the use requirements that there should be gaps on the coating surface, improves the wear resistance and scratch resistance of the surface, and breaks through the constraints The technical bottleneck of surface alloying repair of aircraft overhaul metal parts.
Owner:国营芜湖机械厂
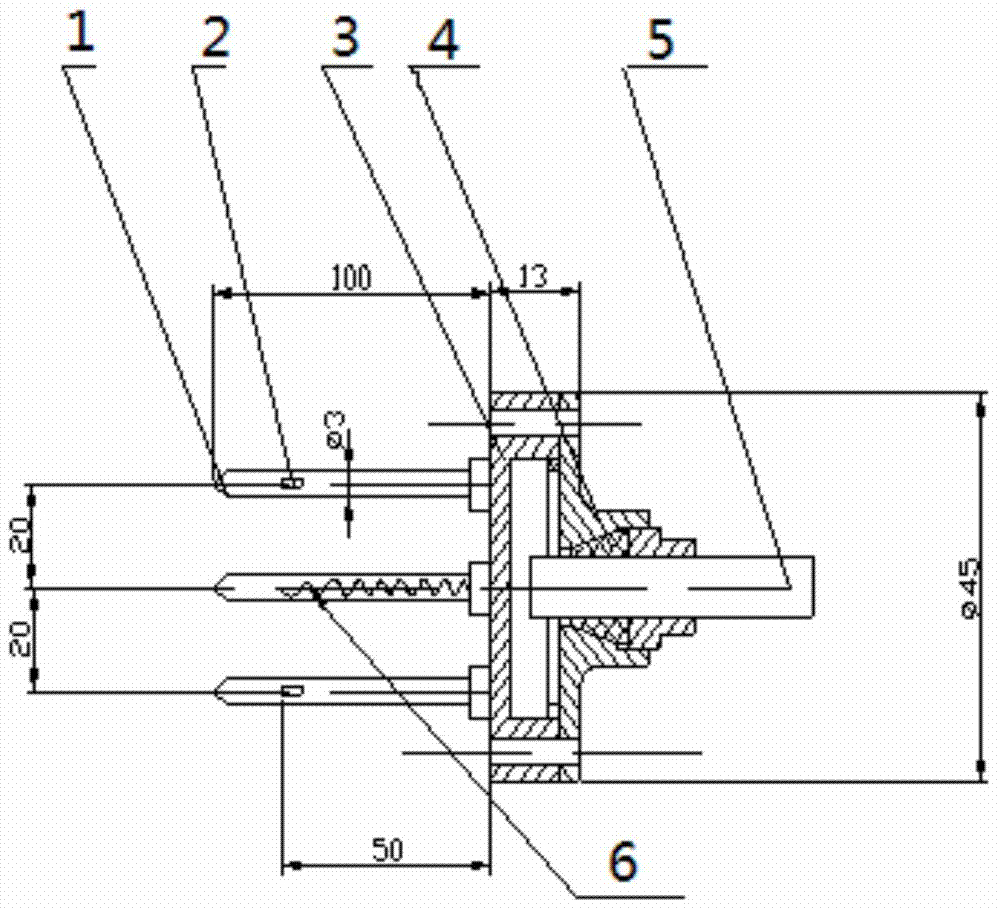
Method and device for measuring saturated soil water flow direction and flow rate based on thermal pulse principle
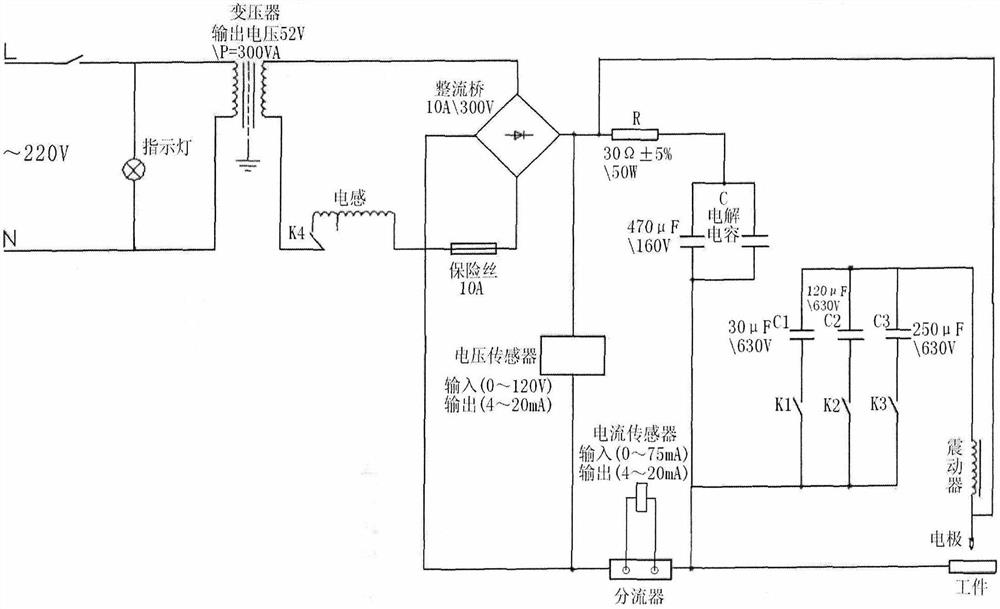
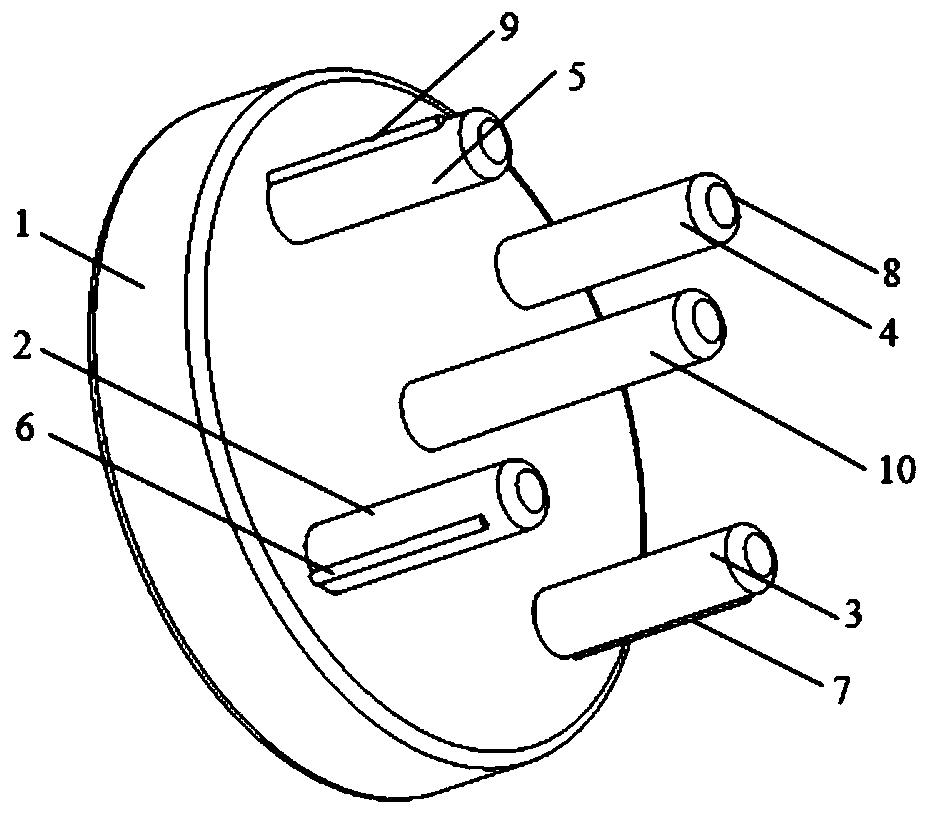
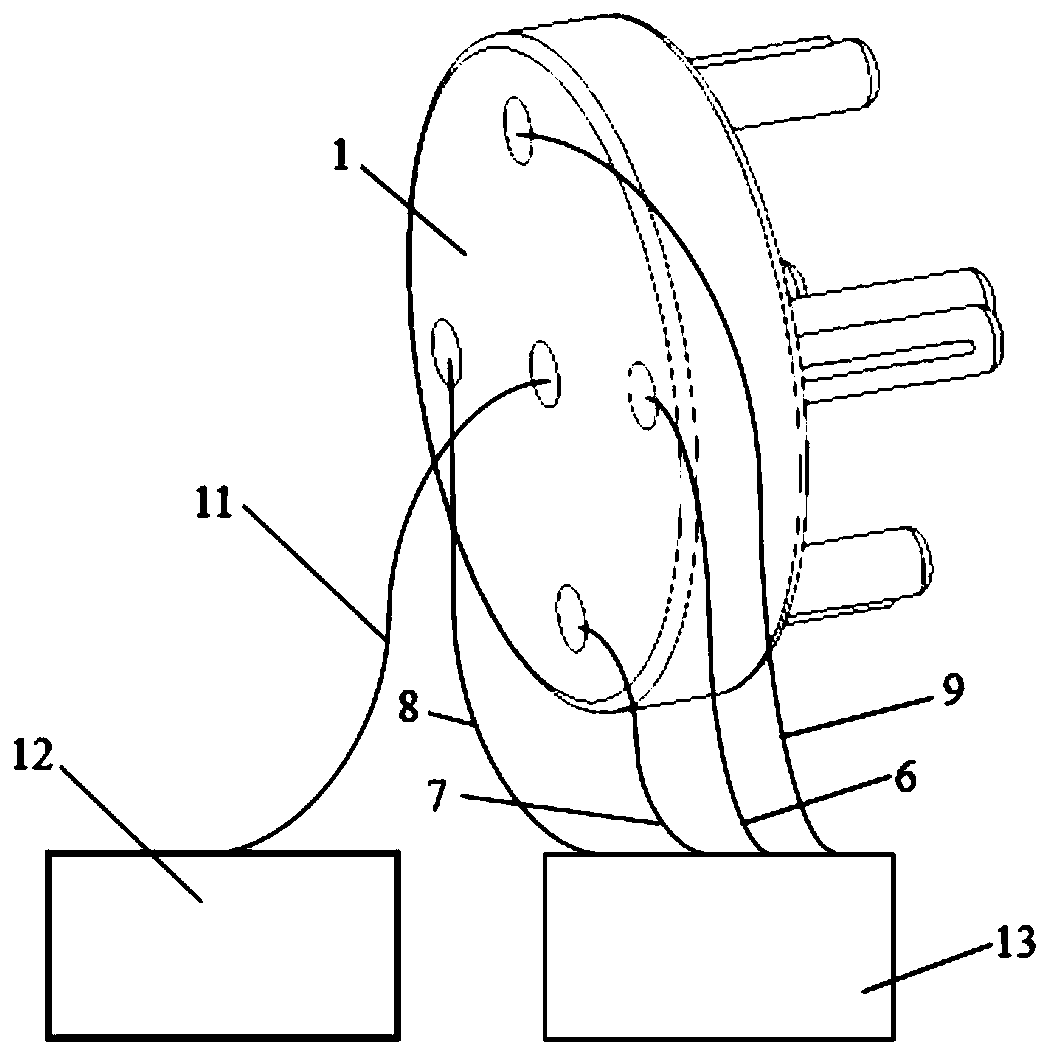
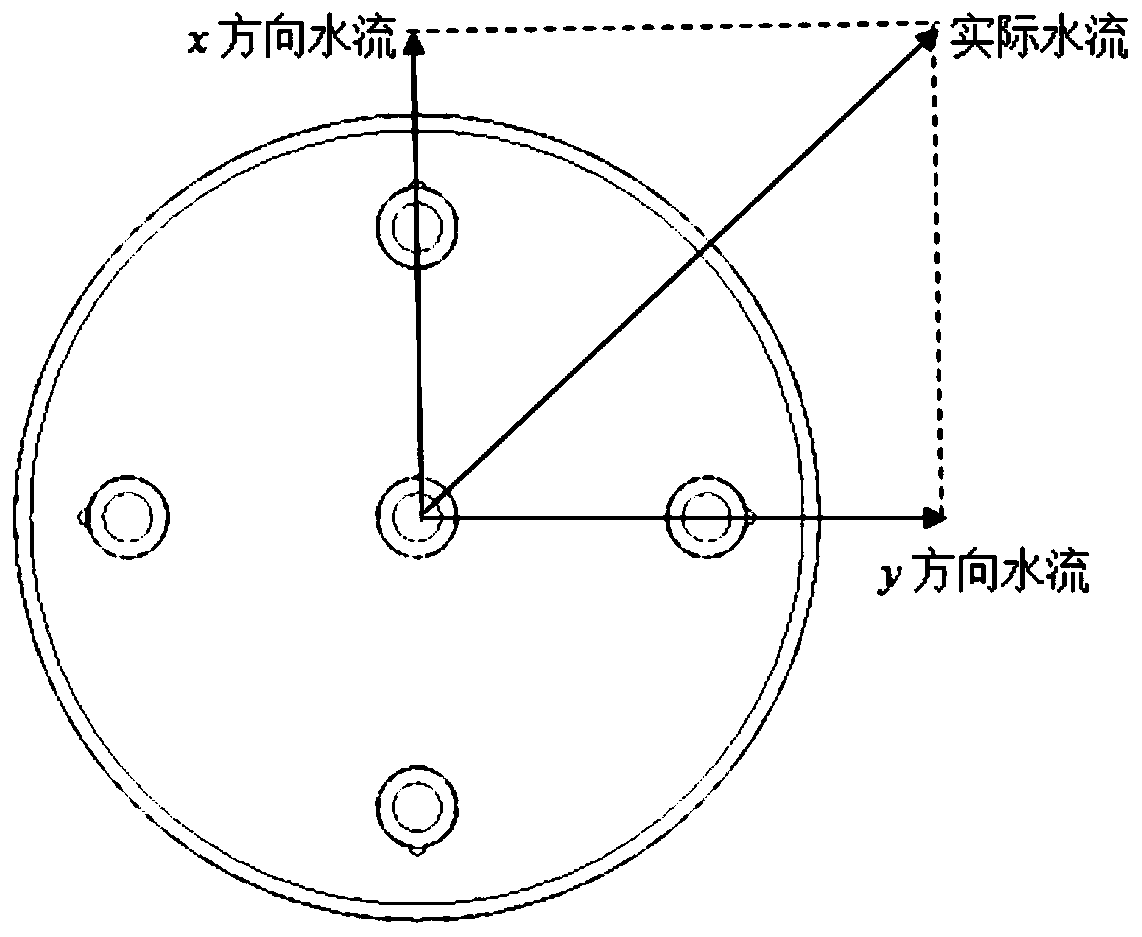
InactiveCN109916947AAccurate flow rateAccurately measure flow velocityMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentSoil water flowPhysics
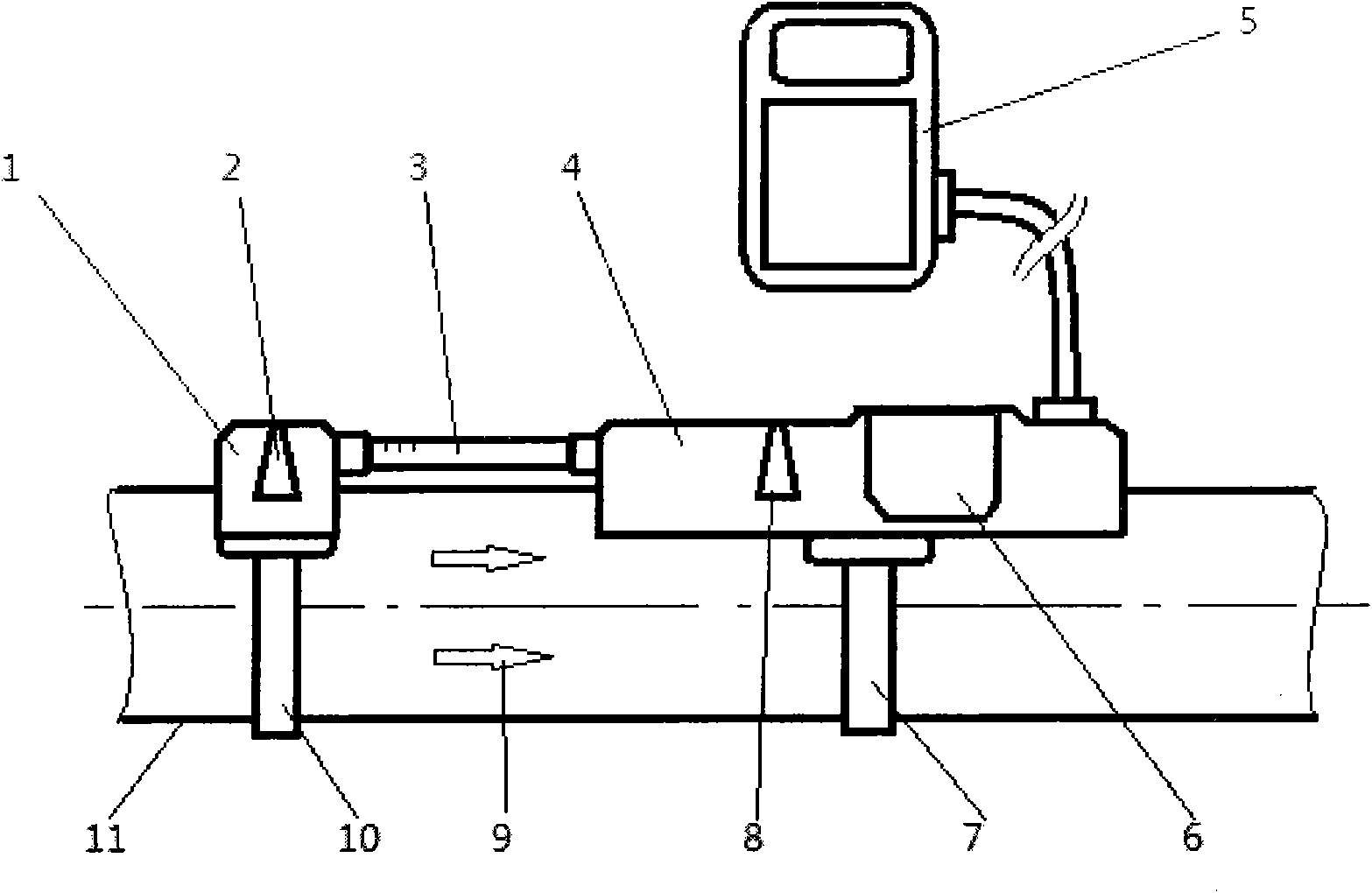
The invention relates to the measurement technology field and especially relates to a method and a device for measuring a saturated soil water flow direction and a flow rate based on a thermal pulse principle. The device comprises an integrated pedestal (1), an X-direction first temperature probe (2), a Y-direction first temperature probe (3), an X-direction second temperature probe (4), a Y-direction second temperature probe (5), a heating probe (10) and a measuring device. A water flow direction is measured through two groups of X-direction and Y-direction probes which are vertical to each other, and an actual water flow direction is vectorially synthesized so that the water flow of the saturated soil water in any directions can be measured, and the soil water flow direction and the flowrate can be accurately measured too. The measured saturated soil water flow rate is accurate.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Non-intrusive flow measuring device for industrial gas pipeline
ActiveCN102128654BDoes not affect on-site workNo throttling pressure lossVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsAviationDischarge measurements
The invention discloses a non-intrusive flow measuring device for an industrial gas pipeline, which is used in the fields of industrial production, energy metering, aerospace and the like to realize the non-intrusive measurement of the air flow in the pipeline and realize the energy-saving, quick and convenient flow monitoring. Mainly based on a thermal type principle, the device adopts a measurement technique based on temperature change and time difference as well as corresponding analysis methods to create innovation in and make improvement on the thermal type flow measuring devices available on the market to improve the application performance and range of these devices. Therefore, the device has an unprecedented development prospect in related fields. The hardware part of the device mainly comprises a thermal pulse generator, a temperature sensor, a temperature controller and a signal acquiring and processing machine. The flow rate is reflected by the influences of the air flow in the pipeline on the time of the transmission of the thermal pulse by the pipe wall, and thus, the non-intrusive measurement is realized. The data process program in the signal acquiring and processing machine can effectively solve the problems such as environmental interferences, so that correct and accurate measurement is realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
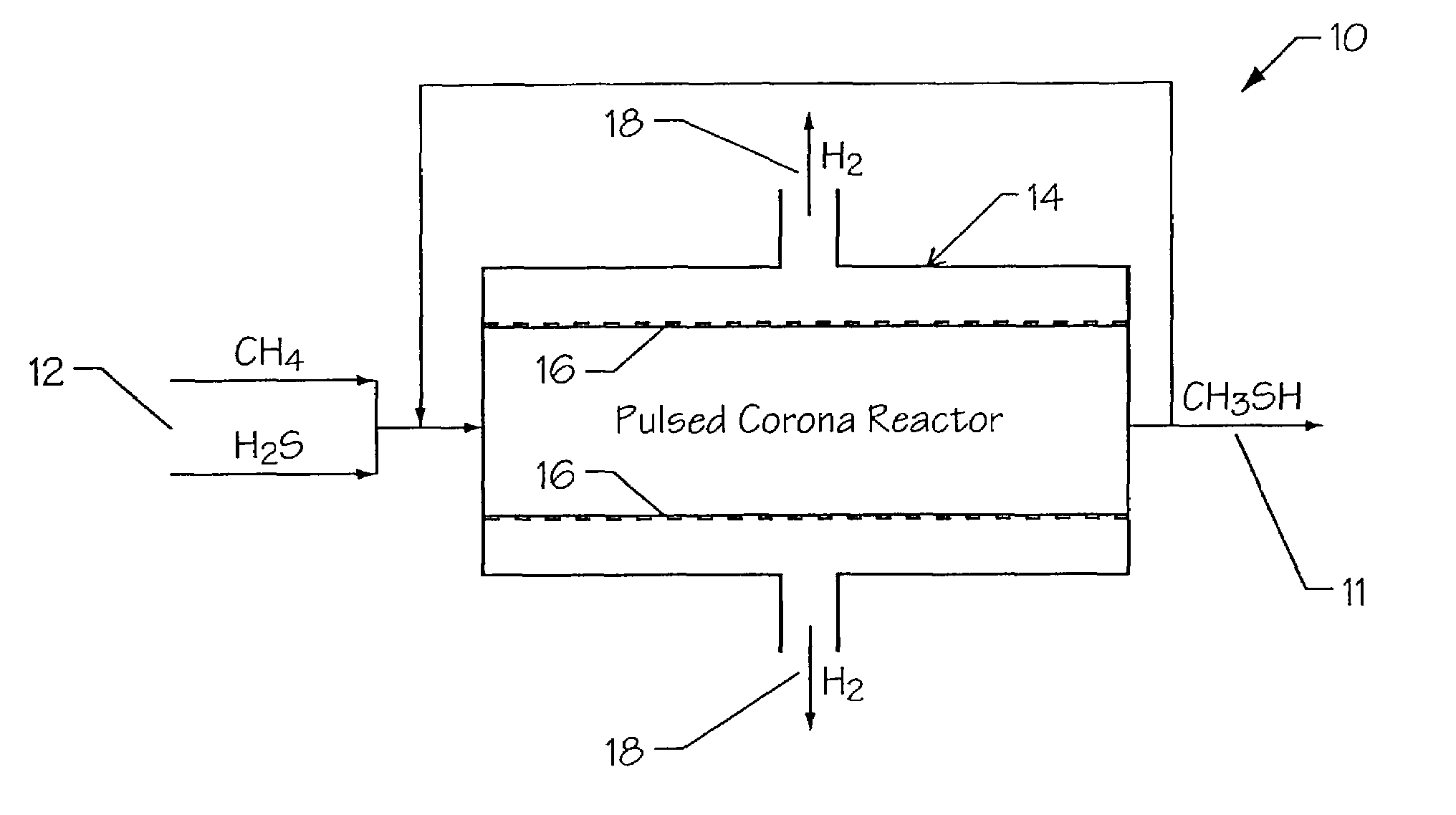
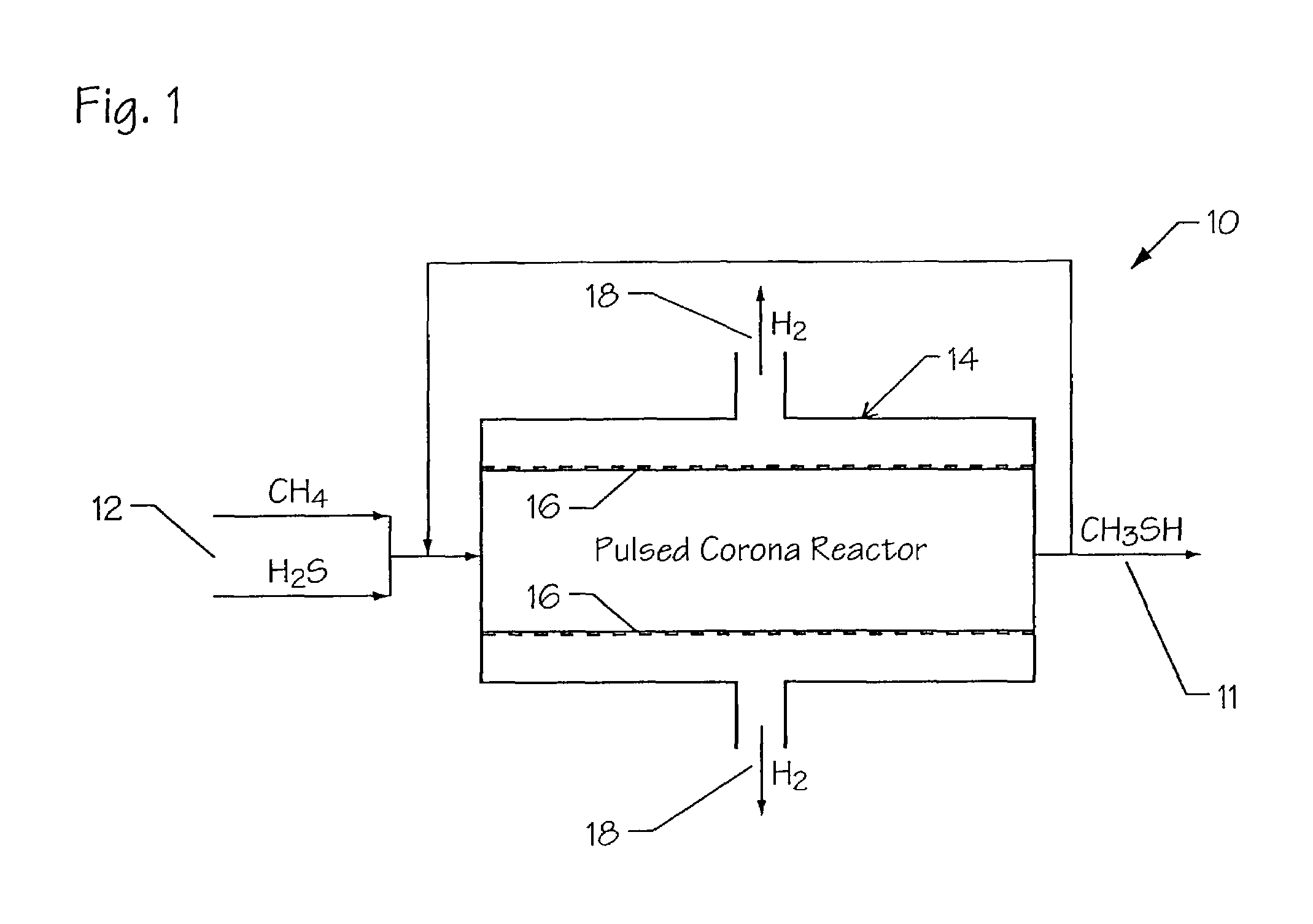
Apparatus and method for production of methanethiol
A method for the production of methyl mercaptan is provided. The method comprises providing raw feed gases consisting of methane and hydrogen sulfide, introducing the raw feed gases into a non-thermal pulsed plasma corona reactor, and reacting the raw feed gases within the non-thermal pulsed plasma corona reactor with the reaction CH4+H2S→CH3SH+H2. An apparatus for the production of methyl mercaptan using a non-thermal pulsed plasma corona reactor is also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Method for adjusting the threshold voltage of a memory cell and chalcogenide material
InactiveCN100505362CEasy to adjustWidely used valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVoltage pulseMicrowave
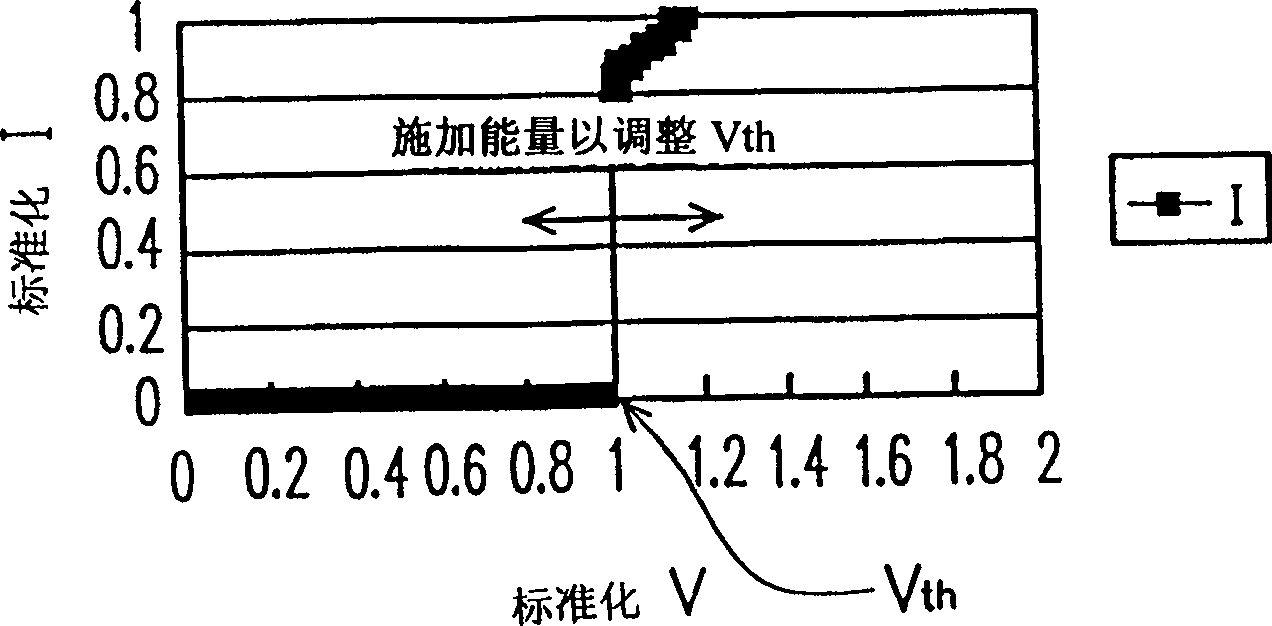
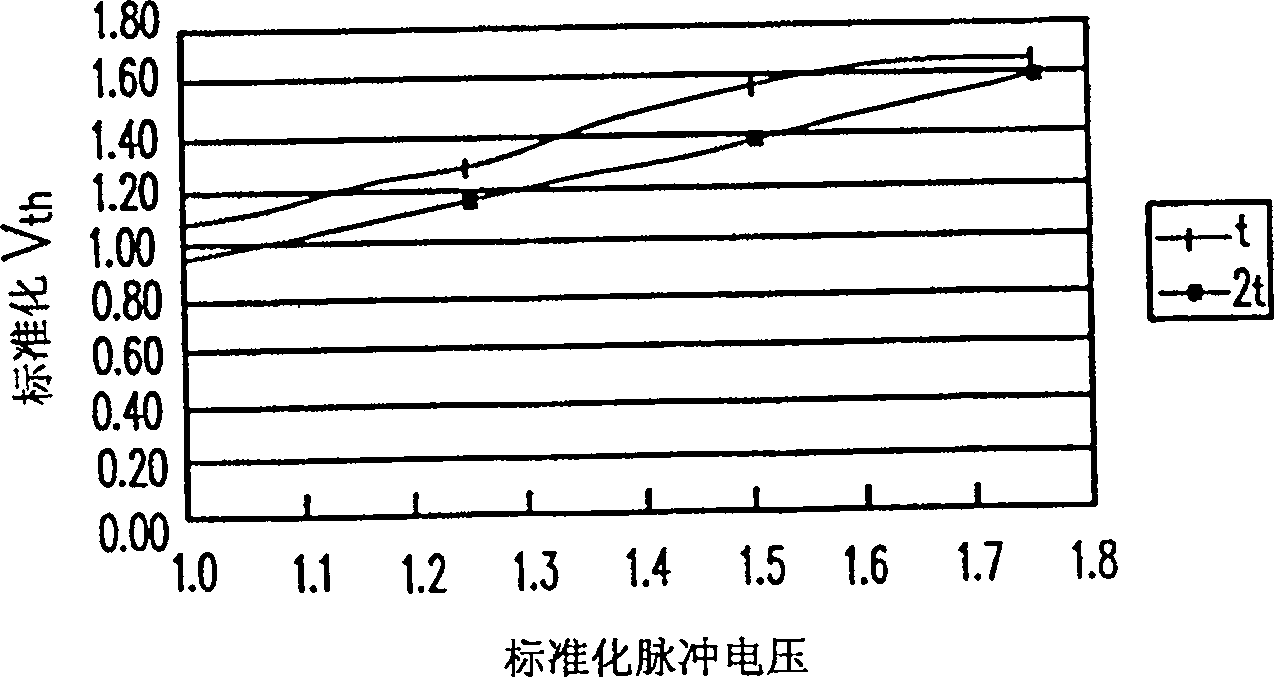
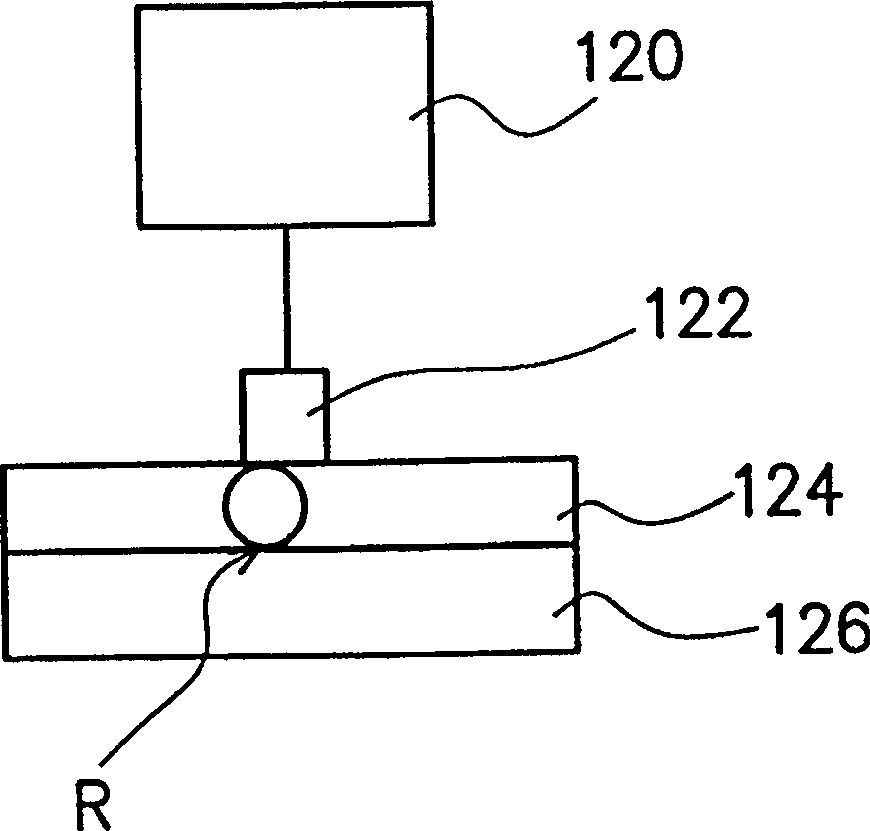
The present invention relates to a method for adjusting the threshold voltage of a memory cell and a chalcogenide material, wherein energy is applied to a film made of a material capable of changing the threshold voltage. By way of example, the thin film may be composed of a chalcogenide material. It can be applied in the form of electrical pulses (voltage pulses or current pulses), optical pulses (laser pulses), thermal pulses, microwave pulses. The energy pulses may be of a predetermined size, have a predetermined shape, and be applied for a predetermined duration to vary the threshold voltage. The present invention also describes a method of tuning the threshold voltage of a chalcogenide material. In this method, energy is applied to the chalcogenide material. The present invention can be used in the application of a large number of memory / solid-state devices, and it can quickly adjust Vth, so it is more suitable for practical use.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com