A soft carbon graphite composite anode material, a preparing method and a lithium ion battery
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and negative electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor sample uniformity and processing performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
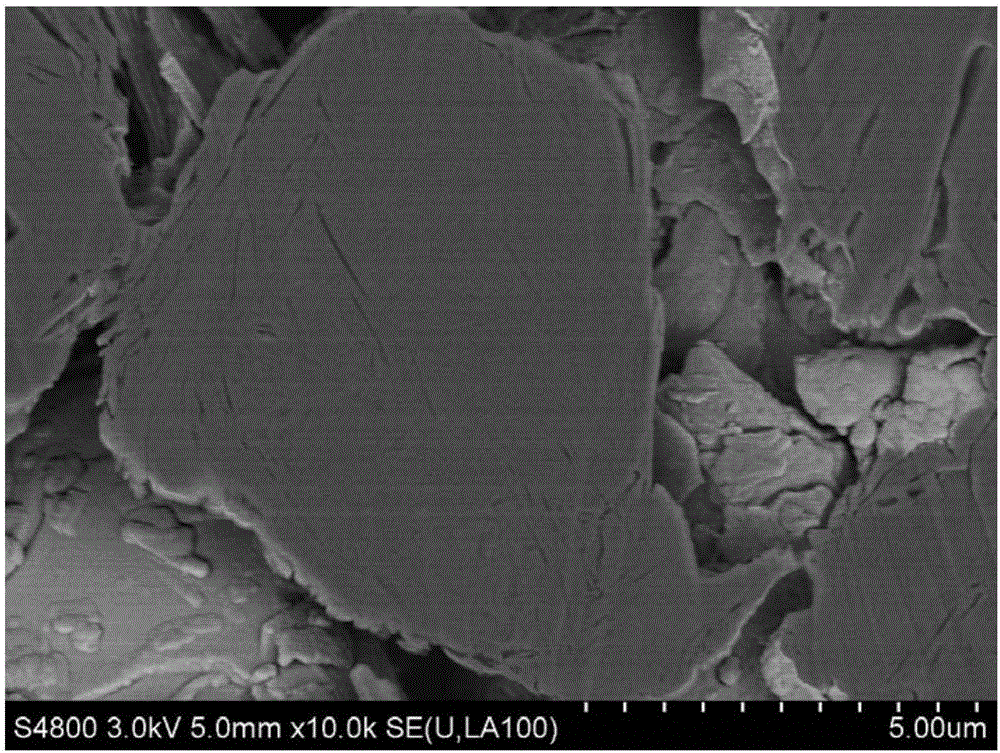
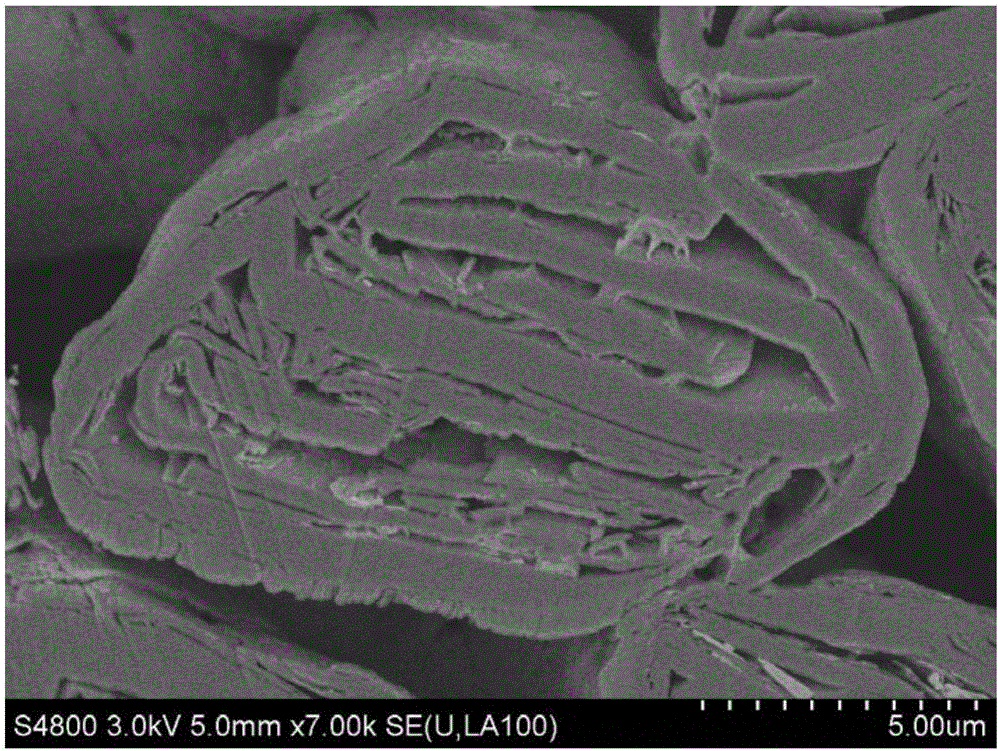
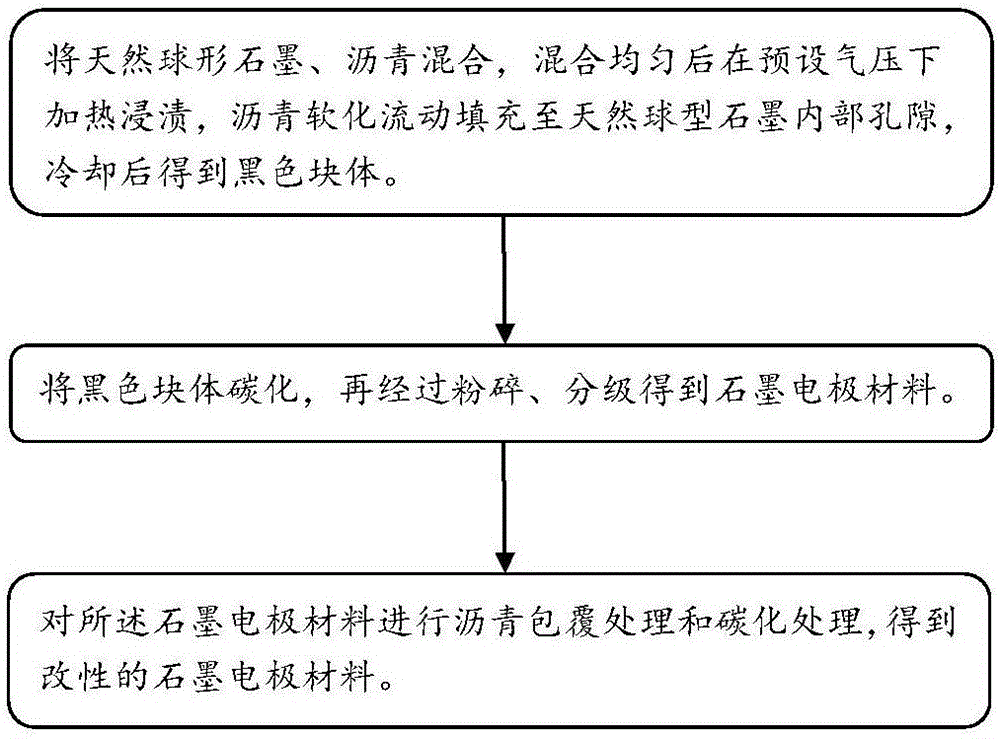
[0029] see figure 1 , the present invention provides a method for preparing a soft carbon graphite composite negative electrode material, the soft carbon graphite composite negative electrode material is mainly used in lithium-ion batteries (not shown), which includes the following steps:
[0030] Step S1, mixing natural spherical graphite and pitch, mixing evenly, heating and impregnating under preset pressure, the pitch softens and flows to fill the internal pores of natural spherical graphite, and obtains an intermediate product after cooling.
[0031] Specifically, the natural spherical graphite and powdered pitch are first weighed and mixed, and then the mixture is put into the reactor for sealing and pressure-holding heating. The internal pores of spherical graphite, after soaking for a period of time, are cooled to obtain intermediate products.
[0032] Wherein, the average particle size range of the natural spherical graphite raw material is 3-20um.
[0033] Wherein,...
Embodiment 1
[0047]Mix natural spherical graphite with an average particle size of 8.6um and powdered impregnated pitch (with a quinoline insoluble content of 0.5%) at a mass ratio of 1:1, then add it to the reactor, seal the reactor, and heat at 3°C Raise the temperature to 300°C per minute, keep the temperature constant for 2 hours, and keep the pressure at 0.2MPa, then take out the sample, and put it into the furnace for carbonization after the sample is cooled. The carbonized sample was pulverized and classified to obtain a graphite sample with an average particle size of 10.6um. The surface of the graphite sample was coated with 2% by mass of petroleum pitch by spray drying, and then carbonized at 1100 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain a composite material.
[0048] Capacity and efficiency test: The composite negative electrode material obtained in Example 1, CMC, and SBR were evenly mixed in a mass ratio of 96.5:1.5:2, then coated on the copper foil current collector, dried, a...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Mix natural spherical graphite with an average particle size of 3.5um and powdered impregnated pitch (with a quinoline insoluble content of 0.5%) at a mass ratio of 1:1, then add it to the reactor, seal the reactor, and heat at 3°C Raise the temperature to 350°C per minute, keep the temperature constant for 2 hours, and keep the pressure at 0.4MPa, then take out the sample, and put it into the furnace for carbonization after the sample is cooled. The carbonized sample was pulverized and classified to obtain a graphite sample with an average particle size of 5.8um. The surface of the graphite sample was coated with 2% by mass coal tar pitch by spray drying, and then carbonized at 1000 °C under a nitrogen and helium mixed gas atmosphere to obtain a composite material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com