Method for recovering valuable metals from waste refractories by virtue of reselection-kerosene aggregative flotation combined process
A waste refractory material and combined process technology, which is applied in the field of valuable metal recovery in waste refractory materials, can solve the problems of waste of resources, high energy consumption, complex process, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient recovery, avoidance of damage, and efficient recovery.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
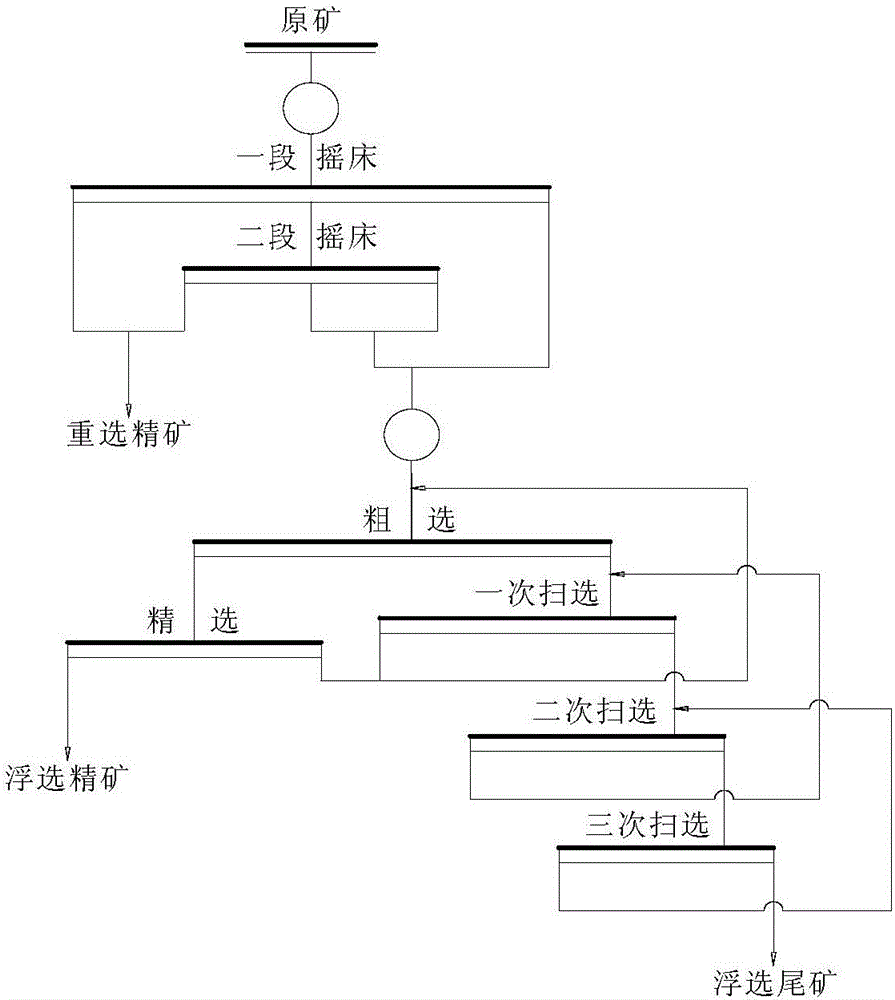
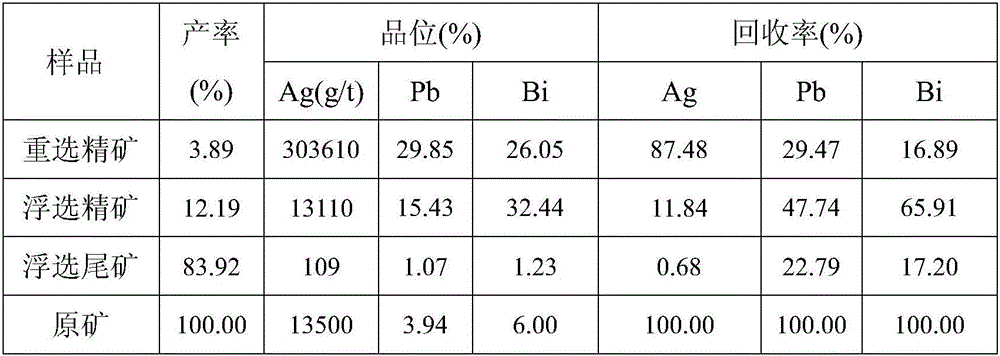
[0032] The present invention takes silver converter refractory bricks from a lead smelter in Chenzhou, Hunan as the research object. The discarded refractory bricks contain 1.35% silver, 3.94% lead, 6.00% bismuth, and the rest are basically magnesium, chromium, iron, aluminum, calcium, silicon, etc. of oxides.
[0033] Crush the waste refractory bricks to less than 3mm, mix and sample, take 500g of test samples and wet grind them with a ball mill, grind for 5 minutes, so that the fineness reaches 0.074mm and the particles account for 65%, the grinding concentration is 66.7%, and repeat the grinding Eight times, mix the sample to make it reach 4000g, mix the sample and carry out the shaking table re-selection experiment. After the sample is subjected to a shaker test, three products of fine, middle and tail can be obtained. In order to improve the recovery rate of the shaker operation, the middle ore product is subjected to a shaker operation again, and the obtained concentrate...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The present invention takes lead converter refractory bricks from a lead smelting plant in Chenzhou, Hunan as the research object. The discarded refractory bricks contain 2054g / t of silver, 18.74% of lead, 1.52% of antimony, and 1.87% of copper, and the rest are basically magnesia oxides.
[0051] Crush the waste refractory bricks to less than 3mm, mix well, take samples, take 500g of test samples and wet-grind them with a ball mill, and grind them for 5 minutes, so that the fineness reaches 0.074mm and the particles account for 68%, and the grinding concentration is 66.7%, and repeat the grinding 8 times, mix the sample to make it reach 4000g, mix the sample and carry out the shaking table re-selection experiment. After a shaker test on the sample, three products of fine, medium and tail can be obtained. In order to improve the recovery rate of the shaker operation, the medium ore product is subjected to a shaker operation again, and the obtained concentrate is mixed wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com