Method for purifying plasma functional proteins from Cohn fraction IV
A technology with four components and functions, applied in the field of protein preparation, can solve the problems of being unsuitable for green production, long production cycle, and numerous steps, and achieve the effect of easy industrial automatic production, high purity and activity, and short purification cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
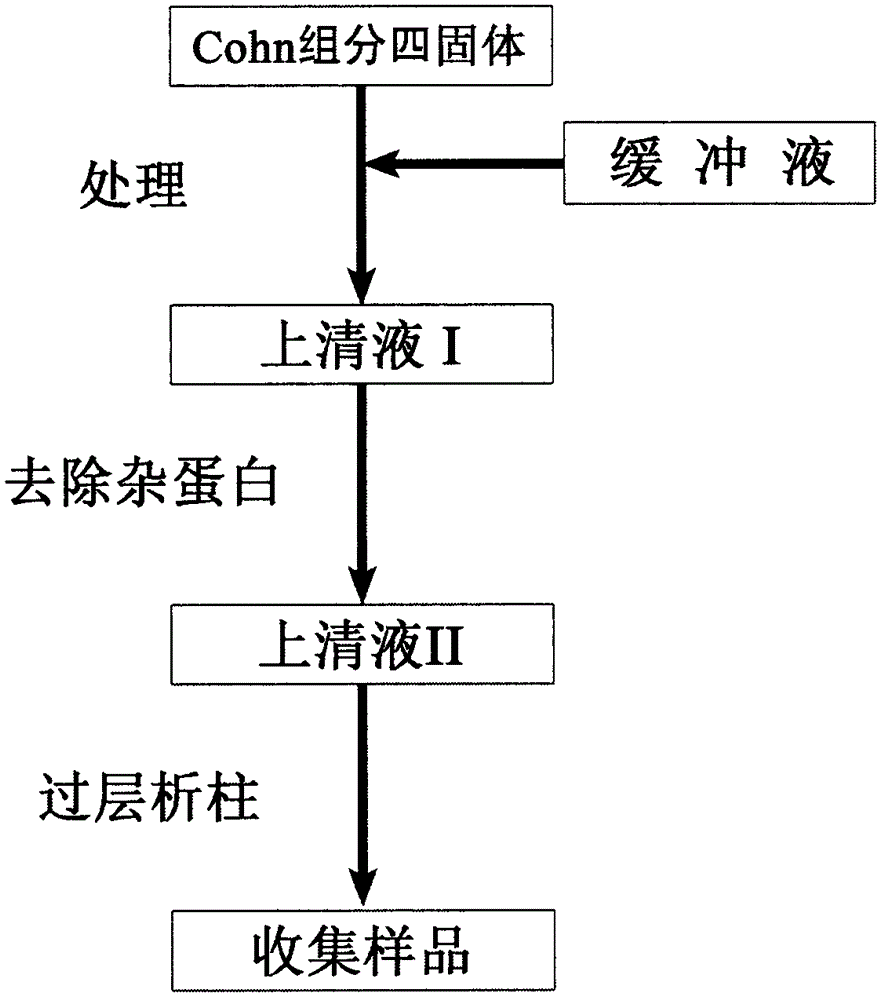
[0024] Dissolve 50 g of Cohn component four solids in 100 mL of Tris buffer (pH 7.5-8.0) and fully dissolve. Then, centrifuge at 10000 rpm for 20 min at 0° C. to remove the filter aid and obtain supernatant I. Adjust the pH value of the supernatant I to 2.0, separate the foreign protein to obtain the supernatant II, and use S-SOURCE 30 to pack the column with a column volume of 40 mL. First equilibrate the column with pH 2.0 maleic acid buffer, equilibrate for 10 column volumes, inject supernatant II, carry out gradient elution with pH 2.0 maleic acid buffer with a concentration of 0 to 10M, and collect each column on the map. peak.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Dissolve 50 g of Cohn component four solids in 150 mL of phosphate buffer (pH 7.0 to 7.5) and fully dissolve. Then, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 25 min at 4°C to remove the filter aid and obtain supernatant I. Adjust the pH value of the supernatant I to 4.0, separate the foreign protein to obtain the supernatant II, and use SP-Sepharose HP to pack the column with a column volume of 40 mL. First equilibrate the column with pH 4.0 formic acid buffer, equilibrate for 10 column volumes, inject the supernatant II, perform gradient elution with pH 4.0 formic acid buffer with a concentration of 0 to 4M, and collect the peaks on the spectrum.
Embodiment 3
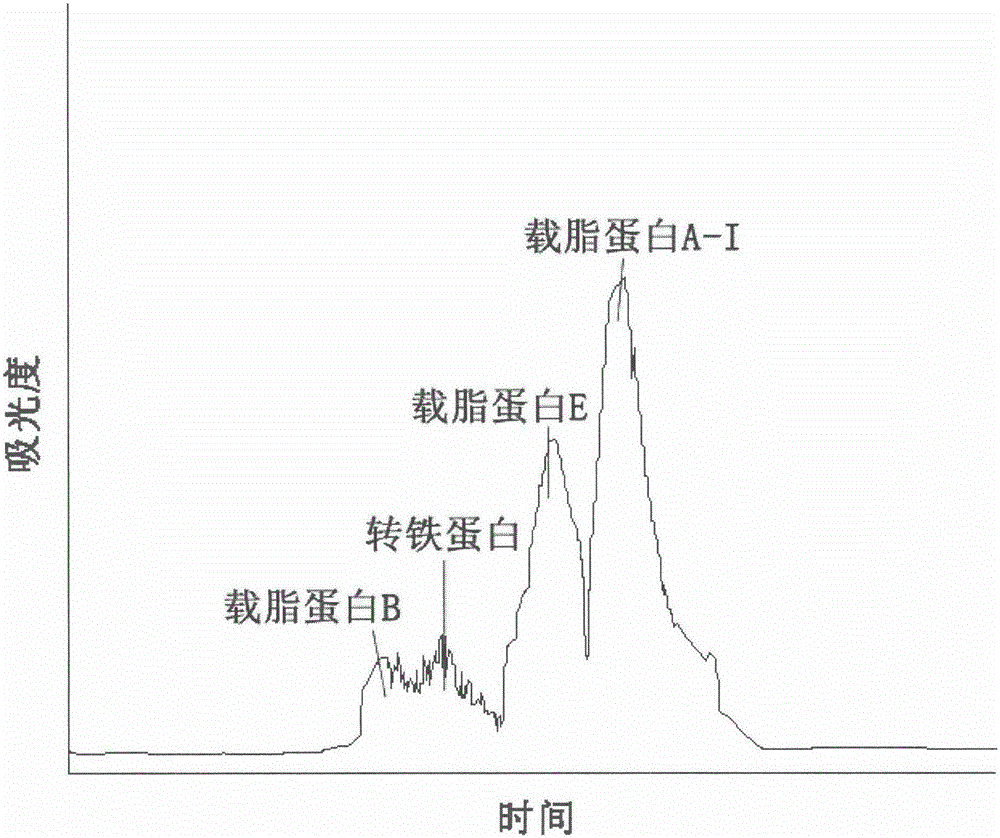
[0028] Dissolve 50 g of solid Cohn component four in 120 mL of pH 7.4 phosphate buffer, and dissolve fully. Then, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 20 min at 4° C. to remove the filter aid and obtain supernatant I. Adjust the pH value of the supernatant I to 7.8, separate the miscellaneous proteins to obtain the supernatant II, and use Q Sepharose to pack the column with a volume of 50 mL. First equilibrate the column with pH 7.8 phosphate buffer, equilibrate for 10 column volumes, inject the supernatant II, perform gradient elution with pH 7.8 phosphate buffer with a concentration of 0 to 2M, and collect the peaks on the spectrum. Chromatogram see figure 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com