Artemisia carvifolia HD-ZIP IV type transcription factor coding sequence and application
A technology of transcription factor and coding sequence, which is applied to the coding sequence and application field of Qinghao HD-ZIPIV transcription factor, can solve the problem of not regulating glandular hair density and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1, the cloning of Artemisia annua AaHD1 gene
[0039] 1. Extraction of Total RNA from Artemisia annua Genome
[0040] Take the leaf tissue of Artemisia annua, grind it in liquid nitrogen, add it to a 1.5mL Eppendorf (EP) centrifuge tube filled with lysate, shake it fully, and extract total RNA according to the instructions of the TIANGEN kit. The quality of total RNA was identified by formaldehyde denaturing gel electrophoresis, and then the RNA content was determined on a spectrophotometer.
[0041] 2. Cloning of Artemisia annua AaHD1 gene
[0042]Using the extracted total RNA as a template, cDNA was synthesized under the action of PowerScript reverse transcriptase; gene-specific primers (SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4) were designed according to the sequence of the AaHD1 gene, and the total cDNA was obtained by PCR. The AaHD1 gene was amplified and sequenced.
[0043] Through the above steps, the full-length coding sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) of the transcrip...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2, construction of plant binary interference expression vector containing AaHD1 gene
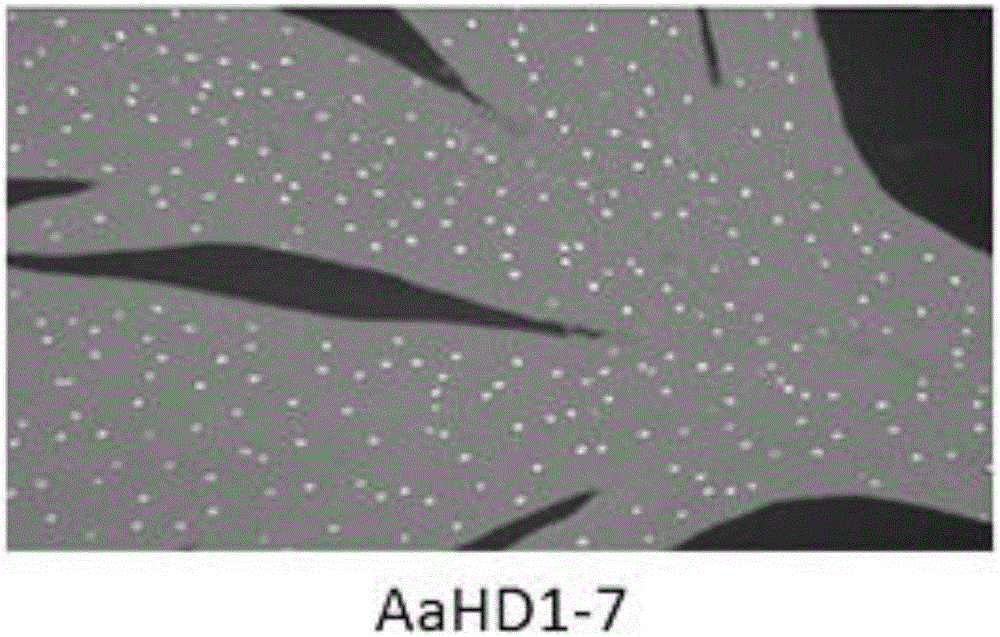
[0045] In order to study the effect of AaHD1 gene on the development of secretory glandular hairs of Artemisia annua, the overexpression vector PHB-AaHD1 overexpressing AaHD1 was constructed. In order to facilitate the construction of the expression vector, the restriction site of BamH1 was introduced into the forward primer, and the restriction site of Xho1 was introduced into the reverse primer. The primers are shown in Table 1;
[0046] Table 1 PCR primers constructed by PHB-AaHD1 vector
[0047]
[0048]
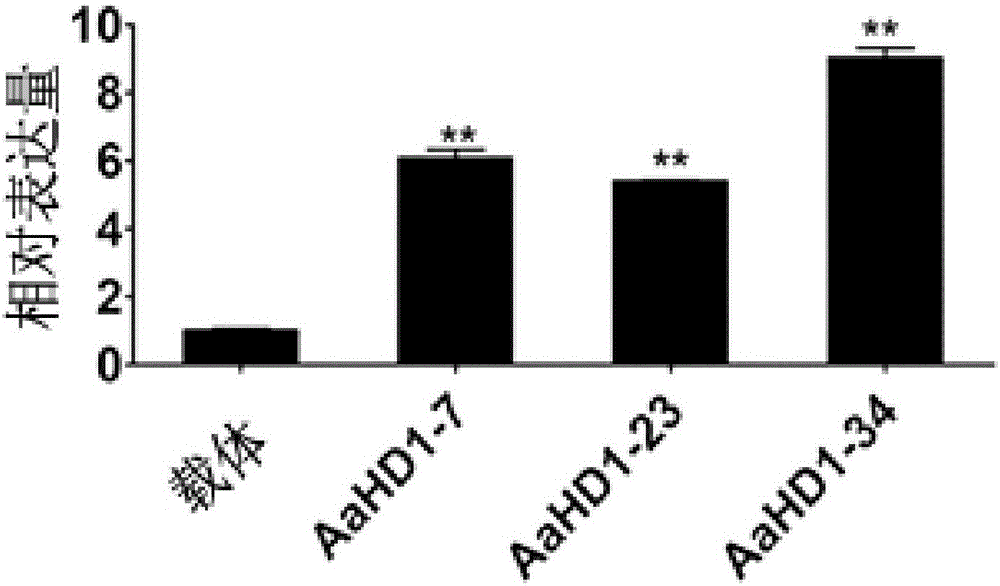
[0049] In this example, the Artemisia annua AaHD1 gene is operably linked to the expression control sequence, and the vector can be used to regulate the content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua through a developmental regulation strategy.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated AaHD1 interference vector genetically transforms Artemisia annua to obtain transgenic Artemisia annua plants
[0051] 1. Acquisition of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Engineering Bacteria Containing AaHD1 Overexpression Vector
[0052] The plant binary overexpression vector containing AaHD1 in Example 2 was transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens (such as EHA105, which is a publicly available biological material in the market, which can be purchased from CAMBIA Company in Australia, and the strain number is Gambar 1 ), and validated by PCR. The results showed that the plant binary interference expression vector containing AaHD1 had been successfully constructed into the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain.
[0053] 2. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated AaHD1 gene transformation of Artemisia annua
[0054] 2.1. Preculture of explants
[0055] Artemisia annua seeds were soaked in 75% ethanol for 1 min, then soaked in 20% NaClO...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com