Preparation method of degradable magnesium alloy and degradable polymer composite
A technology for degrading polymers and composite materials, applied in the field of preparation of degradable magnesium alloys and degradable polymer composite materials, can solve the problem of low mechanical properties of degradable polymers, limited strength of composite materials, low elastic modulus and strength, etc. Problems, achieve the effect of shortening recovery time, increasing biological activity, and improving strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A preparation method of a degradable magnesium alloy and a degradable polymer composite material, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
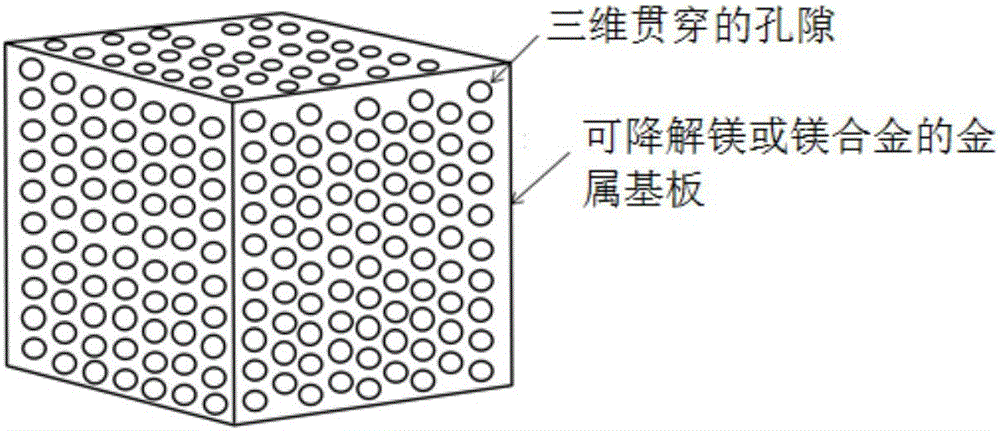
[0025] 1) Using degradable metal magnesium as the metal substrate, and performing 3D drilling on the degradable metal magnesium, so that the degradable metal magnesium metal substrate is covered with three-dimensional through pores with a pore size of 0.3mm and a porosity of 35%;
[0026] 2) Put the metal substrate covered with three-dimensional penetrating pores into a closed injection mold, and press the molten degradable polymer polylactic acid (PLA) into the degradable magnesium by injection molding at a temperature of 180°C. In the three-dimensional penetrating pores of the metal substrate;
[0027] 3) Place it for 3-10 minutes at a temperature of 180°C and a pressure of 20 MPa. After demoulding and cooling, remove the polylactic acid (PLA) outside the holes of the metal magnesium substrate to obtain a mixture o...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for preparing a composite material of a degradable magnesium alloy and a degradable polymer, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0031] 1) The degradable magnesium alloy Mg-0.5Zr-1Ca is used as the metal substrate, and the degradable magnesium alloy is processed so that the metal substrate of the degradable magnesium alloy is covered with three-dimensional through pores;
[0032] 2) Put the metal substrate of the degradable magnesium alloy Mg-0.5Zr-1Ca covered with three-dimensional penetrating pores into a closed injection mold, and melt the degradable polymer polyglycolic acid at a temperature of 240 ° C (PGA) is pressed into the three-dimensional penetrating pores of the metal substrate of the degradable magnesium alloy Mg-0.5Zr-1Ca by extrusion;
[0033] 3) Place it for 3-10 minutes at a temperature of 240°C and a pressure of 20 MPa. After demoulding and cooling, remove the polymer polyglycolic acid (PGA) outside the hole of the magne...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A method for preparing a degradable magnesium alloy and a degradable polymer composite material, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0037] 1) The degradable magnesium alloy Mg-1Mn-2Zn-1Nd alloy is used as the metal substrate, and the degradable magnesium alloy is subjected to 3D drilling treatment, so that the metal substrate of the degradable magnesium alloy is covered with pores with a diameter of 0.2mm and a porosity of 21% three-dimensional through pores;
[0038] 2) Put the metal substrate covered with three-dimensional penetrating pores into a closed injection mold, and press the melted degradable polymer L-polylactic acid (PLLA) into the degradable material by injection at a temperature of 200°C. In the three-dimensional penetrating pores of magnesium alloy;
[0039] 3) Place it for 0.3-1 minute at a temperature of 200°C and a pressure of 100 MPa. After demoulding and cooling, remove the polymer L-polylactic acid (PLLA) outside the hole of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com