A kind of biocontrol actinomycetes strain and application thereof for preventing and treating soybean blight
A technology of actinomycetes and biocontrol agents, applied in the direction of application, bacteria, and biocides, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory chemical control effects and environmental pollution, and achieve the goal of preventing and controlling soybean diseases, reducing agricultural pollution, and facilitating industrial production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 Isolation of antagonistic actinomycetes
[0021] The specific process is as follows:
[0022] 1. Collection of soil samples
[0023] The rhizosphere soil at a depth of 5-10 cm from different soybean plots was collected from Nanyuan Village, Bangshan Town, Longhai City, Fujian Province, divided into packages and marked, and brought back to the laboratory, and separated after natural air drying.
[0024] , Isolation of Actinomycetes
[0025] Separation was performed using the plate dilution method. Weigh 10g of the soil sample, pour it into a conical flask equipped with small glass beads and 90ml of sterile water, shake it for 30min, then let it stand for 5 minutes, dilute it by 10 times successively, and prepare 10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 0.1ml of the suspension of different concentrations was added to Gao's No. 1 medium (adding K with a final concentration of 50mg / L 2 GrO 7 ) plate, spread evenly and place it at 28°C for observation. After 5-7 ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2 Identification of bacterial strain St3
[0027] 1. Observation of morphological characteristics
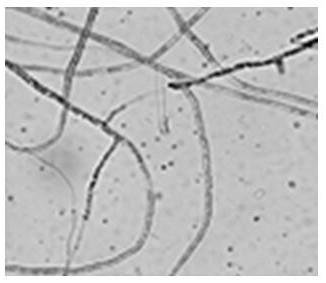
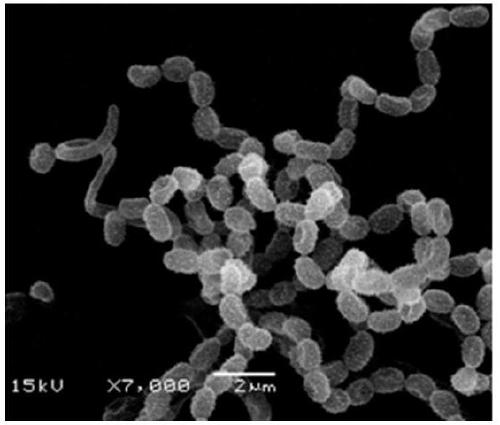
[0028] Strain-inoculate the strain St3 on Gao's No. 1 medium, insert a sterile cover glass at an angle of 45 degrees, and culture it at 28°C for 7 days, then take out the cover glass and observe the growth of hyphae and spores under an optical microscope and an electron microscope. Morphological characteristics. It was found that the spore filaments of strain St3 were helical, often in clusters, and the spore filaments were broken into spores, spores were oval, and the surface was rough ( figure 1 and figure 2 ).
[0029] , Cultivate characteristic observation
[0030] Using the 8 kinds of media recommended by the "Streptomyces Identification Manual", culture the strain St3 at 28°C for 7-10 days, observe the growth of the bacteria, and record the color of the aerial hyphae and basal hyphae and whether soluble pigments are produced. Strain St3 grew well on G...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The optimization of embodiment 3 St3 bacterial strain fermentation technology
[0036] The above strains were inoculated in Gaoshi No. 1 liquid medium at 28 °C, 180 r / min, and cultured for 2 days to make seed liquid. Take 6ml of seed solution and inoculate it in the fermentation medium. Through the screening of carbon and nitrogen sources, single factor test and orthogonal test of nutritional conditions, the optimal fermentation formula of the strain was obtained: starch 2wt.%, glucose 1.5 wt.%, soybean powder 2wt.%, NaCl 0.3 wt.%, CaCO 3 0.2 wt.%, the rest is water. Through exploring the culture conditions, the optimal fermentation conditions were obtained: inoculum size 10% (v / v), bottling volume 60mL / 250mL, initial pH value of the fermentation medium 8.0, 28°C, 200 r / min, and culture for 5 days , resulting in a concentration of 10 8 St3 strain fermentation broth of CFU / ml.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com