Method for quickly and accurately identifying microorganism in sample
A technology of microorganisms and samples, applied in the field of microorganism identification, can solve the problem of low positive rate of bacterial culture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
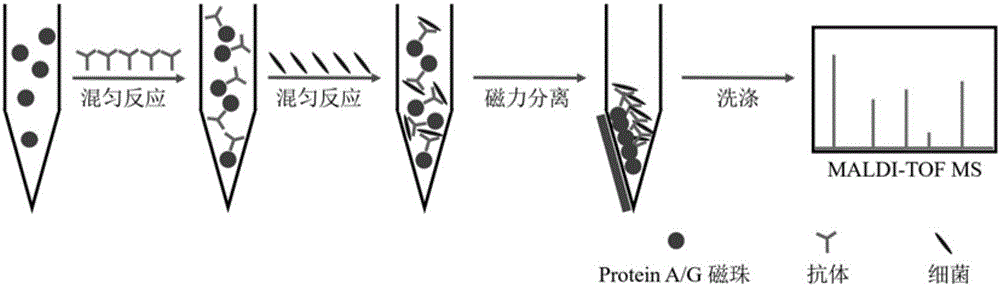
[0045] Target microorganisms are selectively captured using magnetic beads modified with antibodies against the target microorganisms.
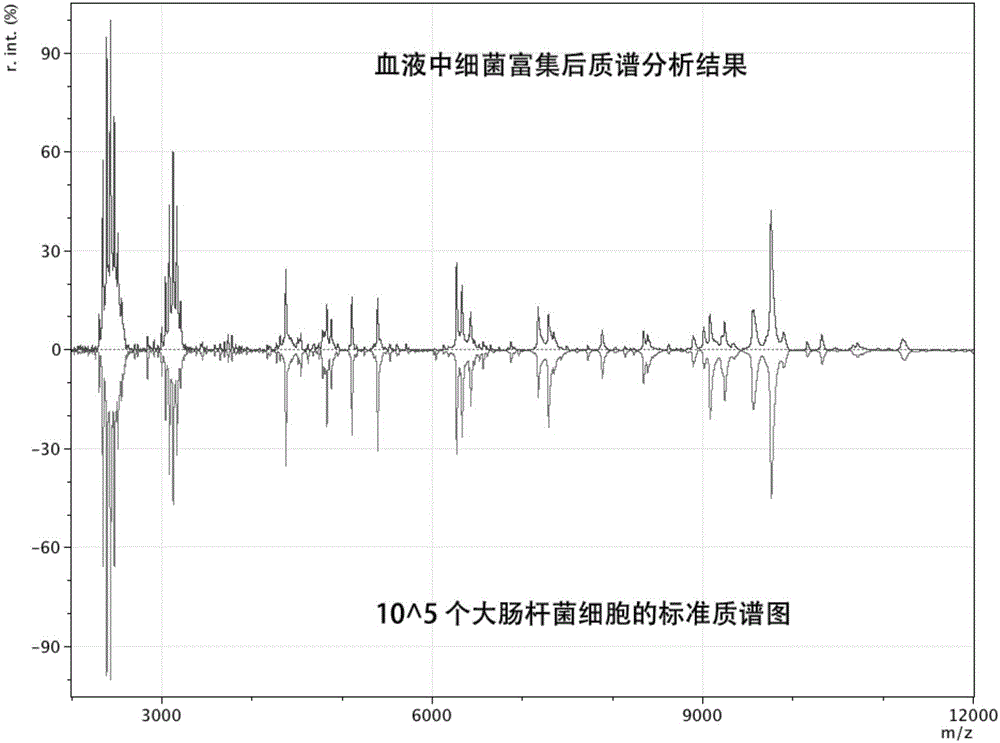
[0046] Take 50 μg of magnetic beads, the diameter of which is about 1 micron, and the surface is modified with recombinant Protein A / G (~50,00 Da). Each set of Protein A / G contains 4 Fc binding sites of Protein A and 2 An Fc-binding site for Protein G. With PBST buffer solution (137mM NaCl, 10mM Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O, 2mM NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O, 0.05% Tween20) and washed twice (20 μL each time), the magnetic beads were dispersed in 50 μL PBST buffer solution. Add 2 μL of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli antibody to the mixture of the above buffer solution and magnetic beads, and react on a constant temperature mixer for 30 min at room temperature. The reacted magnetic beads were washed three times with blocking solution PBST+1% BSA (20 μL each time), the magnetic beads were separated by a magnet, and dispersed in 50 μL PBST buffer solution. ...
Embodiment 2
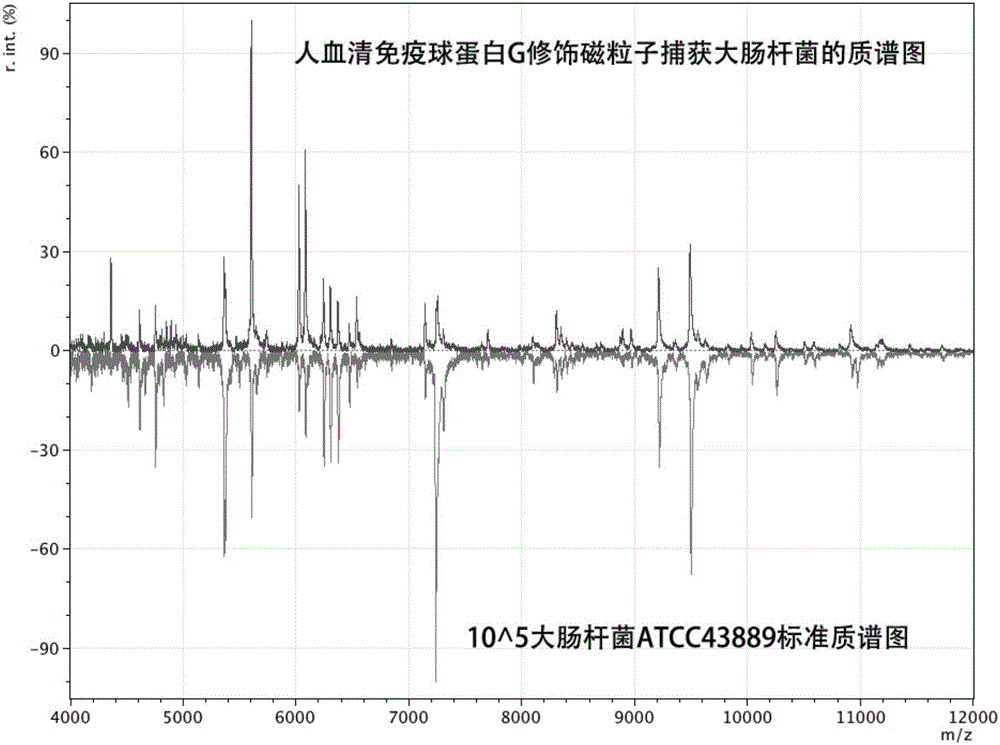
[0050] Using human serum immunoglobulin G to achieve broad-spectrum pathogenic microorganism extraction and enrichment.
[0051] Take 100 μL of Escherichia coli ATCC43889 bacterial solution stored at -80°C in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 9 mL of liquid tryptone soybean broth (TSB) medium, and mix well. Slightly unscrew the cap of the centrifuge tube and culture in a shaker, set the temperature at 37°C, set the rotational speed at 180rpm, and cultivate for 12 hours. At this time, the bacteria enter the end of the logarithmic phase, the activity is the best, and the bacterial concentration is the largest.
[0052] Take 50 μg of the same magnetic beads as in Example 1, wash twice with 20 μL of PBST buffer solution each time, and then disperse the magnetic beads in 50 μL of PBST buffer solution. Add 2 μL of human serum immunoglobulin G to the mixture of the above buffer solution and magnetic beads, and react on a constant temperature mixer for 30 min at room temperature. The rea...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Using human serum immunoglobulin G to achieve broad-spectrum pathogenic microorganism extraction and enrichment.
[0058] Take 100 μL of Vibrio parahaemolyticus solution stored at -80°C in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 9 mL of liquid tryptone soybean broth (TSB) medium, and mix well. Slightly unscrew the cap of the centrifuge tube and culture in a shaker, set the temperature at 37°C, set the rotational speed at 180rpm, and cultivate for 12 hours. At this time, the bacteria enter the end of the logarithmic phase, the activity is the best, and the bacterial concentration is the largest.
[0059] Take 50 μg of the same magnetic beads as in Example 1, wash twice with 20 μL of PBST buffer solution each time, and then disperse the magnetic beads in 50 μL of PBST buffer solution. Add 2 μL of human serum immunoglobulin G to the mixture of the above buffer solution and magnetic beads, and react on a constant temperature mixer for 30 min at room temperature. The reacted magnetic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com