Improved magnesium-nickel-lanthanide series hydrogen storage electrode alloy graphene modification method
An electrode alloy and graphene technology, applied in the field of metal functional materials, can solve the problems of cycle capacity decline, poor kinetic performance, capacity loss, etc., and achieve the effects of improving cycle stability, improving overall performance, and improving discharge capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Preparation of amorphous electrode alloy: according to Mg 65 Ni 27 La 8 Chemical dosage ratio Weigh 100 grams of Mg, Ni, and La metal blocks with a purity greater than 99.5% (purity: 99.5%, purchased from Northwest Nonferrous Metals Research Institute) in a vacuum suspension melting furnace (type CXZGX-0.1, Shanghai Chenxin Electric Furnace Co., Ltd. Company) in repeated smelting, take the smelted metal and place it in the multifunctional amorphous synthesis equipment (LZK-12A type, copper roller surface line speed 0-78.5m / s, Shenyang multifunctional vacuum microcrystalline equipment manufacturing plant), adopt Preparation of Mg by melt rapid quenching method (quenching speed is 30m / s) 65 Ni 27 La 8 Amorphous electrode alloys.
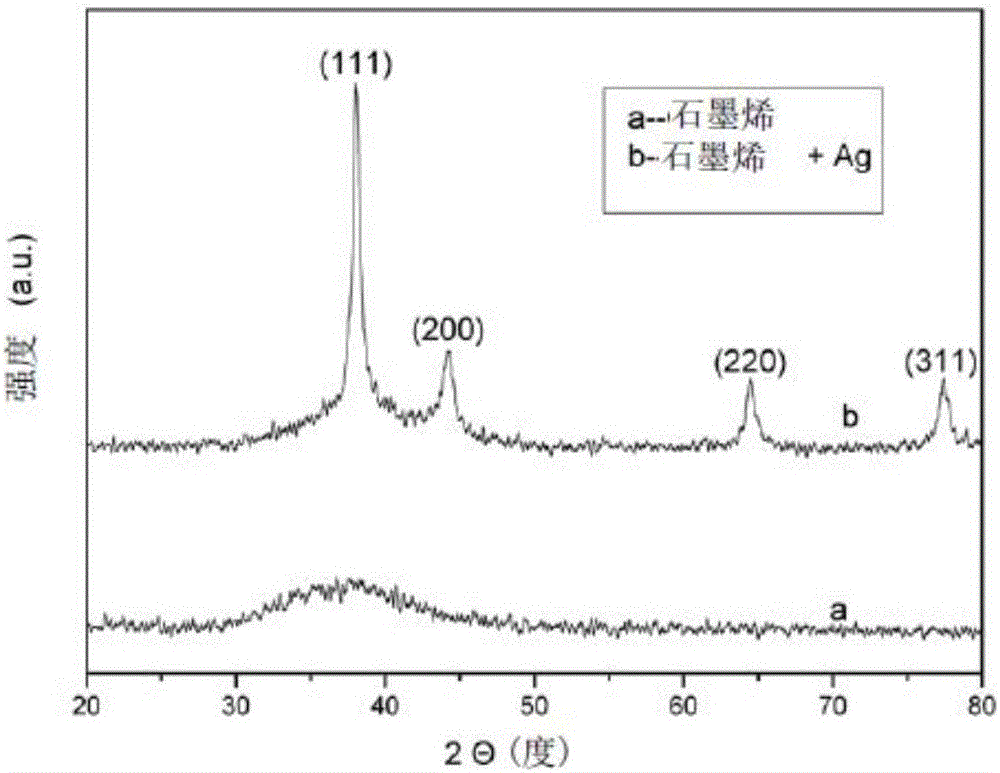
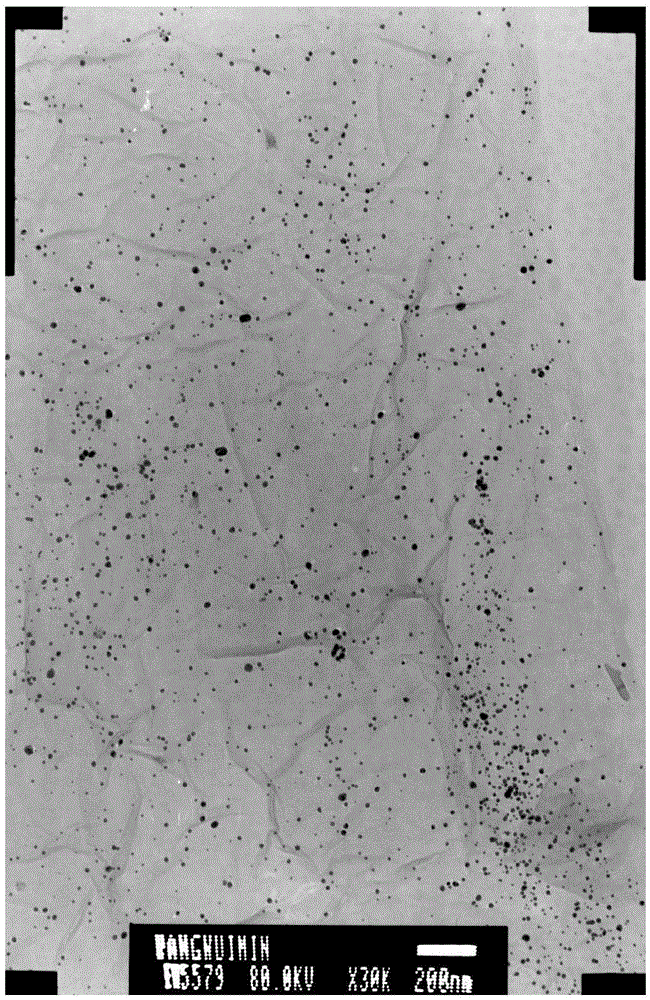
[0037] (2) Preparation of Ag / graphene nanocomposite film: 200mg graphite oxide was added to 200ml distilled water, ultrasonic (KQ116 type, Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Ltd.) was dispersed for 1 hour, then 20mg silver nitrate solid...
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) The preparation of the amorphous electrode alloy is the same as in Example 1. The stoichiometric ratio of the amorphous electrode alloy prepared this time is (Mg 65 Ni 27 ) 95 La 5 alloy (quenching speed is 30m / s).
[0045] (2) The preparation of the Ag / graphene nanocomposite film is the same as in Example 1.
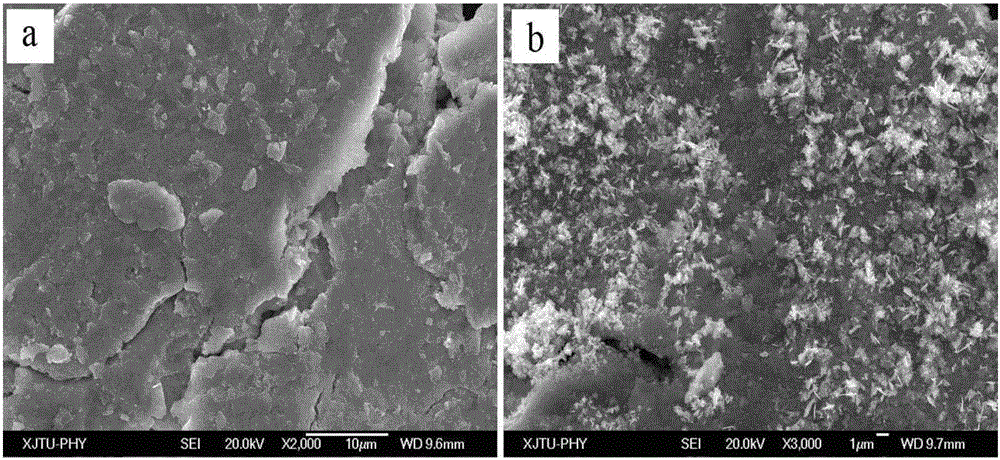
[0046] (3) The preparation and testing of the modified electrode are the same as in Example 1. As shown in Table 2, the surface-modified (Mg 65 Ni 27 ) 95 La 5 The maximum discharge capacity of the alloy is 557.6mAh / g, and the capacity retention rate is 76.84% after 50 cycles; while the unmodified (Mg 65 Ni 27 ) 95 La 5 The maximum discharge capacity of the alloy is 368.4mAh / g, and the capacity retention rate is 43.48% after 50 cycles. It can be found that the maximum discharge capacity is increased by 189.2mAh / g after surface modification of the alloy by this method; the capacity retention rate is increased by 33.36% after 50 cycles.
[0047] T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| retention rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com