Neuropeptide Corazonin and acceptor gene thereof as well as applications to specific control agent of Bactrocera dorsalis
A technology of Bactrocera dorsalis and neuropeptides of Bactrocera dorsalis, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of less research and application of Bactrocera dorsalis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1. Obtaining the Open Reading Frame Sequence of Bacteralis dorsalis Neuropeptide Corazonin and Its Receptor
[0042] 1. Primer design and amplification of the open reading frame sequence of Bacteralis dorsalis neuropeptide Corazonin and its receptor Corazonin receptor
[0043]Based on genome and transcriptome data, using bioinformatics methods, after repeated comparison and analysis of Drosophila neuropeptide Corazonin (Genbank No.NP_524350.1) and Drosophila neuropeptide receptor Corazonin receptor (GenbankNo.AF373862.3), The nested PCR-specific primers for the Bactrocera dorsalis neuropeptide Corazonin and its receptor were designed, and the sequences are as follows:
[0044]
[0045] The total RNA of B. dorsalis was extracted with an RNA extraction kit, and reverse transcribed into cDNA with a reverse transcription kit.
[0046] Amplify the Bacteralis dorsalis neuropeptide Corazonin sequence: 50 μL reaction system contains 24 μL deionized water, 20 μL 2×Pr...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2. Determination of the binding ability of Bacteralis dorsalis neuropeptide Corazonin and its receptor Corazonin receptor based on the method of intracellular calcium ion flow detection
[0059] 1. Construction of CHO cell (Chinese hamster ovary cell) expression plasmid of Bactrocera dorsalis Corazonin receptor
[0060] The Bacteralis dorsalis neuropeptide Corazonin receptor plasmid and the pcDNA3.1 (+) plasmid that are connected to the T vector that are recovered in Example 1 are connected (T4 DNA ligase) after NotI single enzyme digestion respectively, after connection The transformation was carried out with reference to the transformation method in Example 1. After the positive identification of the bacterial liquid was correct (PCR detection was performed with the universal primer T7 / BGH, T7: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG, BGH: TAGAAGGCACAGTCGAGG), the plasmid was extracted with a plasmid extraction kit, and the constructed The pcDNA3.1(+) plasmid of the Corazonin re...
Embodiment 3
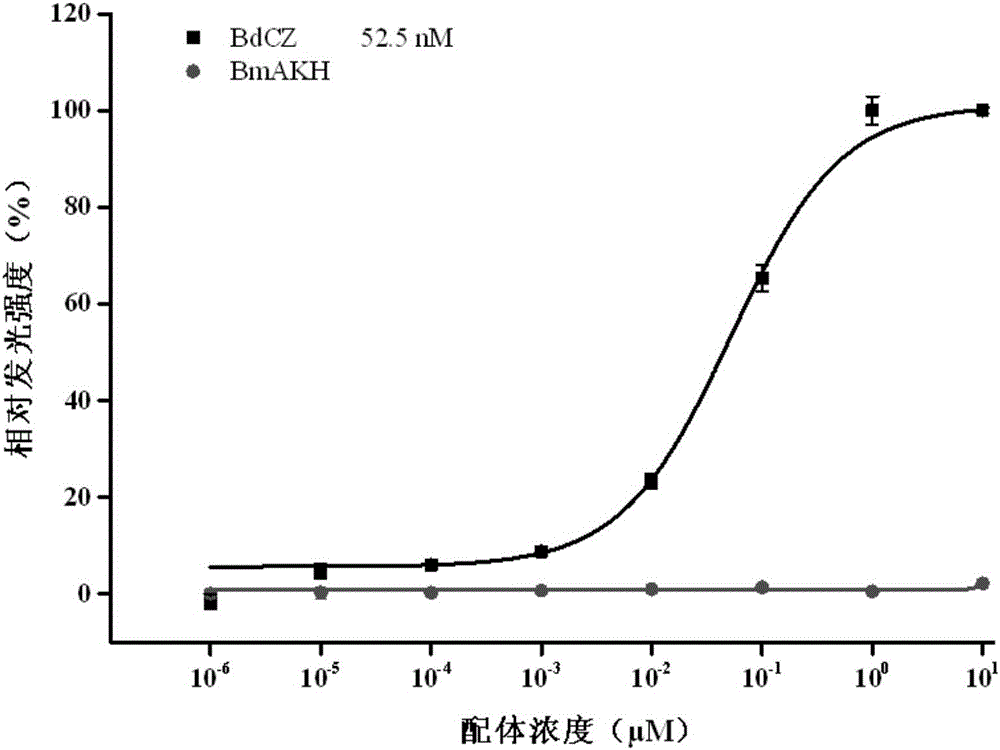
[0075] The results of the detection of the binding ability of the synthesized ligand polypeptide to the Corazonin receptor are as follows: figure 1 As shown, it is shown that the ligand BdCZ has the ability to activate the receptor, while the control BmAKH (polypeptide sequence: Cys-Glu-Leu-Thr-Phe-Ser-Pro-Asp-Thr-NH2) has no activity on the receptor . Among them, the EC50 value (concentration in the maximum luminescence value) of BdCZ is 52.5nM respectively. In this way, BdCZ was identified as the model ligand. Example 3. Determination of Silencing Efficiency of Bacteralis dorsalis Neuropeptide Receptor Corazonin Receptor Based on RNA Interference Method
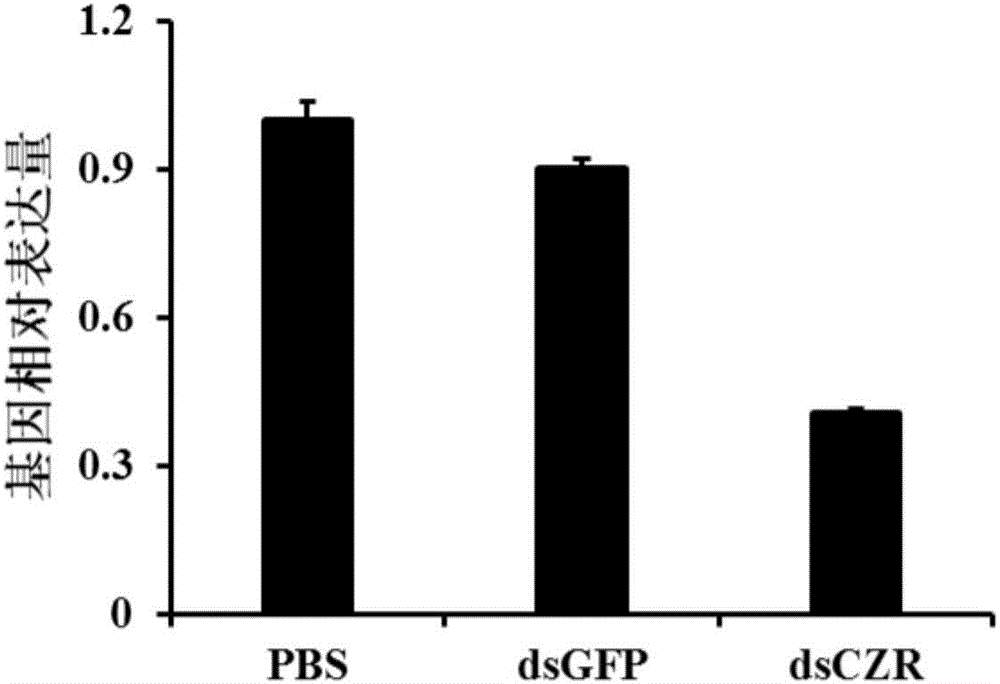
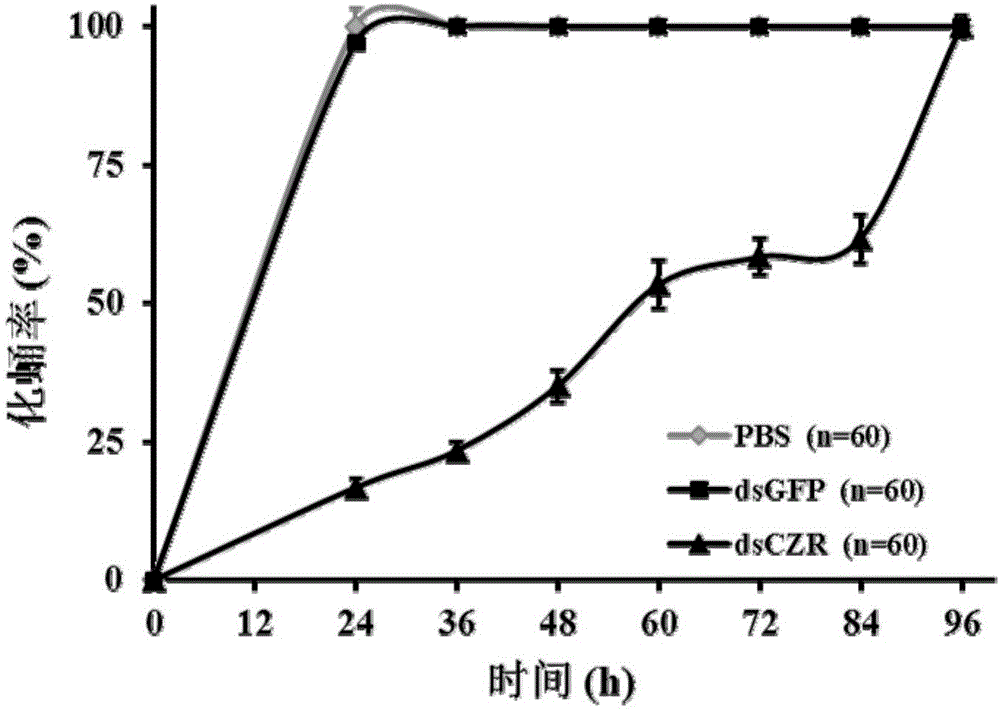
[0076]1) Extract the total RNA of B. dorsalis with an RNA extraction kit, reverse transcribe it into cDNA with a reverse transcription kit, and use the cDNA as a template to perform PCR amplification using primers containing the T7 promoter. The reaction conditions are: Pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3min; denaturation at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com