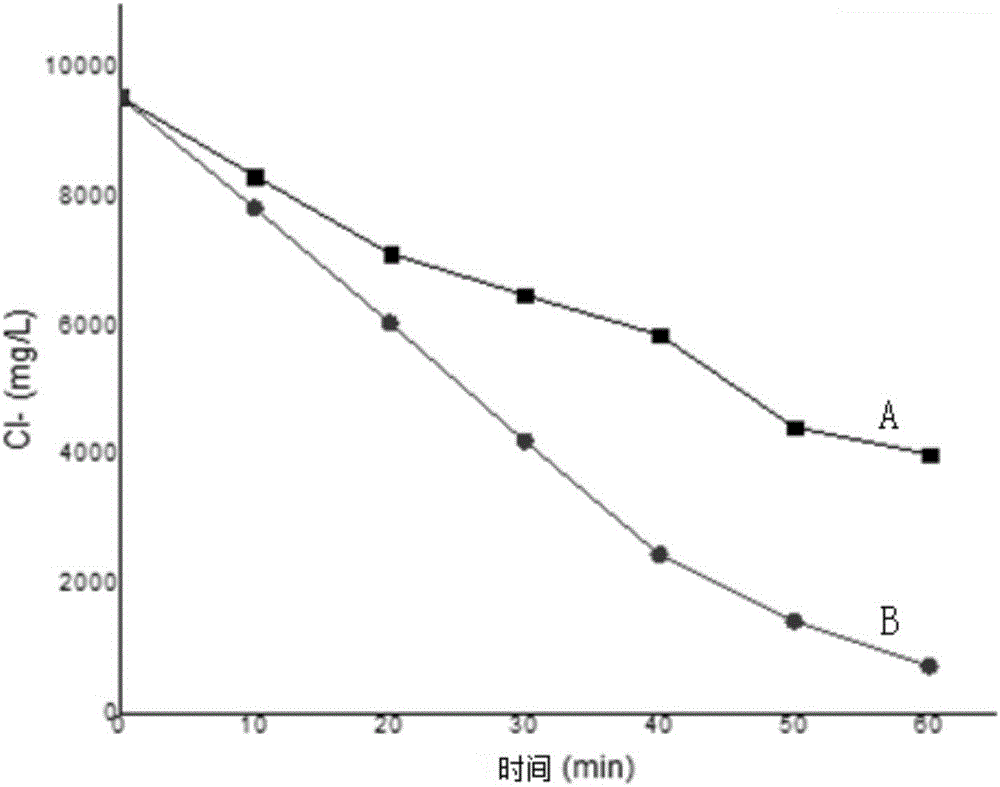
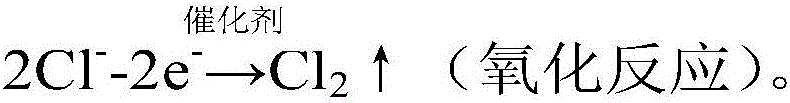Electrochemical reactor and method for electrocatalytically removing chloride ions
A reactor and electrochemical technology, which is applied in the field of electrochemical reactor and electrocatalytic removal of chloride ions, can solve the problems of restricting large-scale application, long electro-adsorption time, long processing time, etc., and is conducive to large-scale industrial application , high electrolysis efficiency and high degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] This embodiment provides a method for electrocatalytically removing chloride ions, which is carried out according to the following process:
[0055] The first step, preparation of Ru-Ti-AC catalytic material:
[0056] Soak the activated carbon with a particle size of 30 meshes in 40% phosphoric acid solution for 40 hours, filter the filter cake; wash the filter cake with deionized water until the pH value of the washing solution after washing is 7; wash the filter cake Dry it in a drying oven at 90°C to obtain pretreated activated carbon for subsequent use.
[0057] Take 20g pretreated activated carbon, 40ml butanol, 2gRuCl 3` nH 2 O (as 100% RuCl 3 ), 7.6ml butyl titanate and 2.304g (40ml 0.3M) citric acid were mixed, stirred evenly to obtain a mixed reaction solution, then hydrazine hydrate was added dropwise in the mixed reaction solution, and the pH value of the mixed reaction solution was adjusted to 6.5; then react in a water bath at 92°C for 0.8h to form a vi...
Embodiment 2
[0066] This embodiment provides a method for electrocatalytically removing chloride ions, which is carried out according to the following process:
[0067] The first step, preparation of Ru-Ti-AC catalytic material:
[0068] Soak the activated carbon with a particle size of 5 mesh for 45 hours in a phosphoric acid solution with a mass concentration of 15%, and filter the filter cake; wash the filter cake with deionized water until the pH value of the washing solution after washing is 6.5; wash the filter cake Dry it in a drying oven at 90°C to obtain pretreated activated carbon for subsequent use.
[0069] Take 20g pretreated activated carbon, 40ml butanol, 2gRuCl 3` nH 2 O (as 100% RuCl 3 ), 7.6ml butyl titanate and 2.304g (40ml 0.3M) citric acid were mixed, stirred evenly to obtain a mixed reaction solution, then in the mixed reaction solution, hydrazine hydrate was added dropwise to adjust the pH value of the mixed reaction solution 7; react in a water bath at 95°C for ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] This embodiment provides a method for electrocatalytically removing chloride ions, which is carried out according to the following process:
[0078] The first step, preparation of Ru-Ti-AC catalytic material:
[0079] Soak the activated carbon with a particle size of 100 mesh for 42 hours in a phosphoric acid solution with a mass concentration of 40%, and filter the filter cake; wash the filter cake with deionized water until the pH value of the washing solution after washing is 7; wash the filter cake Dry it in a drying oven at 70°C to obtain pretreated activated carbon for subsequent use.
[0080] Take 20g pretreated activated carbon, 40ml butanol, 2gRuCl 3` nH 2 O (as 100% RuCl 3 ), 7.6ml butyl titanate and 2.304g (40ml 0.3M) citric acid were mixed, stirred evenly to obtain a mixed reaction solution, then in the mixed reaction solution, hydrazine hydrate was added dropwise to adjust the pH value of the mixed reaction solution 7; react in a water bath at 93°C for ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com