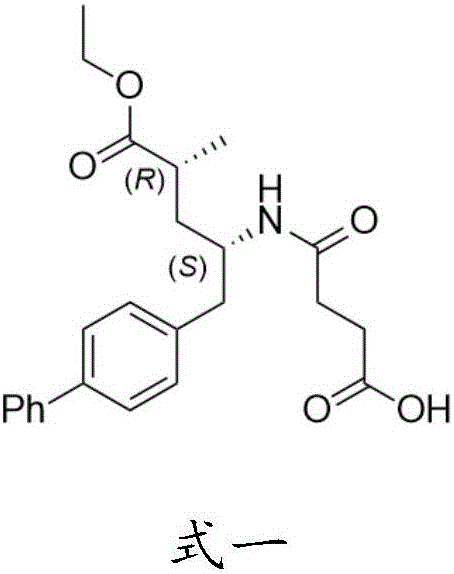
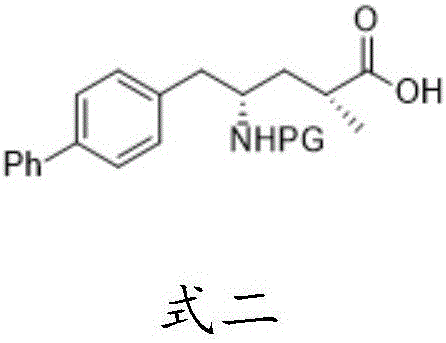
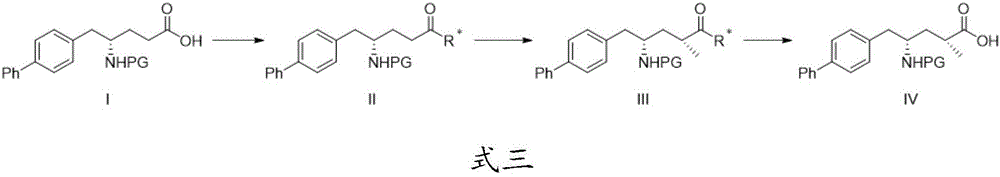
Sacubitril and preparation method of midbody of sacubitril
A technology for sacubitril and intermediates, which is applied in the field of preparation of sacubitril and its intermediates, can solve the problems of difficult separation of sacubitril intermediates, low yield and purity, poor diastereoselectivity and the like , to achieve the effect of improving production efficiency, simple operation, high yield and diastereoselectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The above-mentioned preparation method of a sacubitril intermediate also includes: performing an asymmetric methylation reaction on compound II with a methylating reagent and a base to obtain compound III.
[0029] Further, the methylating agent is any one of methyl iodide, dimethyl sulfate and dimethyl carbonate, preferably methyl iodide. The base is a conventional hydrogen extraction reagent such as an organometallic reagent, such as an alkyllithium reagent, lithium amide reagent, potassium amide reagent, etc., preferably lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) or lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS ), most preferably lithium diisopropylamide. These reagents are commonly used reagents in chemical reactions, can be directly purchased from the market, and can be used together to obtain methylated products with high yields.
[0030] Further, the asymmetric methylation reaction is carried out at -80 to -50°C, preferably at -78°C. This temperature range is the preferred value ob...
Embodiment 1
[0038] This example provides a preparation method of compound II, which uses Boc as a protecting group, compound I and chiral prosthetic group react to get the compound Its concrete preparation steps are as follows:
[0039]Add 320mL toluene into the three-neck flask, start stirring, add compound I (16g, 1eq), triethylamine (13.1g, 3eq) and compound IV-a (8.37g, 1.1eq), pH=7~8. Slowly added pivaloyl chloride (5.67g, 1.1eq) to the reaction system, heated to 100°C and refluxed for 16h. After the reaction, dilute with ethyl acetate, wash with water and saturated sodium bicarbonate in sequence, collect the organic phase, dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, and distill the filtrate to remove the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product. The crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain compound II-a (21.0 g, yield 91%).
Embodiment 2
[0041] This example provides a preparation method of compound II, which uses Boc as a protecting group, compound I and chiral prosthetic group react to get the compound Its concrete preparation steps are as follows:
[0042] Add 320mL toluene to the three-neck flask, start stirring, add compound I (16g, 1eq), triethylamine (13.1g, 3eq) and compound IV-b (7.27g, 1.1eq), pH=7~8. Slowly added pivaloyl chloride (5.67g, 1.1eq) to the reaction system, heated to 90°C and refluxed for 16h. After the reaction, dilute with ethyl acetate, wash with water and saturated sodium bicarbonate in sequence, collect the organic phase, dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, and distill the filtrate to remove the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product. The crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain compound II-b (17.7 g, yield 86%).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com