Method for producing ethanol by fermentation of fresh sugar-containing biomasses
A biomass fermentation and biomass technology, applied in the fields of biomass energy and fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of low concentration, low ethanol yield and high separation cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0048] According to some embodiments of the present invention, the method further includes a step of separating and purifying the ethanol-rich fermented mash to obtain an ethanol product.
[0049] In some embodiments of the present invention, the separation and purification method includes one or more of ordinary distillation, vacuum rectification, liquid-liquid extraction, pervaporation, steam permeation, steam stripping, vacuum extraction and adsorption .
[0050] According to the present invention, the separation and purification are carried out after the anaerobic fermentation is terminated, or in-situ separation is carried out coupled with the anaerobic fermentation process.
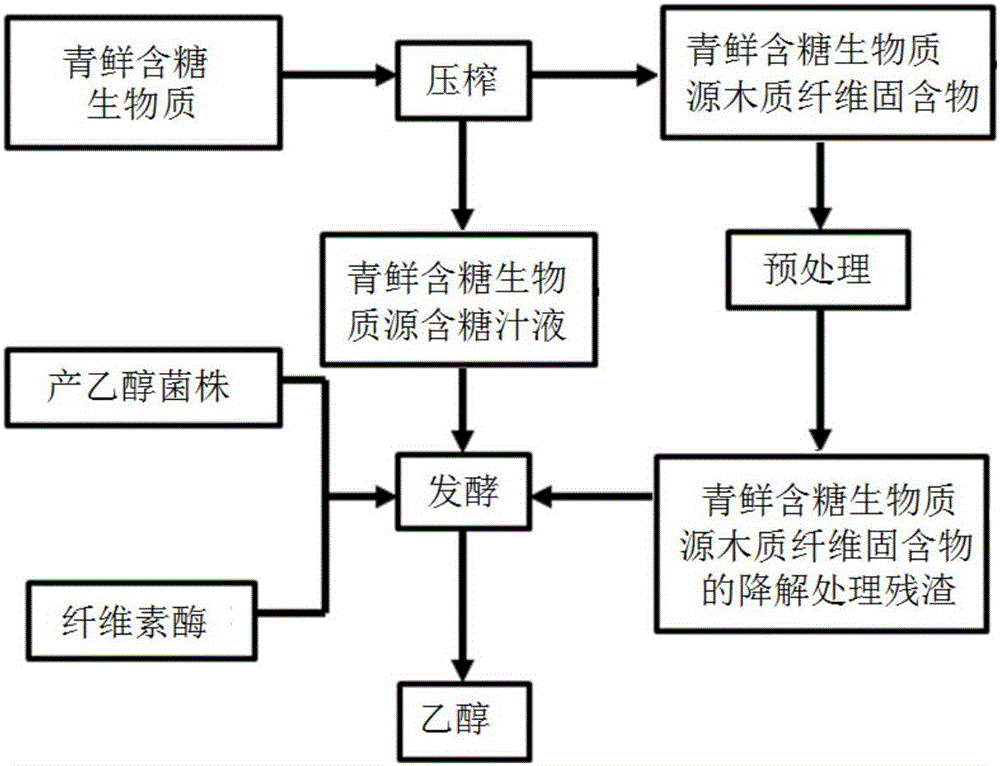
[0051] In some specific embodiments of the present invention, the method for producing ethanol by fermentation of fresh sugar-containing biomass comprises the following steps:
[0052] (1) Raw material squeezing: squeeze fresh and fresh sugar-containing biomass raw materials to realize solid-liquid...
Embodiment 1
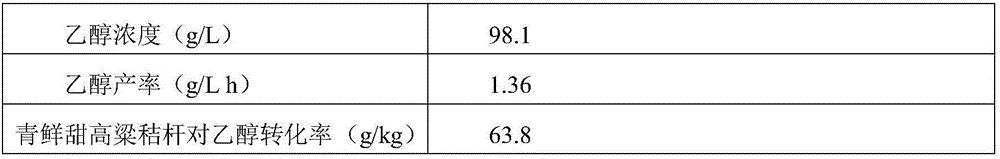
[0069] Example 1: Ethanol was produced by fermenting green and fresh sweet sorghum stalks as raw materials.
[0070] (1) Pressing of fresh and fresh sweet sorghum stalks: take 1 kg of fresh and sweet sorghum stalks grown in the field, and after peeling, obtain about 654 ml of sugar-containing juice and fiber residue after repeated pressing three times; Contains about 144g / L of free sugar. In addition, as measured by ICP-MS and Kjeldahl method, the contents of inorganic ions and nitrogen and phosphorus contained in the sugary juice are shown in Table 1:
[0071] Table 1 Inorganic ions and nitrogen and phosphorus contents in sugary juice from fresh and fresh sweet sorghum straw
[0072] element Content (mg / L) K 262.76 Na 17.6 Ca 143.86 Mg 263.45 Fe 2.07 mn 0.34 P 128.69 N 1480
[0073] (2) Degradation treatment of fiber residues: Dry the remaining about 294g fiber residues at 105°C overnight to dryness to obtain 216g...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Production of ethanol by fermenting green and fresh sweet sorghum stalks as raw materials.
[0082]Steps (1), (2) are the same as in Example 1.
[0083] (3) Preparation of fermented liquid: 118.5 g of fiber residue after alkali degradation treatment is pulverized to 60 meshes, divided into 4 parts, and one part is fully mixed with the sugary juice prepared in step (1), and placed In addition, 1.7g / L urea, 1g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and 2g / L anhydrous magnesium sulfate were added to the fermenter, and sterilized at 121°C for 25min to obtain a fermented liquid for later use.
[0084] (4) Preparation of seed liquid: the ethanol-producing strain is the high-temperature resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae H5 screened by evolutionary engineering in the laboratory. The composition of the strain seed synthetic medium was (g / L): 0.8 sucrose, 20 glucose, 5 soybean peptone, 3 yeast powder, tap water, and the pH was adjusted to 5.5 with 1 mol / L HCl. The strain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com