Gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA (N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide) high-molecular copolymer, and preparation method and application thereof
A high molecular copolymer, galactose technology, applied in the field of gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA high molecular copolymer and its preparation, can solve the problems of hematopoietic system and immune function, limited clinical research, large toxic and side effects, etc. Achieve good biocompatibility, prolong residence time, and enhance targeting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
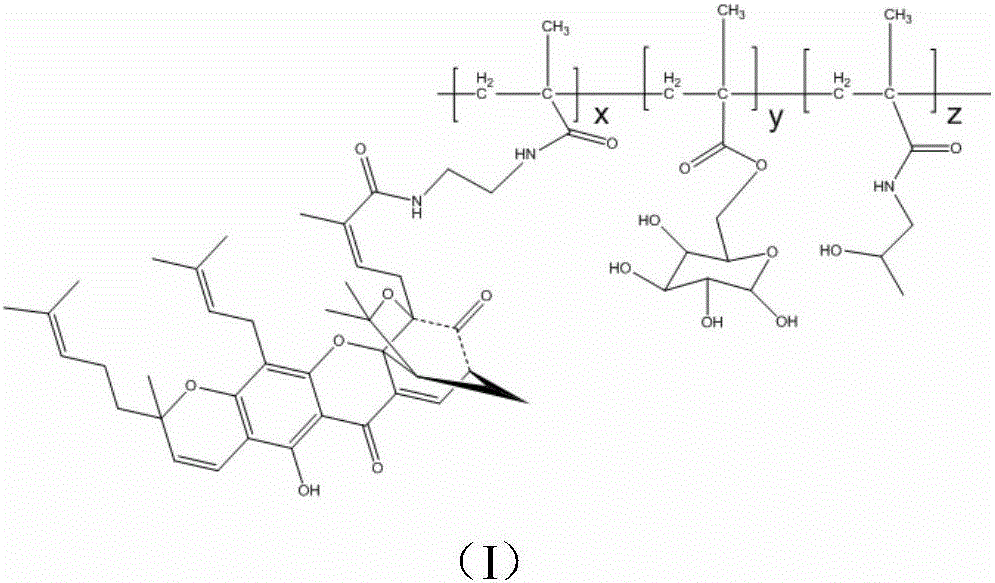
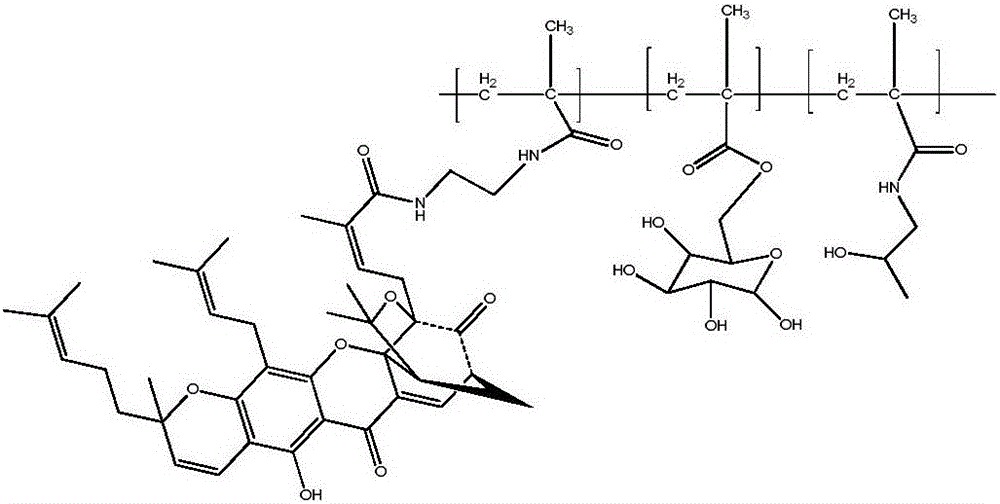
[0030] Embodiment 1 A kind of gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA polymer copolymer
[0031] Its structure is as follows:
[0032]
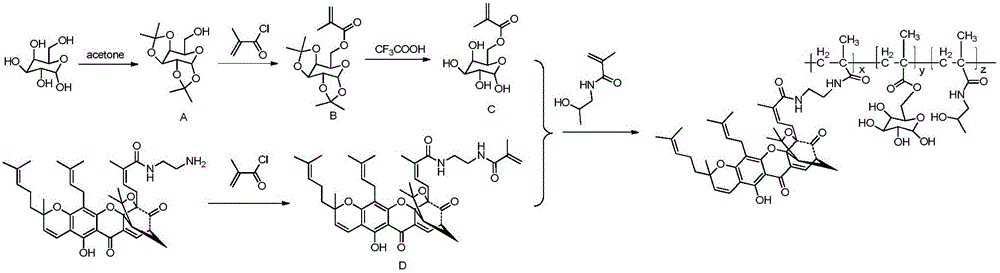
[0033] The preparation method of the compound is as follows: first, the galactose derivative C is prepared by using D-galactose as a raw material; The galactose derivative C, the gambogic acid derivative D and HPMA are condensed into a gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA polymer copolymer.
[0034]
[0035] in,
[0036] 1. The synthesis of galactose derivative C specifically comprises the following steps:
[0037]
[0038] 1.1) Dissolve 2.0g (11.2mmol) of D-galactose in 100mL of acetone, add 1.0-2.5mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, stir overnight at room temperature, the solution turns bright yellow, add 20% potassium carbonate solution 20mL, a large amount of Suction filtration, distill off the acetone in the filtrate, extract the remaining filtrate with 5×40ml of chloroform, wash the chloroform with 2×15mL of distilled water, add anhydrous sodium...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The pharmacodynamics test of embodiment 2 gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA macromolecule copolymer
[0048] The copolymer provided in Example 3 was used as the test sample, which showed excellent anti-tumor effects as shown in the following pharmacodynamic tests.
[0049] Growth inhibitory activity against various cancer cells (GI 50 ) Assay method: After the tumor cells were digested with trypsin, they were dispersed into single cells and suspended in RPMI1640 medium containing penicillin (25 U / ml) and streptomycin (25 μg / ml). Cells were seeded in 96-well culture plates (Corning Incorporated) at 37°C with 5% CO 2 After culturing for 24 hours under the condition of 100% relative humidity, the culture solution was discarded, and the culture solution containing a series of concentrations of test samples (equivalent to an equivalent amount of gambogic acid) was added. Parallel wells were set for each concentration, and cultured After 24 hours, discard the culture solution co...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The safety test (acute toxicity) of embodiment 3 gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA polymer copolymer
[0058] Gambogic acid-galactose-HPMA macromolecular copolymers were administered by intragastric administration to mice, and the results showed that the copolymers had certain toxicity to the circulatory system, and the animals in the high-dose group showed little movement in 10 to 24 hours after administration. Rats excrete thin feces, and there is light yellow thin feces pollution around the anus. Death occurred within 24 to 48 hours after administration. The dead mice were dissected, the liver turned white, and the rest of the organs were normal. The surviving mice in each group were continuously observed for 14 days, and no abnormalities were found in food intake, drinking water, general status and activities. After the observation period, the mice were sacrificed, and no abnormalities were found in the liver and major organs by naked eye observation.
[0059] The copol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com