Remediation agent and remediation method for in-situ remediation of water body and sediment
An in-situ repair agent and repair agent technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as increased treatment costs, hidden dangers, water quality safety, etc., to improve water quality The effect of water quality and substrate environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
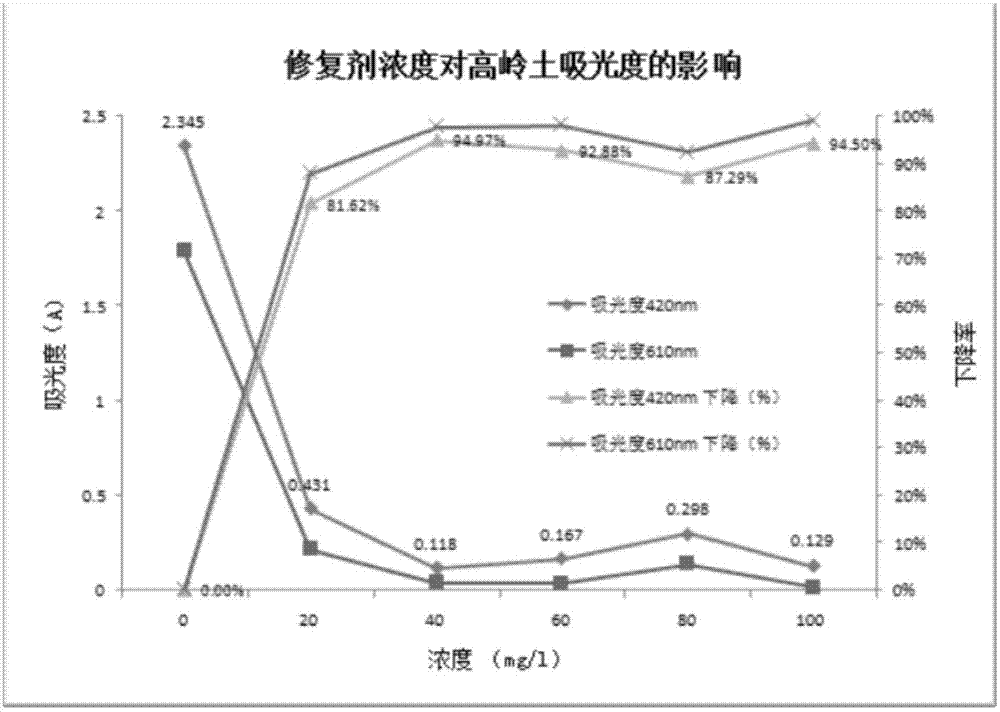
[0032] Embodiment 1: turbidity reduction test
[0033] In this experiment, the concrete definite formula of composite restorative agent is: 5% by weight Na 2 h 2 Y, 40% quaternary ammonium chitosan, 10% dried and crushed filamentous algae, 10% attapulgite, 10% calcium chloride, 5% magnesium sulfate, 10% gypsum powder, and 10% cement powder.
[0034] In order to understand the turbidity-reducing effect of the composite restorative, 0.5% kaolin suspension was prepared, and different concentrations of turbidity-reducing tests were done. The specific tests and results are as follows:
[0035] Prepare 7L of 0.5% kaolin suspension with tap water, put it in a plastic bucket, and use a 5W small water pump (for the water cluster tank) to carry out self-circulation stirring in water for 5 hours before use. Use six 2L beakers to measure the fully mixed suspension, put it into a stirrer, and add the compound restoration agent, the dosage is 0mg / l, 20mg / l, 40mg / l, 60mg / l, 80mg / l, 100mg ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: water restoration experiment
[0039] Specific formulation of the restorative: 10% by weight Na 2 h 2Y, 25% quaternary ammonium chitosan, 2% dried and crushed filamentous algae, 20% attapulgite, 8% calcium chloride, 10% magnesium sulfate, 20% gypsum powder, and 5% cement powder.
[0040] In order to verify the improvement effect of the restoration agent on the water body indicators, an experiment was carried out on the comprehensive wastewater of the factory. The specific method is to take 5L of water sample to the laboratory, mix the water sample evenly, take 1.0L from one beaker as the control group; take 1.0L from each of the other 3 beakers as the test group, put it into the stirring bar, and add the composite repair Dosage of 40 mg / l was placed on a magnetic stirrer, first rotated at high speed (600r / min) for 2 minutes, then rotated at low speed (60r / min) for 4 minutes, and then stood still for 30 minutes.
[0041] Detection Indicator R...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The method for in-situ restoration of water body and sediment comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Prepare the restoration agent according to the requirements of the water body to be treated or the restoration of the sediment. The concrete formula of restoration agent is: 5% by weight Na 2 h 2 Y, 40% quaternary ammonium chitosan, 10% dried and crushed filamentous algae, 10% attapulgite, 10% calcium chloride, 5% magnesium sulfate, 10% gypsum powder, and 10% cement powder.
[0046] Step 2: First use the restoration agent to conduct a small laboratory test to obtain the best application dosage and provide reference for application.
[0047] Step 3: Start fan aeration or water agitator and sediment mixer for 5-10 minutes while injecting restoration agent to promote full mixing of water body / sediment to be restored and restoration agent.
[0048] Step 4: Shut down the aeration and stirring system, so that the restoration agent absorbs heavy metals, N, P, organi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com