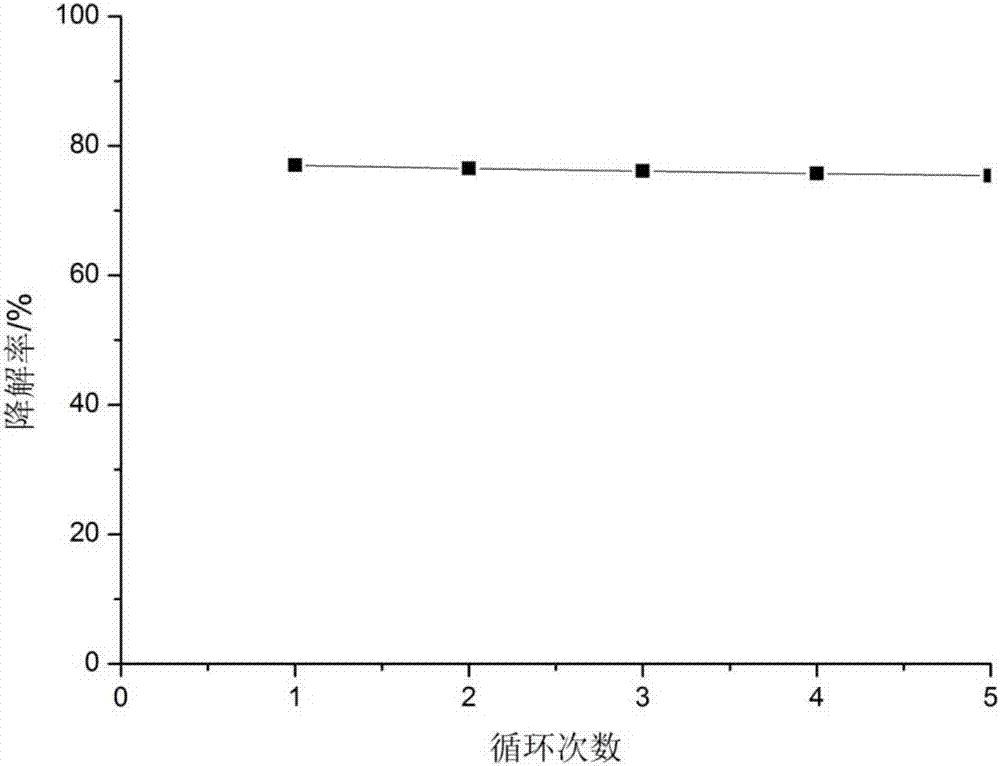
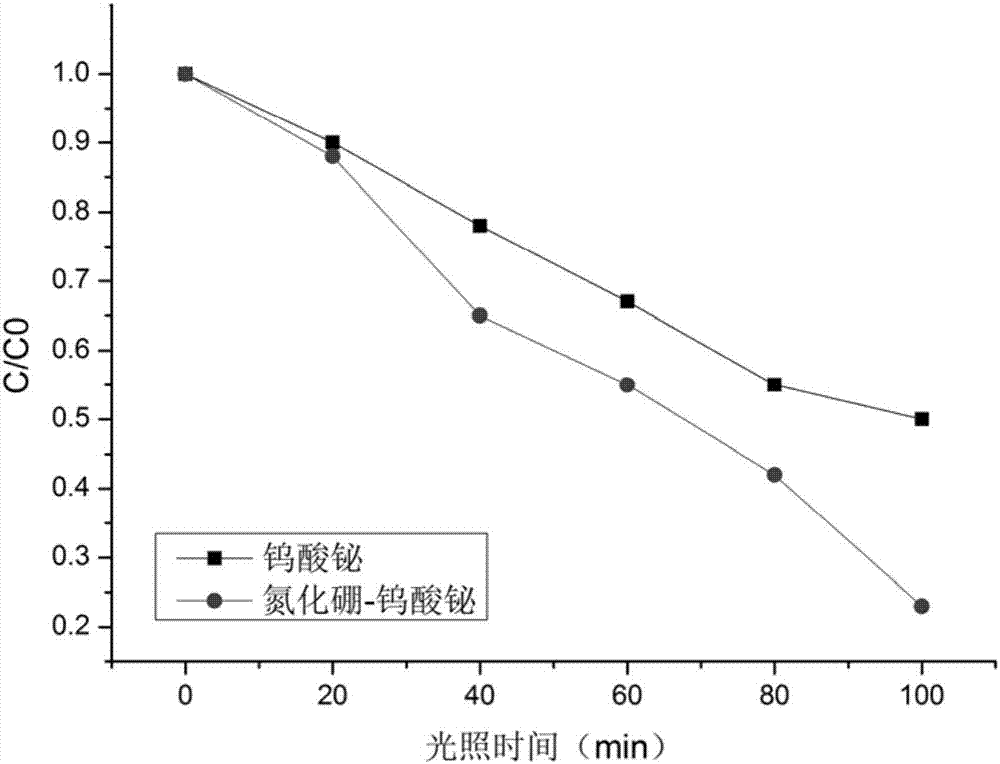
A method of treating rhodamine B dye waste water through photocatalytic degradation
A dye wastewater and a treatment method technology, applied in the field of photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye wastewater treatment, can solve the problems of few photocatalytic active sites, low efficiency of rhodamine B, weak component binding ability, etc., and achieve reaction conditions Easy control, high photocatalytic activity and photocatalytic stability, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A treatment method for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0026] a. Add 100ml of rhodamine B solution with a concentration of 20mg / L in a 200ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 50mg of boron nitride-bismuth tungstate composite photocatalyst into the rhodamine B solution, and stir magnetically for one hour in the dark reached adsorption equilibrium. Measure the concentration with an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, which represents the initial concentration of the solution to be degraded and is recorded as C 0 .
[0027] b. The rhodamine B solution added with boron nitride-bismuth tungstate photocatalyst in step a is subjected to a photocatalytic reaction under the irradiation of a 500W xenon lamp of a visible light source and starts timing, and the distance between the light source and the liquid surface is 20cm. Draw 5ml of solution from the reaction system of each group every 20min, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 5min...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A treatment method for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0043] a. Select dye wastewater from a printing and dyeing factory in Jiangyin City, Jiangsu Province. The main pollutant of the dye wastewater is rhodamine B. After testing, the concentration of rhodamine B exceeds 120mg / L. The dye wastewater is diluted to a concentration of rhodamine B of 20mg / L.
[0044] b. by the ratio of boron nitride-bismuth tungstate composite photocatalyst and rhodamine B dye wastewater to the ratio of 50g: 100L, add boron nitride-bismuth tungstate composite photocatalyst in the above-mentioned diluted rhodamine dye wastewater, in Stir magnetically in the dark for one hour to reach adsorption equilibrium. Measure the concentration with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer, which represents the initial concentration of the solution to be degraded and is recorded as C 0 .
[0045] Wherein, the boron nitride-bismuth tungstate composite photoca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com