Method for biosynthesis of L-ascorbyl palmitate
A technology of ascorbyl palmitate and ascorbic acid, which is applied in the field of functionalized ionic liquid modified lipase to catalyze the synthesis of L-ascorbyl palmitate, can solve the problems of limited modification effect and great influence on enzyme activity, achieve rapid reaction and improve selectivity , Solve the effect of many by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This example compares and studies the reaction difference between modified lipase and free enzyme in the catalytic synthesis of AP in an organic medium.
[0039] Catalyzed reaction with free lipase only:
[0040] Add 0.2mM L-ascorbic acid, 1.0mM palmitic acid, 24mg / mL3A molecular sieve and substrate total amount and 1.2% (mass percentage) lipase in bioreactor, 3mL tert-butanol, water bath 60 ℃, reaction time is 24h . After the reaction, the yield of AP was about 44.9%.
[0041] Functional ionic liquids covalently modify lipase-catalyzed reactions:
[0042] Activation of functionalized ionic liquid: Mix 0.30g 6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrole[1,2-α]-3-carboxyethylimidazolium bromide with 0.2g CDI(1,1′-carbonyldiimidazolium ) was dissolved in 5mL DMSO, and reacted at room temperature for 2h to obtain the activated functionalized ionic liquid, which was untreated and refrigerated at 4°C for future use. Covalent modification of enzymes: After activation, the functionalized ionic l...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This example comparatively studies the reactions of covalently modified lipases in different ionic liquids to catalyze the synthesis of AP.
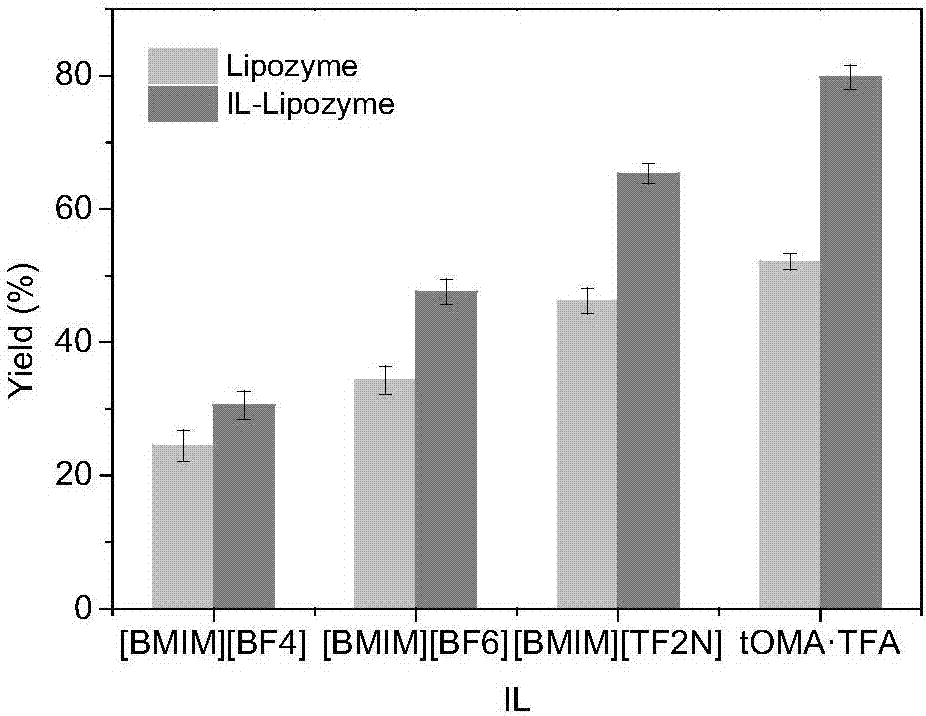
[0047] Add 0.2mM L-ascorbic acid, 1.0mM palmitic acid, 24mg / mL3A molecular sieve and 1.2% (mass percentage) of the total sum of substrates to the bioreactor to modify lipase covalently, 3mL[BMIM][PF 6 ], [BMIM][PF 4 ], [BMIM][TF 2 N], tOMA·TFA (Trioctylmethylammonium Trifluoroacetate), set the reaction temperature to 60°C, and the reaction time to 24h. After the reaction, calculate the product AP yield, such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0049] This example explores the reaction of covalently modified lipase to catalyze the synthesis of AP in isooctane / tOMA·TFA in an ionic liquid / organic solvent mixed system.
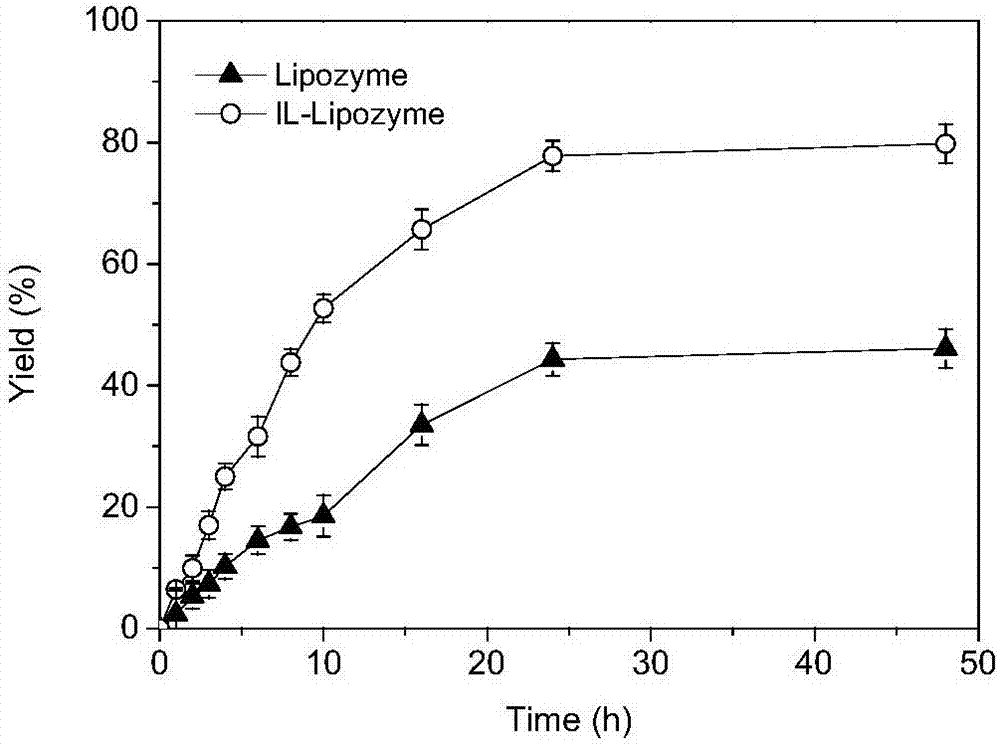
[0050] Add 0.2mM L-ascorbic acid, 1.0mM palmitic acid, 24mg / mL3A molecular sieve and 1.2% (mass percentage) covalently modified lipase of substrate total sum in bioreactor, and 3mL isooctane / ionic liquid (4 :1, v / v), set the reaction temperature at 60°C. After the reaction, calculate the product AP yield, such as figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com