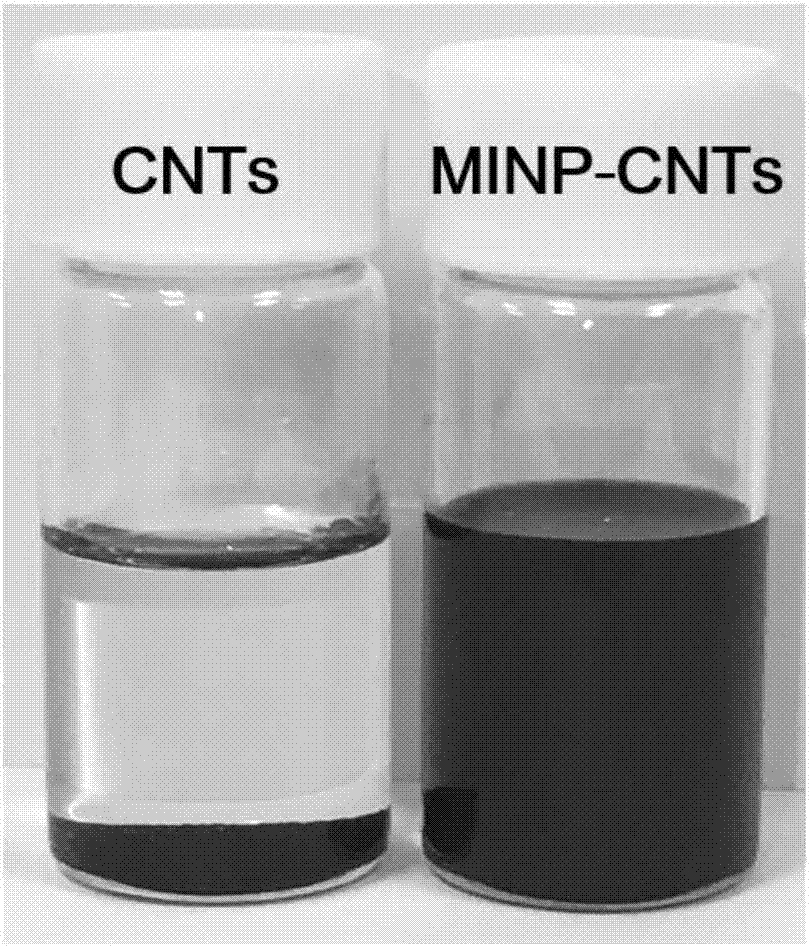
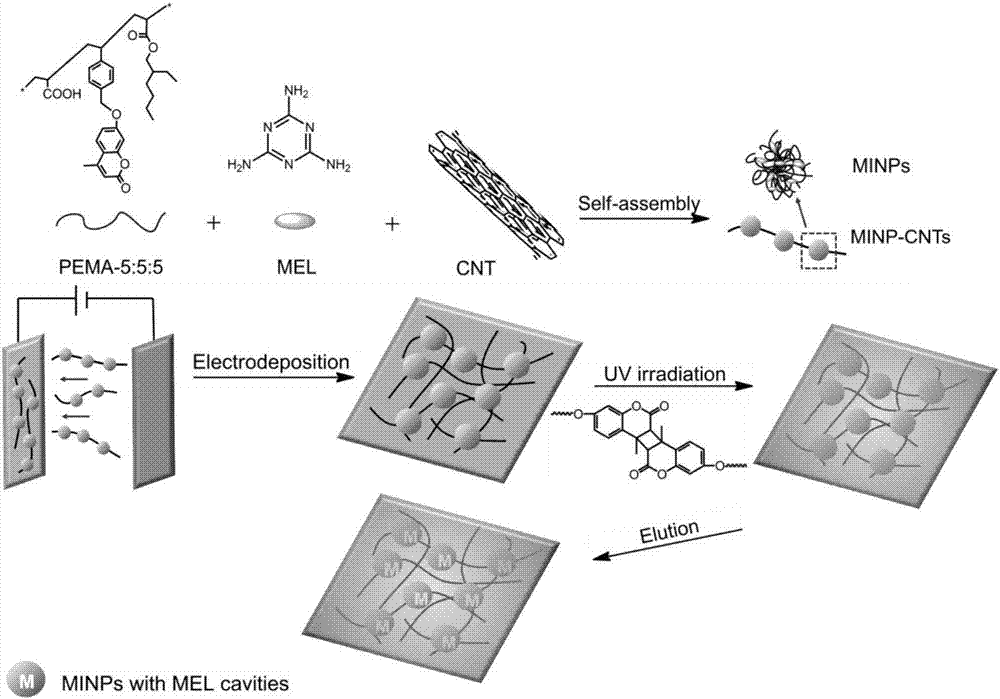
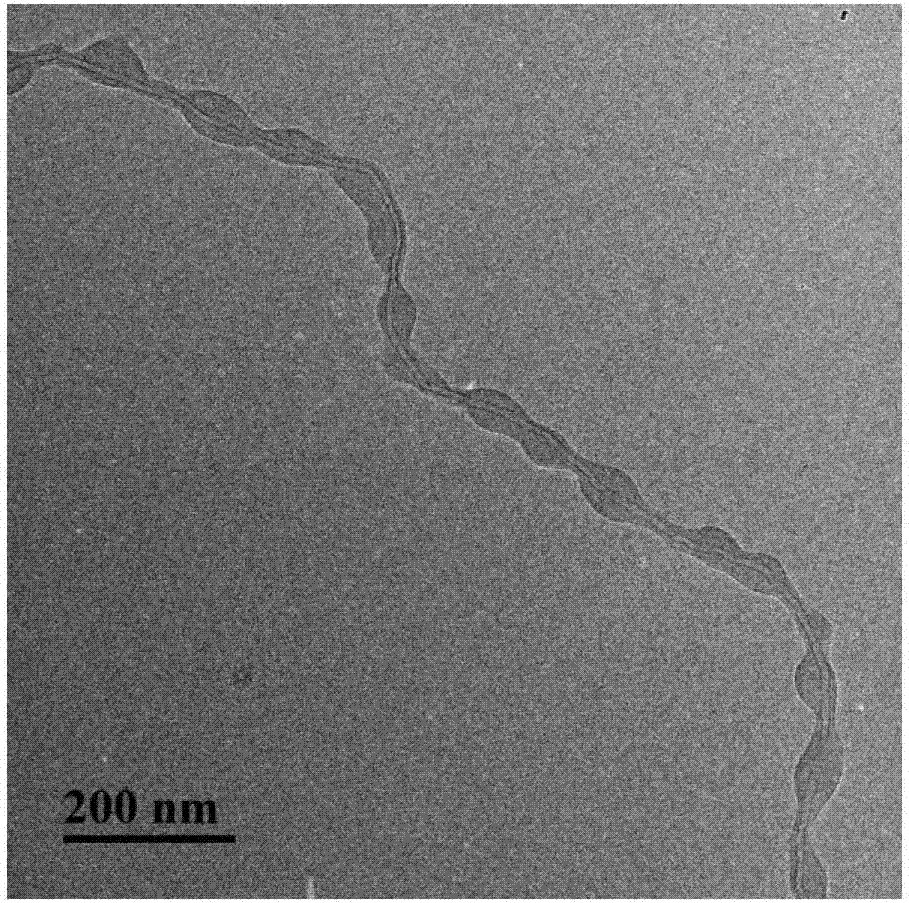
Method of preparing flexible molecularly imprinted sensor based on carbon nano tube-loaded polymeric micelle
A technology of carbon nanotubes and molecular imprinting, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve application limitations, limitations of preparation methods, molecularly imprinted polymer micelles and carbon nanotubes Weak force and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing specific surface area, increasing adsorption capacity, excellent sensing performance and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method for preparing a flexible molecularly imprinted sensor based on carbon nanotube-loaded polymer micelles, characterized in that the preparation steps are as follows:
[0032] (1) Synthesis of amphiphilic photosensitive polymer
[0033] Under normal pressure, acrylic acid, 7-(4-vinylbenzyloxy)-4-methylcoumarin, and isooctyl acrylate are dissolved in dioxane at a molar ratio of 5:5:5; Azobisisobutyronitrile (2% of the total molar ratio of the monomers) is dissolved; react under nitrogen protection and 65°C for 24 hours; after the reaction, use petroleum ether as a precipitant and tetrahydrofuran as a solvent for repeated precipitation dissolved, and the resulting product was vacuum-dried to obtain the amphiphilic photosensitive polymer PEMA-5:5:5.
[0034] (2) Preparation of carbon nanotube-loaded polymer micelles
[0035] Dissolve the above-mentioned amphiphilic photosensitive polymer PEMA-5:5:5 in N,N-dimethylformamide to prepare a 5 mg / ml polymer solution, add c...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A method for preparing a flexible molecularly imprinted sensor based on carbon nanotube-loaded polymer micelles, characterized in that the preparation steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Synthesis of amphiphilic photosensitive polymer
[0041] Under normal pressure conditions, methacrylic acid, 7-(4-vinylbenzyloxy)-4-methylcoumarin, and isooctyl acrylate were dissolved in dioxane at a molar ratio of 5:1:4; The initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (1% of the total molar ratio of the monomers) is dissolved; under nitrogen protection, 65°C, react for 12h; After repeated precipitation and dissolution, the resulting product was vacuum-dried to obtain the amphiphilic photosensitive polymer PEMM-5:1:4.
[0042] (2) Preparation of carbon nanotube-loaded polymer micelles
[0043] Dissolve the above-mentioned amphiphilic photosensitive polymer PEMM-5:1:4 in tetrahydrofuran to prepare a 10 mg / ml polymer solution, add carbon nanotubes, and ultrasonically disperse for 12 hours to obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Synthesis of amphiphilic photosensitive polymer
[0048] Under normal pressure conditions, acrylic acid, 7-(4-vinylbenzyloxy)-4-methylcoumarin, and lauryl methacrylate are dissolved in dioxane at a molar ratio of 5:4:1; azobisisoheptanonitrile (according to 3% of the total molar ratio of the monomers) and make it dissolve; under nitrogen protection, 65 ℃ of conditions, react for 48h; The precipitate was dissolved, and the obtained product was vacuum-dried to obtain the amphiphilic photosensitive polymer PEML-5:4:1.
[0049] (2) Preparation of carbon nanotube-loaded polymer micelles
[0050] Dissolve the above-mentioned amphiphilic photosensitive polymer PEML-5:4:1 in dioxane to prepare a 1 mg / ml polymer solution, add carbon nanotubes, and ultrasonically disperse for 24 hours to obtain a uniformly dispersed amphiphilic photosensitive polymer / carbon nanotube dispersion (the concentration of carbon nanotubes is 0.1 mg / ml); slowly drop caffeine solution (5 mg / ml) in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com