Cheap and high-quality mixed phase-change energy storage material
An energy storage material and mixed-phase technology, which is applied in heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of large volume change, small thermal conductivity, supercooling, etc., and achieves simple preparation process, good thermal stability, The effect of high energy storage density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
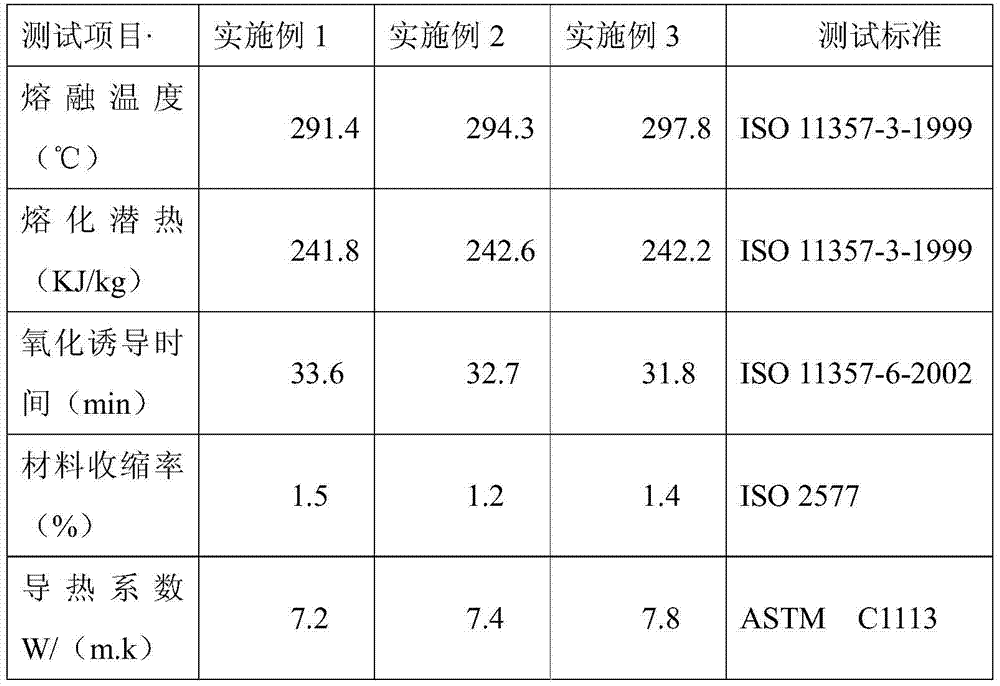
Embodiment 1
[0026] The mixed phase-change energy storage material of this embodiment contains the following components in parts by weight: 55 parts by weight of 2,2-dimethyl-propanol; 25 parts by weight of borax; crosslinking agent: 2,4-toluene 2 parts by weight of diisocyanate; thickener: 2 parts by weight of polyvinyl alcohol (molecular weight: 16000).
[0027] Preparation method: Mix 55 parts by weight of 2,2-dimethyl-propanol with crosslinking agent: 2 parts by weight of 2,4-toluene diisocyanate, mix at 50°C for 6 hours to prepare 2,2-dimethyl - propanol prepolymer. Then the formed 2,2-dimethyl-propanol prepolymer was stirred and mixed with 25 parts by weight of borax in a high-speed mixer at 95°C, and the speed of the mixer was set to 2000rpm. After 3 hours, add thickening Agent: 2 parts by weight of polyvinyl alcohol (molecular weight: 16,000) is solidified at low temperature, and the method of nitrogen gas flow through the refrigerant can be selected for low temperature solidifica...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The mixed phase change energy storage material of this embodiment contains the following components in parts by weight: 56 parts by weight of 2,2-dimethyl-propanol; 28 parts by weight of borax; crosslinking agent: hydroxyethyl acrylate 3 Parts by weight; thickener: polyethylene wax (molecular weight 2000) 3 parts by weight.
[0031] Preparation method: Mix 56 parts by weight of 2,2-dicarboxymethyl-propanol; mix with 3 parts by weight of crosslinking agent: hydroxyethyl acrylate, mix at 60°C for 4 hours to prepare 2,2-dicarboxymethyl-propanol propanol prepolymer. Then the formed 2,2-dicarboxymethyl-propanol prepolymer was stirred and mixed with 28 parts by weight of borax in a high-speed stirrer at 105° C., and the speed of the stirrer was set at 1800 rpm. After continuing for 4 hours, adding Thickening agent: 3 parts by weight of polyethylene wax (molecular weight: 2000) can be solidified at low temperature, and can be solidified at low temperature by passing nitrogen ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The mixed phase change energy storage material of this embodiment, its raw material contains the following components in parts by weight: 58 parts by weight of 2,2-dimethyl-propanol; 30 parts by weight of borax; crosslinking agent: hydroxyethyl methacrylate 4 parts by weight of ester; thickener: 6 parts by weight of polyethylene wax (molecular weight: 3000).
[0034] Preparation method: 58 parts by weight of 2,2-dicarboxymethyl-propanol; mix with crosslinking agent: 4 parts by weight of hydroxyethyl methacrylate, mix at 65°C for 6 hours to prepare 2,2-dicarboxymethyl - Propanol prepolymer. Then the formed 2,2-dicarboxymethyl-propanol prepolymer was stirred and mixed with 30 parts by weight of borax in a high-speed stirrer at 105° C., and the speed of the stirrer was set at 2300 rpm for 4 hours, and then added Thickening agent: 6 parts by weight of polyethylene wax (molecular weight: 3000) can be solidified at low temperature, and can be solidified at low temperature by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com