Process for direct imaging growth of graphene on insulation substrate
A technology of insulating substrate and process method, which is applied in the direction of metal material coating process, gaseous chemical plating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of graphene transfer damage, graphene doping, poor substrate adhesion, etc., to achieve Save process steps and process time, improve adhesion, avoid the effect of doping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: applied in the graphene field effect transistor
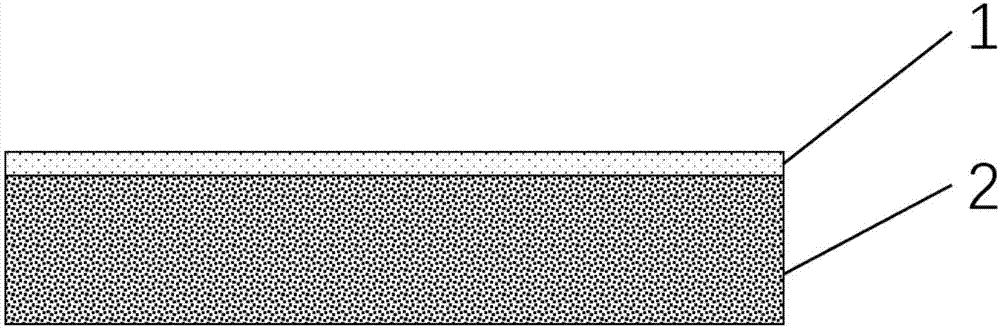
[0045] like Figure 8 As shown, wherein 1 is graphene, 4 is a titanium-platinum electrode, and 5 is a silicon substrate with a 300nm silicon dioxide layer. Graphene field effect transistors were prepared with titanium and platinum as the source and drain electrodes, heavily doped silicon substrates as the gate, and graphene as the conductive channel. The advantage of using titanium-platinum as the electrode is that the titanium-platinum electrode can be prepared in advance, and then graphene can be directly grown by CVD. Titanium-platinum has a high melting point and can withstand the temperature of CVD to directly grow graphene. In this way, after the graphene is grown, the device is finished, so there is no need to prepare electrodes through photolithography-sputtering-stripping, which can minimize the doping of graphene during the device process. Specific steps are as follows:
[0046] S1 After cleani...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: a graphene field effect transistor using graphite as source and drain electrodes.
[0051] like Figure 9 As shown, graphite is prepared by CVD method as the source and drain electrodes, the heavily doped silicon substrate is used as the gate, and then graphene is directly grown as the conductive channel to prepare a graphene field effect transistor, in which 1 is graphene and 6 is graphite The electrode, 5, is a silicon substrate with a 300nm silicon dioxide layer. The advantages of using graphite as the source-drain electrode are: 1) Graphite has a very high melting point and can remain stable at the growth temperature of graphene. 2) Graphene and graphite are both carbon materials, and their work functions are similar. Using graphite as an electrode can reduce the contact resistance between graphene and the electrode. 3) Graphite is a carbon material with large reserves in nature, low cost and more environmentally friendly. Specific steps are as foll...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3: using quartz as a substrate to directly grow a graphene film.
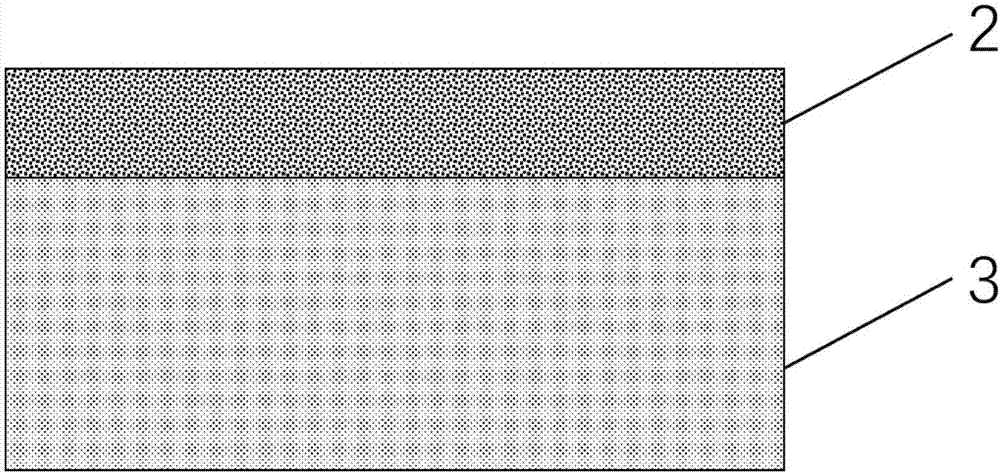
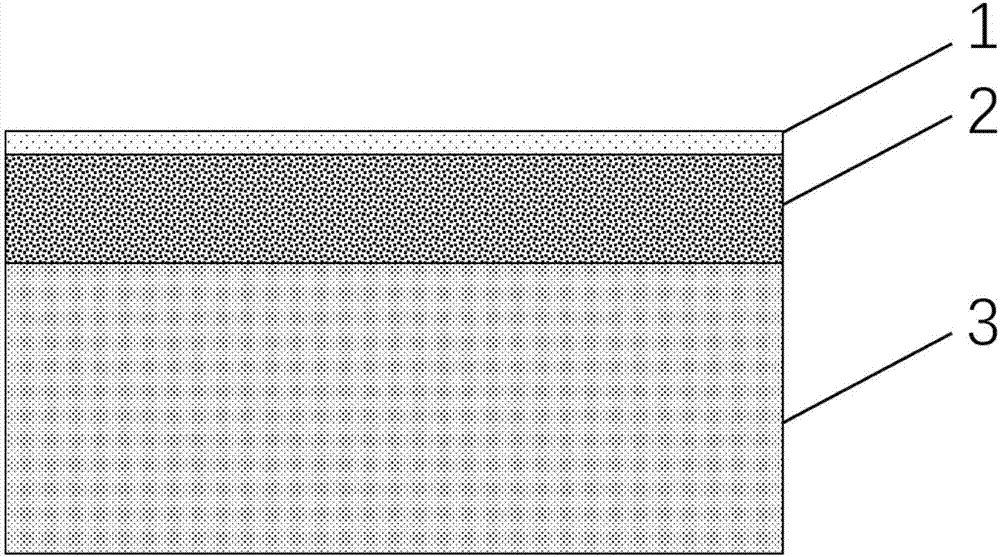
[0056] like Figure 10 As shown, the graphene film is directly grown on a quartz substrate, wherein, 1 is graphene, and 7 is a quartz substrate. The main component of quartz is silicon dioxide, which can withstand the temperature of direct growth of graphene. The specific process steps are as follows:
[0057] S1 sputters a layer of 60nm thick copper film on the quartz substrate, such as Figure 10.1 shown.
[0058] S2 uses Black Magic vertical cold wall CVD equipment to prepare graphene at a temperature of 960°C, methane flow rate of 30 sccm, hydrogen gas flow rate of 20 sccm, air pressure of 6 mbar, and growth time of 5 min. A layer of graphene film is grown on the copper film, such as Figure 10.2 shown.
[0059] S3 keeps this temperature and the gas flow constant, and continues annealing to completely volatilize the copper, and the graphene will eventually fall on the quartz substrate,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com