Ion-imprinted nanocellulose adsorbing material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of nanocellulose and adsorption materials, which is applied in the field of ion-imprinted nanocellulose adsorption materials and its preparation, can solve problems such as nanocellulose preparation methods that have not been seen before, and achieve high selectivity, large specific surface area, and high adsorption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
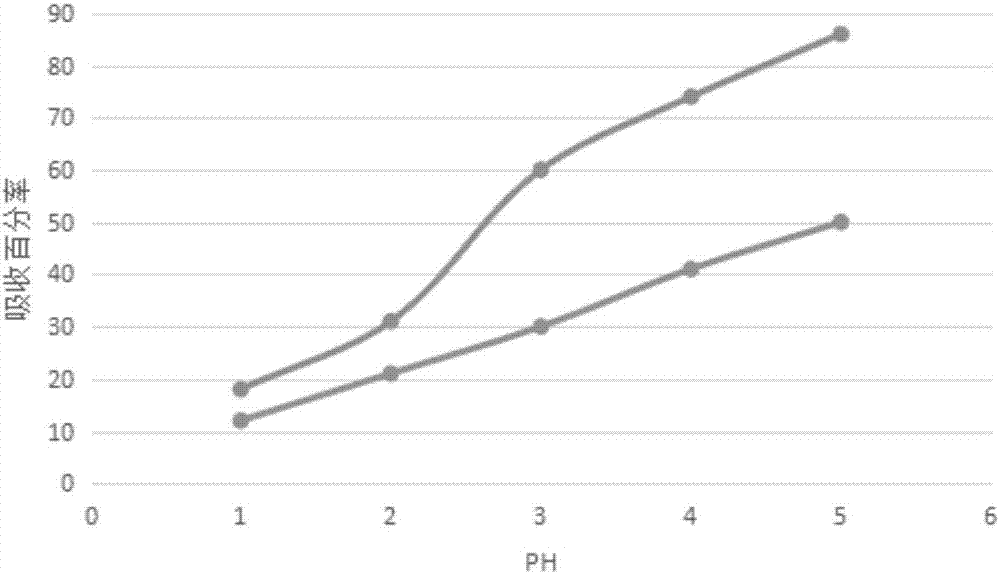
Examples
Embodiment 1
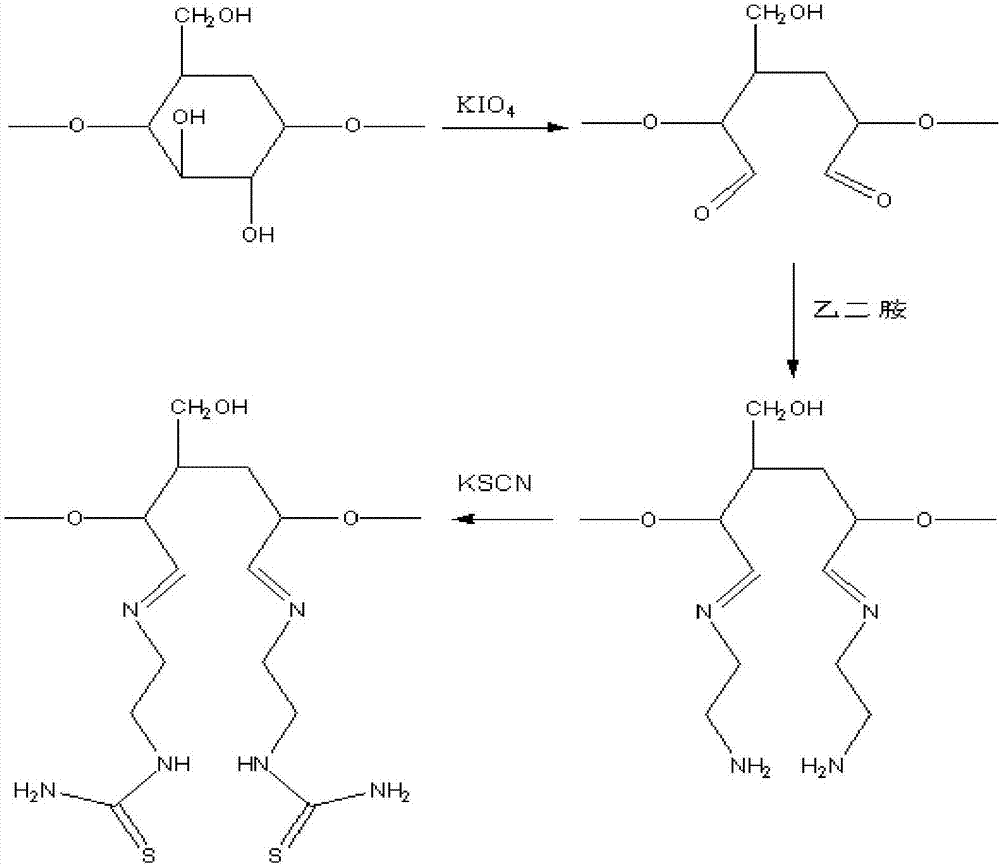
[0038] (1) Disperse 1g of nanocellulose in 200ml of water, then add 0.7g of potassium periodate, stir the reaction under light-shielding conditions, add 10ml of ethylene glycol after the reaction is completed, and wash the reaction product to obtain oxidized Nanocellulose;
[0039] (2) Disperse the oxidized nanocellulose in step (1) in 200ml of water, then add 10ml of anhydrous ethylenediamine, stir and react at 30°C, and wash the reaction product with distilled water to obtain aminated nanocellulose;
[0040] (3) the aminated nanocellulose of step (2) is dispersed in 200ml water, then adding mass fraction is 10% potassium thiocyanate solution (mass ratio=1:1 of potassium thiocyanate and nanocellulose) and 10ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid, stirred and reacted at 30°C, washed with distilled water after the reaction, to obtain nanocellulose with a thiourea structure;
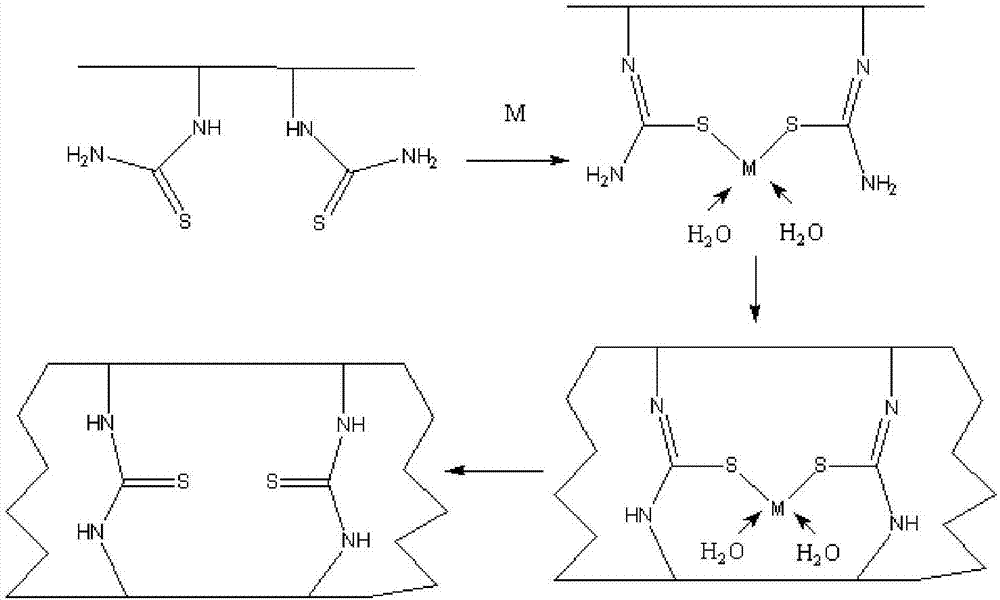
[0041] (4) uniformly disperse the nanocellulose with thiourea structure in step (3) in water, then add the mercu...
Embodiment 2
[0053] (1) Disperse 1g of nanocellulose in 200ml of water, then add 1g of potassium periodate, stir the reaction under light-shielding conditions, add 10ml of ethylene glycol to terminate the reaction, and wash the reaction product to obtain oxidized nanocellulose cellulose;
[0054] (2) Disperse the oxidized nanocellulose in step (1) in 200ml of water, then add 10ml of anhydrous ethylenediamine, stir and react at 30°C, and wash the reaction product with distilled water to obtain aminated nanocellulose;
[0055] and 10ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid, stirred and reacted at 30°C, washed with distilled water after the reaction, to obtain nanocellulose with a thiourea structure;
[0056] (4) step (3) nano cellulose with thiourea structure is evenly dispersed in water, then add lead nitrate aqueous solution (with lead nitrate as solute, according to the total amount of lead ions) that is 1.25:10 with the total mass ratio of nano cellulose Mass calculation, the total mass ratio of l...
Embodiment 3
[0067] (1) Disperse 1g of nanocellulose in 200ml of water, then add 1.3g of potassium periodate, stir the reaction under light-shielding conditions, add 10ml of ethylene glycol after the reaction is completed, and wash the reaction product to obtain oxidized Nanocellulose;
[0068] (2) Disperse the oxidized nanocellulose in step (1) in 200ml of water, then add 10ml of anhydrous ethylenediamine, stir and react at 30°C, and wash the reaction product with distilled water to obtain aminated nanocellulose;
[0069] (3) the aminated nanocellulose of step (2) is dispersed in 200ml of water, then adding mass fraction is 15% potassium thiocyanate solution (mass ratio=1.5:1 of potassium thiocyanate and nanocellulose) and 10ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid, stirred and reacted at 30°C, washed with distilled water after the reaction, to obtain nanocellulose with a thiourea structure;
[0070] (4) step (3) nano cellulose with thiourea structure is evenly dispersed in water, then add copper ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com