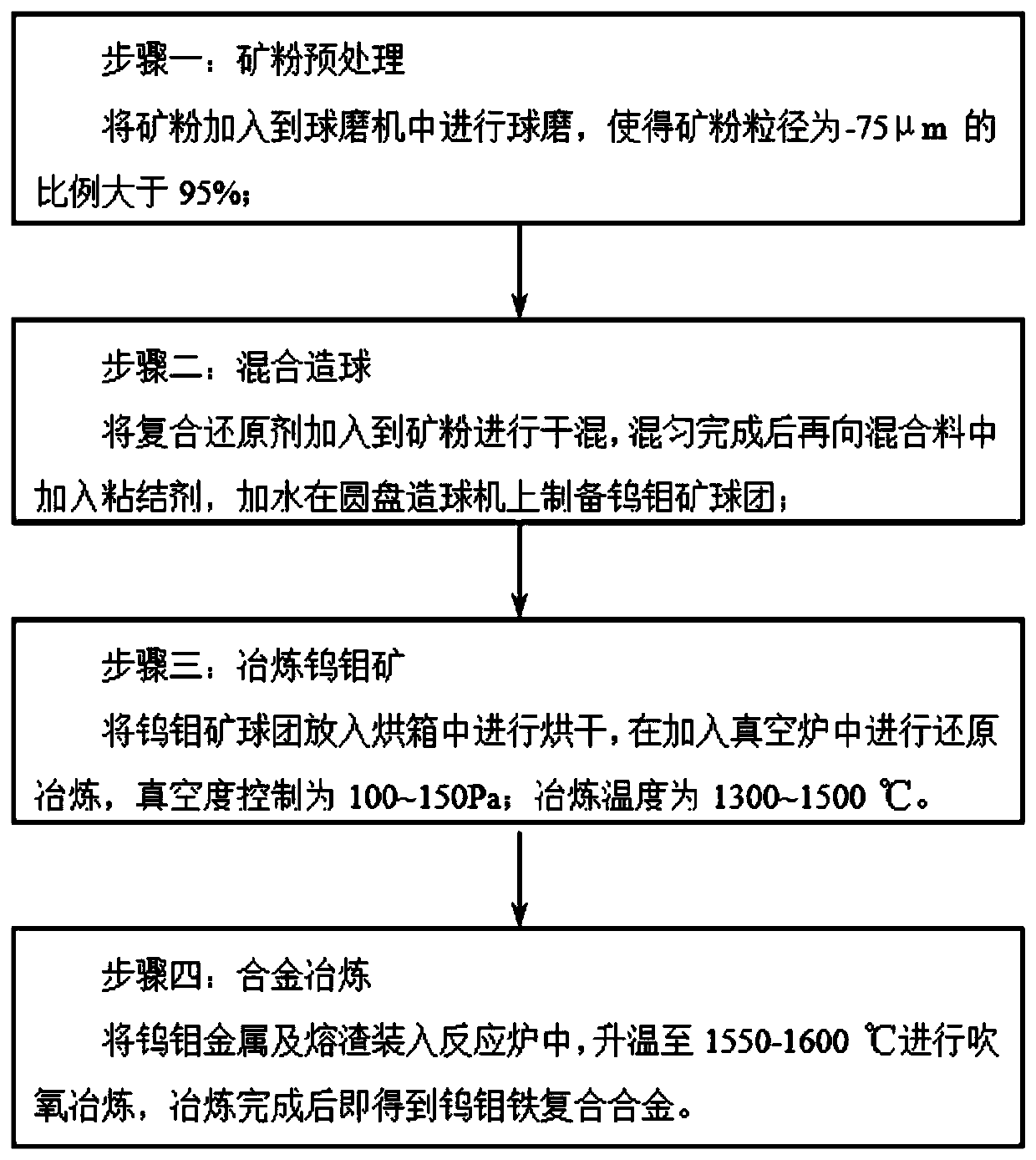
A method for smelting tungsten-molybdenum ferroalloy using low-grade tungsten-molybdenum ore
A low-grade tungsten-molybdenum ore technology is applied in the field of resource utilization of low-grade tungsten-molybdenum ore, which can solve problems such as difficult smelting of low-grade tungsten-molybdenum ore, and achieve the effects of improving reduction efficiency, good reduction effect and reducing reaction resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The composite reducing agent adopted in the present invention includes modified silicon carbide, modified quartz and additives; the modified silicon carbide is a mixture of silicon carbide powder and silicon powder, and the modified quartz is coated with The quartz coating component, the coating component is pitch; the coating component and quartz are mixed and stirred at a temperature of 50-90°C to obtain modified quartz, wherein the mass ratio of the quartz to the coating component of the modified quartz is 6 -7:1, this embodiment is 7:1.
[0039] That is, first add quartz into the reaction kettle to raise the temperature to 40-50°C, keep it warm for 20 minutes, and then raise the temperature to 50-90°C, which is 60°C in this example; then add the asphalt powder into the reaction kettle, and coat the asphalt powder on Modified quartz was obtained on the surface of the quartz and kept warm for 10 minutes.
[0040] Modified silicon carbide Add kaolin to silicon carbide...
Embodiment 2
[0090] The basic content of this example is the same as that of Example 1, except that the additives also include plastic powder and biomass, and the mass ratio of coke powder, plastic powder and biomass is 5:2:2. Soak the biomass and biomass in the alkaline solution of NaOH and NaCl at 60-80°C, and dry after soaking; after drying, stir the coke powder, plastic powder and biomass at 150-250°C Mixing, so that the plastic powder and biomass and coke powder adhere together, wherein the particles of the plastic powder and biomass are less than 250 mesh. The plastic powder is any one or a mixture of polyethylene, polyoxymethylene, polyamide, polypropylene, polystyrene, polycarbonate, polymethyl methacrylate and polyester. The plastic powder in this embodiment is polypropylene, polystyrene, polycarbonate; the mass ratio of polypropylene, polystyrene, polycarbonate is: 3:1:2. CO and H produced by decomposition of biomass and plastic powder in additives 2 Other reducing gases such a...
Embodiment 3
[0092] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1, except that the reducing agent also includes aluminum powder, and the aluminum powder-300 mesh is 80%, that is, the particles smaller than 300 in the aluminum powder account for 80% ; The aluminum powder is externally prepared, and the aluminum powder accounts for 1.2% of the total mass of modified silicon carbide and modified quartz. The temperature is raised to 1300-1500°C for smelting. In this embodiment, it is 1380°C. The smelting time is 1-3h. The embodiment is 3h, and the reduction process is completed. Samples were cooled to room temperature, crushed and analyzed (W, Mo, P content). Among them, the reduction rate of tungsten is 73.1%, and that of molybdenum is 66.9%.
[0093] During the reduction process, the aluminum powder in the composite reducing agent releases a large amount of heat in the process of reducing the oxide, which promotes the fusion of the composite reducing agent and the or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com