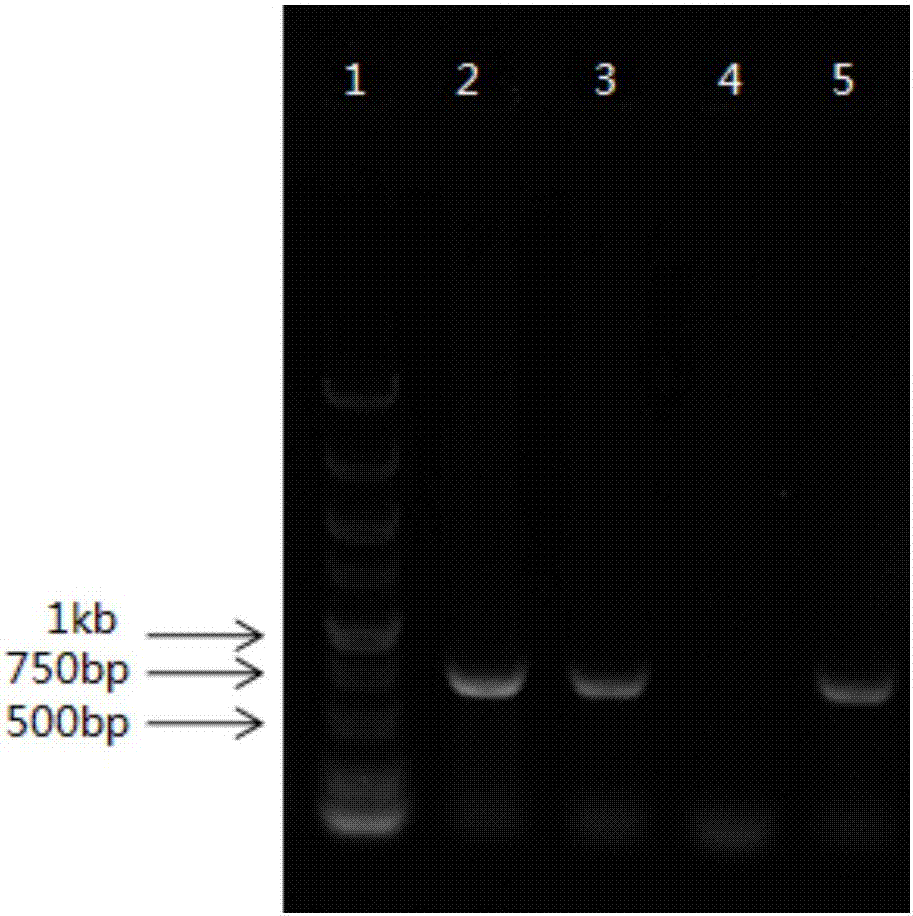
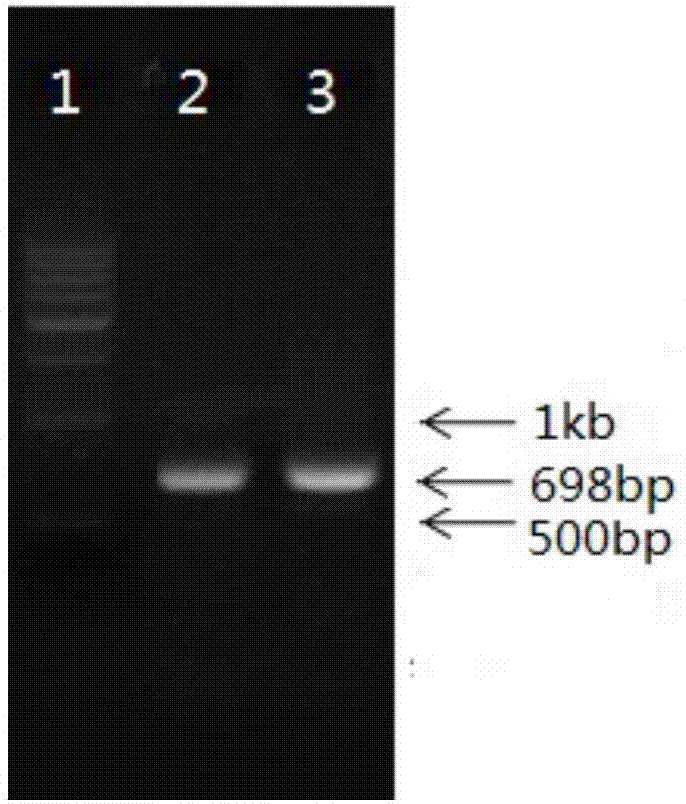
Method for detecting haptoglobin (Hp) classified type
A technology of haptoglobin and polymerase, which is applied in the field of biomedicine and can solve problems such as low accuracy rate and complex typing methods for detecting haptoglobin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Step 1: Saliva sample collection and processing
[0053] Rinse your mouth 30 minutes before sampling to remove food residues and residual microorganisms. Do not eat, drink, brush your teeth, smoke or chew gum within 30 minutes after rinsing your mouth; relax your cheeks and rub gently for 15-30 seconds to produce saliva, collect 2ml of saliva into a sterile collector.
[0054] Step 2: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction from saliva samples
[0055] (1) Take 500ul (microliter) saliva sample, add 1ml (milliliter) buffer (100mmol / L (mmol / liter) Tris-HCl (trishydroxymethylaminomethane-hydrochloric acid buffer), pH8.0,0.5 %SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfonate), 10mmol / LEDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)) and 6ul 20mg / ul (mg / microliter) of proteinase K, shake and mix on a vortex instrument;
[0056] (2) Treat the saliva treated in step (1) in a water bath at 55°C for 20 minutes;
[0057] (3) Add 600ul of phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), mix by inverting, cent...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Step 1: Peripheral blood sample processing and DNA extraction
[0079] (1) Take 2ml of peripheral blood containing EDTA anticoagulant, put it in a 10ml sterilized centrifuge tube, add 6mL 0.1mM EDTA, treat for 15 minutes to break the red blood cells, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, and collect the precipitate;
[0080] (2) Add 1ml 0.1mM EDTA to the precipitate, mix well, transfer to a 2ml sterilized centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 5400rpm for 5min, and discard the supernatant;
[0081] (3) Add 1ml of buffer solution (100mmol / LTris-HCl, pH8.0, 0.5% SDS, 10mmol / LEDTA) and 6ul of 20mg / ul proteinase K to the precipitate, shake and mix on a vortex instrument, and then treat in a water bath at 55°C 20min;
[0082] (4) Add 600ul of phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), mix by inverting, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 5min, and take the supernatant;
[0083] (5) Add 600ul of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) to the supernatant of step (4), centri...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Step 1: Same as Step 1 of Example 2.
[0104] Step 2: Gene PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification and product identification
[0105] (1) PCR amplification:
[0106] Use 10X Mix buffer, its composition is to contain Tris-HCl (final concentration: 12mmol / L), pH is 8.6, potassium chloride (final concentration: 40mmol / L), magnesium chloride (final concentration 1.8mmol / L), Taq enzyme (final concentration: 0.8U), a mixed solution of dNTP (final concentration: 250umol / L), and the DNA extracted from the saliva sample were used as templates for PCR amplification. Amplification primers are as follows:
[0107] F: 5'-ATAATACAGTTCGCGAGCTTCT-3';
[0108] R: 5'-GGGCAAGATACTCAACCTGTC-3'.
[0109] The PCR reaction procedure is as follows:
[0110] 92°C for 3min; 92°C for 48s, 55°C for 40s, 74°C for 45s, 26 cycles; 70°C for 10min; 8°C∝.
[0111] That is, pre-denaturation at a temperature of 92°C for 3 minutes; denaturation at a temperature of 92°C for 48 seconds, anneal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com