Starch-based microporous hemostatic material having antibacterial function, and preparation method and application of the material
A hemostatic material, starch-based technology, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, pharmaceutical science, absorbent pads, etc., to achieve high water absorption, good degradation performance, and good biocompatibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0065] Preparation method of starch-based microporous hemostatic material
[0066] The preparation method of the starch-based microporous hemostatic material of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0067] (1) Preparation of microporous starch
[0068] Add starch and enzymes into phosphate buffer, stir at 40-80°C and pH 4-8, carry out enzymolysis reaction, 3-16 hours later, separate by suction filtration and dry to obtain microporous starch; ,
[0069] The mass ratio of starch and enzyme is 1: (0.01-0.3);
[0070] The mass-volume ratio of the total amount of starch and enzyme to the phosphate buffer is 100g: (150-1000) mL;
[0071] (2) Cationization of microporous starch
[0072] The microporous starch, cationic modifier, catalyst and water prepared in step (1) are mixed and stirred in a certain proportion, and the reaction is carried out for 4-30 hours with continuous stirring and heat preservation at 30-80℃. After centrifugal washing, the mixed solution is dried to obt...
Embodiment 1
[0110] (a) Preparation of microporous starch
[0111] Add 100g corn starch and 3g saccharification enzyme to 300mL pH=6 phosphate disodium hydrogen phosphate aqueous buffer solution, stir well, carry out enzymatic hydrolysis reaction at 45℃ for 8h, vacuum filter and wash, and freeze-dry Dry in the machine for 20 hours to obtain corn microporous starch.
[0112] (b) Cationization of microporous starch
[0113] Dissolve 10g of corn microporous starch in 45g of water, add 0.25g of potassium hydroxide and 3.0g of methylene dimethylamine hydrochloride, stir evenly, react at 50℃ for 20h, and proceed with a mixture of water and isopropanol Centrifugal washing, drying in a freeze dryer for 20 hours to obtain aminated corn microporous starch. The sample shape is like figure 1 Shown.
Embodiment 2~5
[0115] Examples 2 to 5 repeat the experimental steps of Example 1, except for some experimental conditions, as shown in Table 1-2.
[0116] Table 1 Preparation of microporous starch
[0117]
[0118] Table 2 Cationization of microporous starch
[0119]
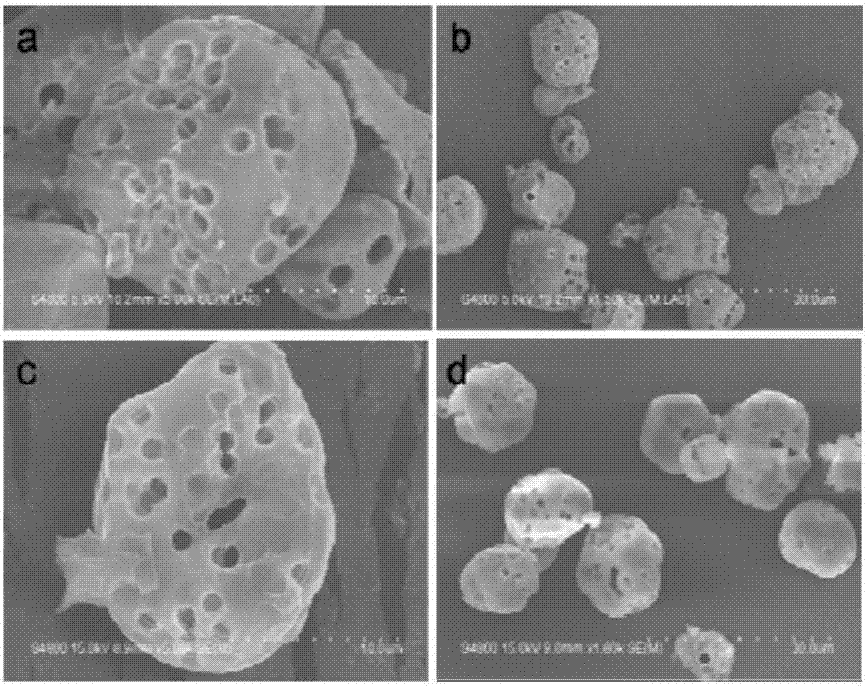
[0120] Observe the microporous starches obtained in step (a) in Example 1 by scanning electron microscopes (see figure 2 (a) and 2(b)) and the amino-loaded microporous starch obtained in step (b) (see figure 2 (c) and 2(d)). It can be seen from the figure that the particle diameter of the microporous starch not loaded with amino groups is about 10-20 μm, the diameter of the pores is about 1-4 μm, and the micropores remain intact after the amino group modification.
[0121] The amino-loaded microporous starch prepared in Example 2-5 has a particle diameter of about 9-30 μm and a pore diameter of about 0.5-5 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com