Process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater through combination of MBR and membrane separation method
A technology of printing and dyeing wastewater and membrane separation method, which is applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of high salinity of effluent, failure to achieve water reuse, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing separation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
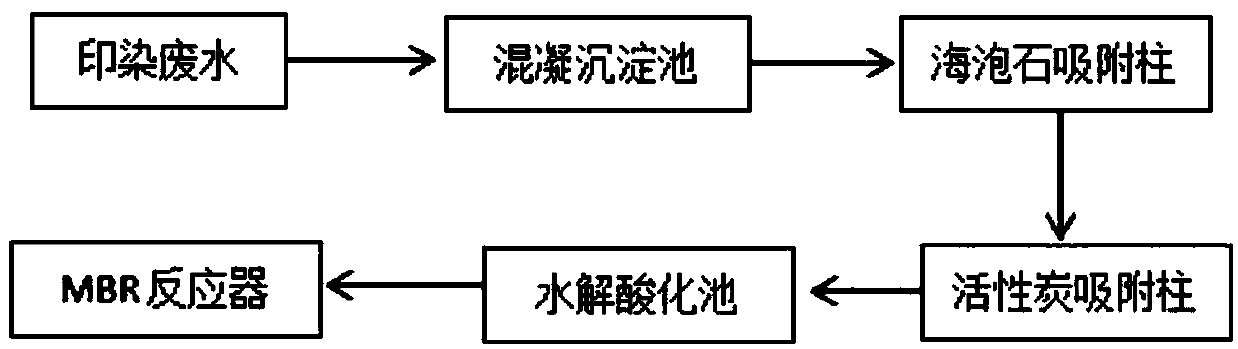
[0023] A process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater in combination with MBR and membrane separation method, the specific process is:
[0024] (1) The printing and dyeing wastewater is directly pumped into the coagulation sedimentation tank, and the flocculant polymerized ferric chloride and carboxymethyl chitosan in the coagulation sedimentation tank work together to remove suspended solids or colloidal particles. Ferric chloride and 7mg carboxymethyl chitosan, wherein the wastewater is pumped into the sedimentation tank and first stirred for 20 minutes, so that the flocculant can absorb the suspended matter or colloidal particles in the wastewater, form and then statically settle for 2 hours;
[0025] (2) The supernatant from the upper part of the coagulation sedimentation tank is pumped into the activated carbon adsorption column, and the supernatant is pumped into the sepiolite adsorption column. The small particles of impurities in the supernatant are adsorbed on t...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater in combination with MBR and membrane separation method, the specific process is:
[0030] (1) The printing and dyeing wastewater is directly pumped into the coagulation sedimentation tank, and the flocculant polyferric chloride and carboxymethyl chitosan in the coagulation sedimentation tank work together to remove suspended solids or colloidal particles, and add 40 mg of polymerized ferric chloride per liter of printing and dyeing wastewater Ferric chloride and 9mg carboxymethyl chitosan, wherein the wastewater is pumped into the sedimentation tank and stirred for 25 minutes at first, so that the flocculant can adsorb the suspended solids or colloidal particles in the wastewater, form and then statically settle for 2.5 hours;
[0031] (2) The supernatant from the upper part of the coagulation sedimentation tank is pumped into the sepiolite adsorption column, and the supernatant is pumped into the sepiolite adsorption...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater in combination with MBR and membrane separation method, the specific process is:
[0036] (1) The printing and dyeing wastewater is directly pumped into the coagulation sedimentation tank, and the flocculant polymerized ferric chloride and carboxymethyl chitosan in the coagulation sedimentation tank work together to remove suspended solids or colloidal particles, and add 50 mg of polymer to each liter of printing and dyeing wastewater Ferric chloride and 15mg carboxymethyl chitosan, wherein the wastewater is pumped into the sedimentation tank and first stirred for 30 minutes, so that the flocculant can absorb the suspended matter or colloidal particles in the wastewater, form and then statically settle for 3 hours;
[0037] (2) The supernatant from the upper part of the coagulation sedimentation tank is pumped into the circulation adsorption column. The circulation adsorption column includes a sepiolite adsorption col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com