Photocatalyst for treating dye in high-salt wastewater and preparation method of photocatalyst
A technology of high-salt wastewater and photocatalyst, applied in the field of photocatalysis, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory dye treatment effect, and achieve the effects of improving photocatalytic effect, reducing operating cost and improving separation effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Put melamine into a crucible with a lid, place it in a muffle furnace, raise the temperature to 400°C at a rate of 1°C / min, keep it for 100 min, and cool it to room temperature to obtain a yellow powder; then mix it with a certain amount of Mixed with deionized water (the mass percentage of water is 99.5%), ultrasonicated at room temperature for 0.5h, poured into a hydrothermal kettle, heated at 120°C for 6h, cooled to room temperature and centrifuged, and the obtained solid matter was Dry in an oven at 40°C for 5 hours to obtain a khaki solid; then mix with bismuth nitrate (molar ratio 1:4×10 -4 ) for grinding, and then put it into a crucible with a lid, raise the temperature to 400°C at a heating rate of 1°C / min, keep it for 3h, and then cool to room temperature to obtain the optical fiber of bismuth oxycarbonate nanoparticles supported by porous graphite nitrogen carbide nanosheets. catalyst.
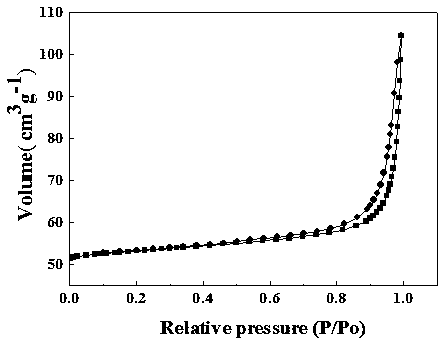
[0034] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that through the detection of ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Put melamine into a crucible with a lid, place it in a muffle furnace, raise the temperature to 600 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min, keep it for 500 min, and cool it to room temperature to obtain a yellow powder; then mix it with a certain amount of Mix with deionized water (the mass percentage of water is 98.5%), after ultrasonication at room temperature for 3 hours, pour it into a hydrothermal kettle, heat at 240°C for 30 hours, cool to room temperature and centrifuge, and put the obtained solid matter in an oven Dry at 100°C for 30h to obtain a khaki solid; then mix with bismuth nitrate (molar ratio 1:4×10 -2) for grinding, and then put it into a crucible with a lid, raise the temperature to 600°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, keep it for 6h, and cool to room temperature to obtain porous graphite nitrogen carbide nanosheets loaded with bismuth oxycarbonate nanoparticles catalyst of light.
[0040] Evaluation conditions: In 40 mg / L high-salt dye wastewater containing methyl...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Put melamine into a crucible with a lid, place it in a muffle furnace, raise the temperature to 530 °C at a rate of 2.5 °C / min, keep it for 200 min, and cool it to room temperature to obtain a yellow powder; then mix it with a certain amount of Mix with deionized water (the mass percentage of water is 99.0%), after ultrasonication at room temperature for 1h, pour into a hydrothermal kettle, heat at 180°C for 12h, cool to room temperature and centrifuge, and put the obtained solid matter in an oven Dry at 70°C for 10 hours to obtain a khaki solid; then mix with bismuth nitrate (molar ratio 1:8×10 -3 ) for grinding, and then put it into a crucible with a lid, raise the temperature to 500°C at a heating rate of 2.5°C / min, keep it for 4h, and then cool to room temperature to obtain porous graphite nitrogen carbide nanosheets loaded with bismuth oxycarbonate nanoparticles catalyst of light.
[0043] Evaluation conditions: In high-salt dye wastewater containing 20 mg / L rhoda...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com