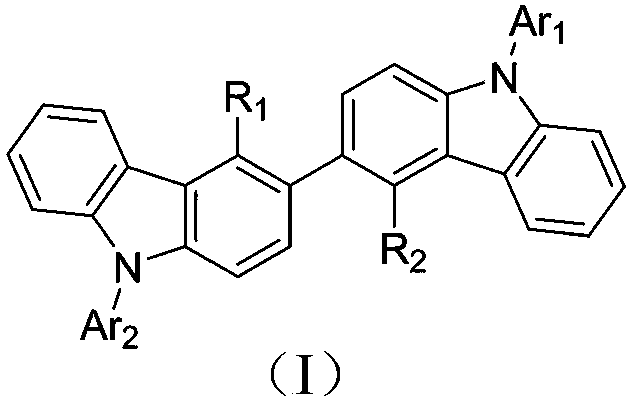
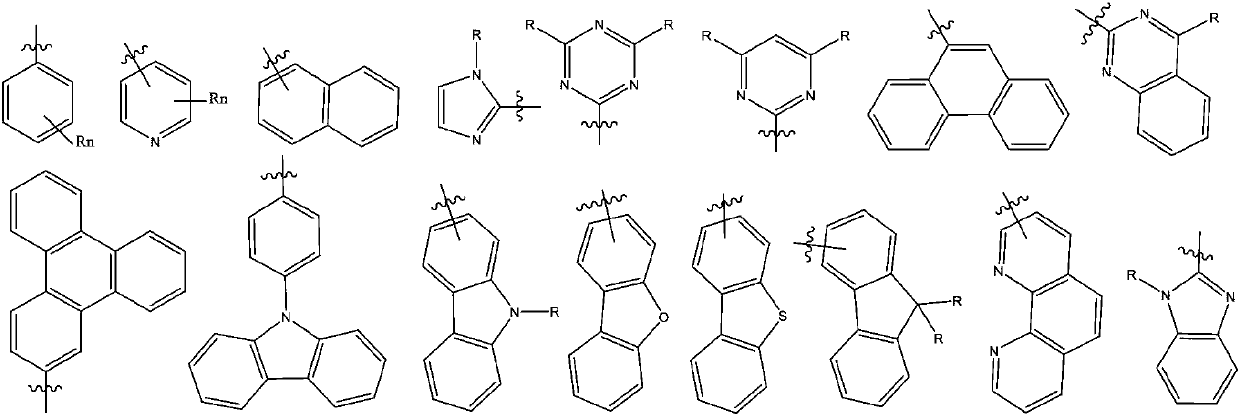
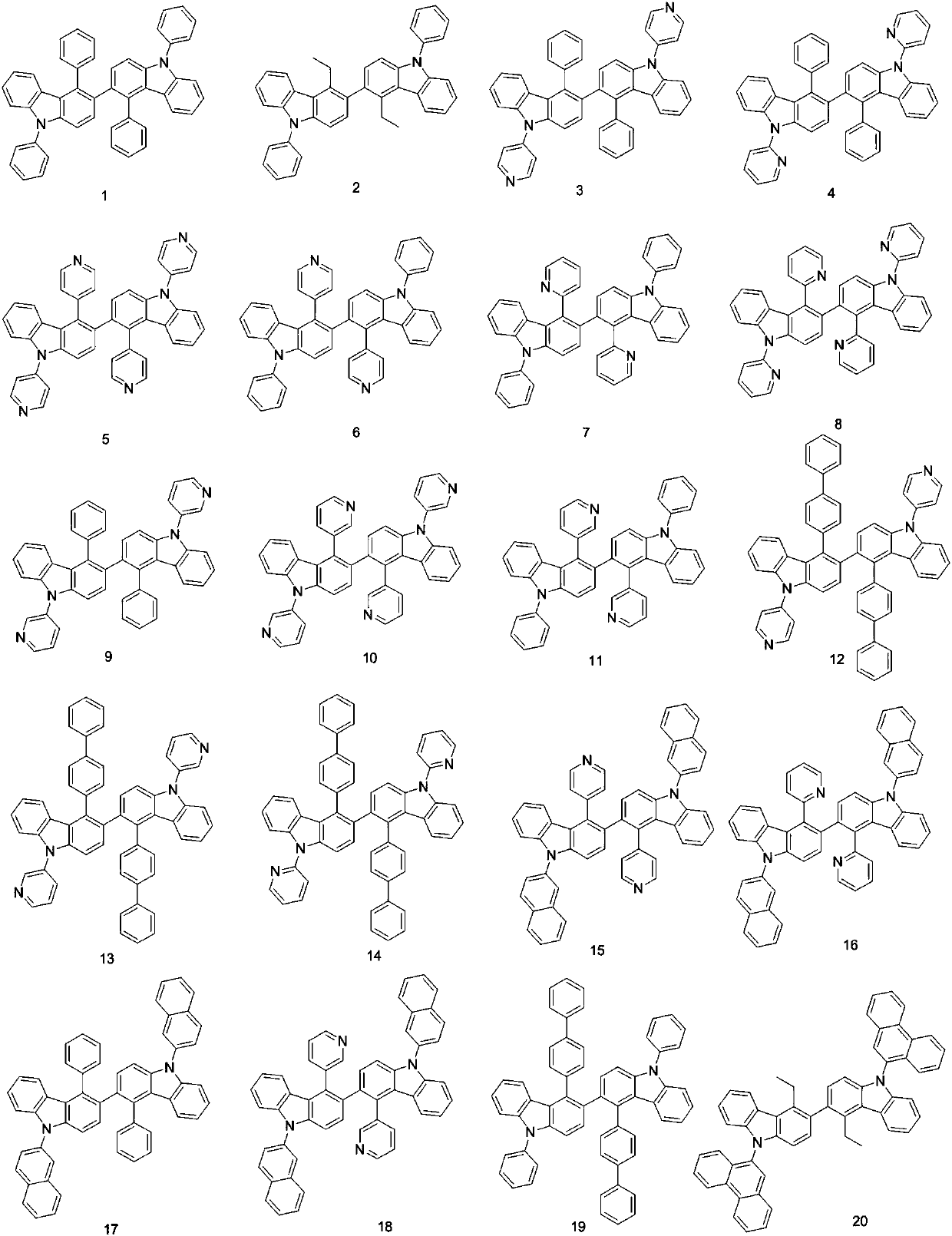
Bicarbazole derivatives and organic light emitting device thereof
An organic light-emitting device and biscarbazole technology, applied in the field of biscarbazole derivatives and organic light-emitting devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] The preparation method of the biscarbazole derivatives of the present invention can be obtained through the following reactions.
[0040]
[0041] The biscarbazole derivatives represented by the formula (I) of the present invention can be prepared by Suzuki coupling reaction and Ullmann reaction, using conventional reaction conditions well known to those skilled in the art. The present invention has no special limitation on the sources of the raw materials used in the above-mentioned various reactions, and can be prepared by using commercially available product raw materials or using preparation methods well known to those skilled in the art.
[0042] The present invention also provides an organic light-emitting device, comprising an anode, a cathode, and several organic functional layers between the anode and the cathode, and the organic functional layers at least contain the biscarbazole derivatives.
[0043] The above-mentioned organic functional layer at least in...
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: the preparation of compound 1
[0047] Preparation of intermediate 1-A:
[0048]
[0049]Weigh compound 1-a (30.6g, 251mmol), compound 1-b (90.81g, 251mmol), tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium (11g, 10mmol) and potassium carbonate (84.2g, 609mmol), the reaction The product was dissolved in a solvent of toluene (1L) / EtOH (200mL) / distilled water (200mL), heated at 90°C for 2 hours, and after several layers of vacuum distillation, it was ground with methanol, and the obtained solid was dissolved in dichloromethane and filtered through silica gel. , triturated with dichloromethane and hexane to give compound 1-c (62.65, 80%).
[0050] Compound 1-c (11.73g, 37.6mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (140mL), and a hexane solvent and 2.5M n-butyllithium (18mL, 45.1mmol) were added dropwise at -78°C, followed by stirring for 1 hour. After slowly adding trimethyl borate (13 mL, 56.4 mmol) dropwise, stirred for 2 h. Then 2M hydrochloric acid was added dropw...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: the preparation of compound 3
[0064] Preparation of Intermediate 3-B:
[0065]
[0066] Weigh intermediate 1-A (13.21g, 41mmol), compound 3-g (8.41g, 41mmol), cuprous iodide (3.9g, 20.5mmol), ethylenediamine (1.4mL, 20.5mmol) and cesium carbonate (40g, 123mmol), and added to toluene (250mL) in the above order, and stirred at reflux. The intermediate 3-B (13.59 g, 83%) was obtained by extraction with ethyl acetate, vacuum distillation, dichloromethane and hexane column.
[0067] Mass Spectrum m / z: 398.03 (calculated: 398.04). Theoretical element content (%)C 23 h 15 BrN 2 : C, 69.19; H, 3.79; Br, 20.01, N, 7.02. Measured element content (%): C, 69.20; H, 3.79; Br, 20.01, N, 7.01. The above results confirmed that the obtained product was the target product.
[0068] Preparation of compound 3:
[0069]
[0070] Compound 3-B (15.01 g, 37.6 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (140 mL), and a hexane solvent and 2.5M n-butyllithium (18 mL, 45....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com