[0003] At present, the methods for measuring the chloride
ion permeability of concrete include the
electric flux method and the rapid chloride
ion transfer coefficient method (RCM): the
electric flux method was proposed by Whiting and developed into two standards of AASHTO T277 and ASTM C1202 in the United States. It is currently the most popular rapid evaluation method of concrete permeability in the world. This method is also adopted by the current standard of China "Standard for Test Methods of Long-term Performance and Durability of Ordinary Concrete (GB / T 20082-2009)". The specific process of this method is in Inject 0.3mol / L NaOH and 3% NaCl solutions into the plexiglass
liquid injection pools on both sides of the test piece respectively. After the test piece is saturated with water in vacuum, a 60V
DC voltage is applied to both ends. The effect of Cl- on the
electric field and concentration difference Under accelerated
diffusion, measure the total
electricity (
coulomb) passing through the concrete specimen within 6 hours. The total
electricity is related to the permeability of Cl-. The greater the electricity passing through the specimen per unit time, the greater the permeability of the concrete; this method The operation is simple, but the polarization reaction generated by applying a high
DC voltage of 60V will increase the temperature of the solution and affect the test results. If the test
voltage is lowered, the test time will be greatly prolonged; the RCM method is based on Tang Luping's rapid chloride
ion migration It was proposed by the coefficient method and was listed as the Nordic standard. After improvement, it was adopted by China's "Standards for Test Methods of Ordinary Concrete Long-term Performance and Durability". Soak the test piece in
calcium hydroxide solution for several hours and power it on for 6-24 hours. Although it is simple, practical and accurate, it requires that the aggregate particle size of the test piece should not be greater than 25mm, the packaging process is cumbersome, and the test time varies with different test pieces; In addition, Shi Meilun et al. used
AC impedance spectroscopy to evaluate the
diffusion resistance of ions in it. The
test equipment is expensive and the test steps are complicated.
[0004] A kind of method disclosed in
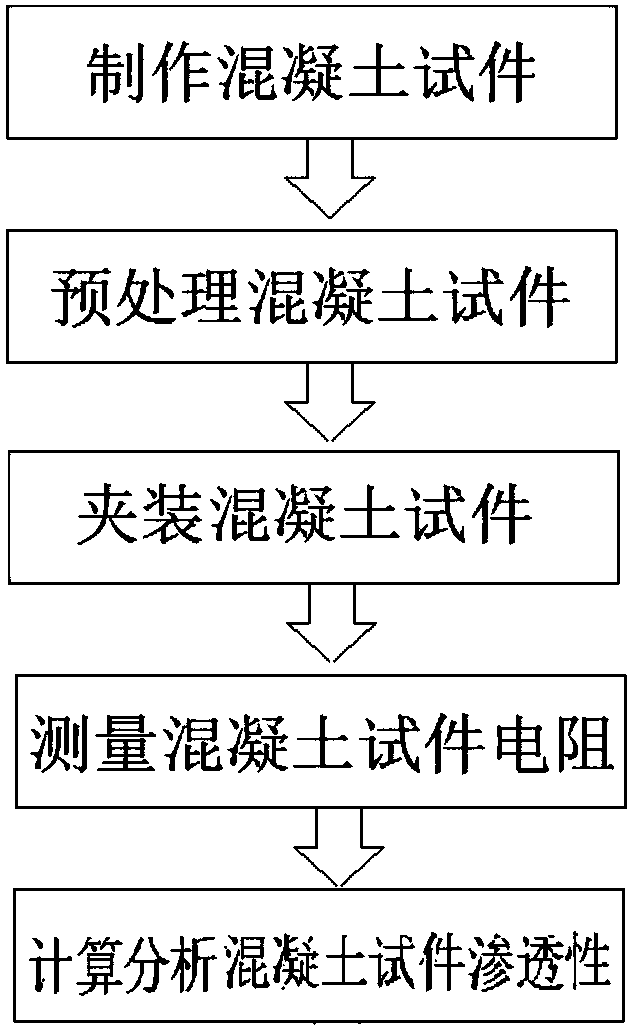
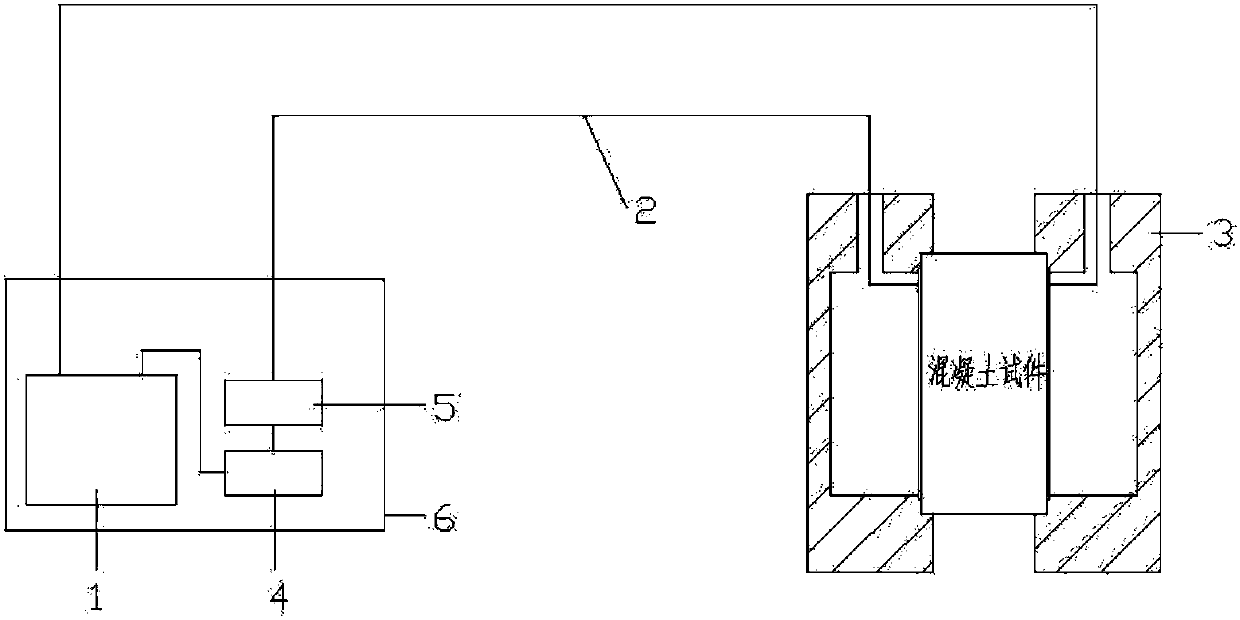
Chinese patent 201310075619.4 to quickly measure the chloride ion permeability resistance of concrete comprises the following steps: (1) prepare test block: after concrete is
cut into 3-5cm thick test block, carry out vacuum saturation treatment; (2) Install the test block: take the
filter paper and stainless steel plate with the same cross-sectional shape and size as the test block, paste the
filter paper on the stainless steel plate, and evenly drop 0.3-1mol / L
sodium hydroxide solution on the
filter paper; take out the concrete test block, Paste the stainless steel plate covered with filter paper on both ends of the concrete, and pressurize to ensure that the filter paper is in
close contact with the concrete; (3) Perform an
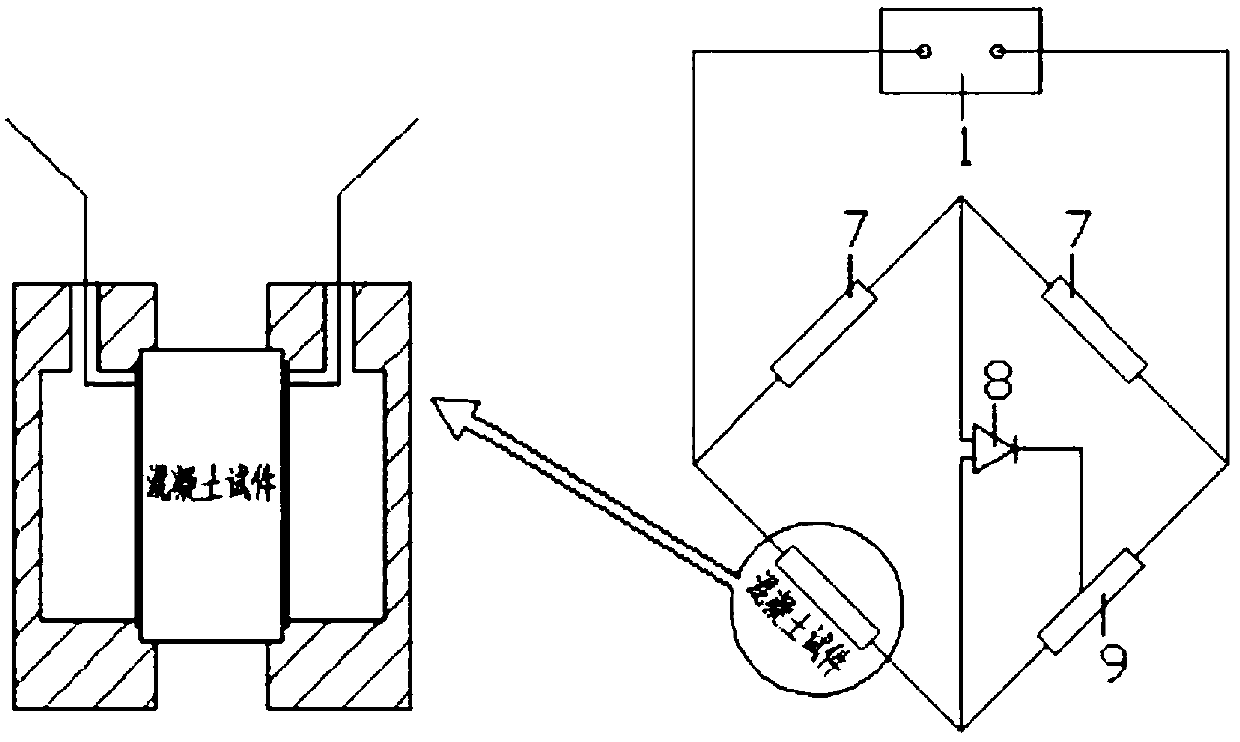
AC impedance test on the concrete test block installed in step (2): the AC voltage is 0.5 ~ 1V, The frequency sweep range is 50Hz to 5000Hz, draw a Nyquist diagram, read the real part value of the impedance at the minimum point of imaginary impedance, that is, the characteristic real impedance, and use the formula (1) to calculate the
conductivity, that is, the characteristic
conductivity: (1) where: is the characteristic
conductivity L is the thickness of the specimen, the unit is m; A is the cross-sectional area of the specimen, the unit is m2; it is the characteristic real impedance, the unit is; (4) The conductivity value obtained by formula (1) , into the formula (2) to obtain the
electric flux value Q: (2) where: Q is the electric flux, and the unit is C; (5) The electric flux calculated according to the formula (2) and the ASTMC1202 permeability rating criterion can be Obtain the chloride ion permeability resistance of the tested concrete test block; it needs to convert the characteristic conductivity obtained by the test into equivalent electric flux to evaluate the chloride ion permeability resistance of concrete, the test results are not intuitive enough, and the equipment used for the test is expensive, Difficult to popularize and apply;
Chinese patent 201410204199.X discloses a method for predicting the anti-chloride ion permeability of concrete based on water-binder ratio monitoring, which includes the following steps: (1) design the mix ratio for the concrete components on site, and keep the raw materials and mix ratio The amount of cementitious materials, crushed stones, and water
reducing agent remains unchanged, and the quality of mixing water and sand remains unchanged, and the
mass ratio of water and sand is changed to prepare concrete test specimens with different water-binder ratios, and the concrete is tested The actual water-binder ratio of the test specimen is obtained to measure the water-binder ratio; (2) test respectively the chloride ion
diffusion coefficients of 28d and 56d of the concrete test pieces of different water-binder ratios; (3) according to the measured water-binder ratio of step (1)
Adhesive ratio and the
chlorine ion diffusion coefficient measured in step (2), respectively fitting concrete components based on fixed raw materials and mix ratios of cementitious materials, crushed stones, and water reducing agents in different measured water-binder ratios and concrete The characteristic relationship curve between chloride ion diffusion coefficients at 28d and / or 56d age; (4) During the construction of the concrete member, test the water-binder ratio of the freshly mixed concrete on site, relying on the characteristic relationship curve in step (3) , calculate the
chlorine ion diffusion coefficient of the freshly mixed concrete at the age of 28d and 56d to obtain the predicted value of the chloride ion diffusion coefficient; (5) compare the predicted value of the chloride ion diffusion coefficient with the control value specified in the specification or design requirements comparison to determine whether the concrete’s chloride ion permeability resistance meets the specification or design requirements; Concrete test specimens involve multiple conversions and curve drawing, the measurement process is complicated, and the accuracy of the measurement results cannot be guaranteed
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More