Polylactic acid composite material and method for preparing same
A composite material, polylactic acid technology, used in textiles and papermaking, fiber processing, plant fibers, etc., can solve the problems of unstable performance of reinforced polylactic acid, limited large-scale production and application, and high price, so as to achieve improved material strength, Efficient utilization, increased roughness effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
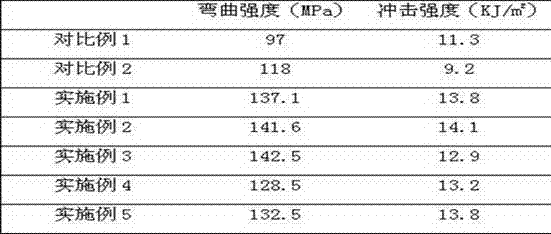
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: Preparation of polylactic acid composite material
[0025] The ratio of raw materials is: polylactic acid 75%, modified fiber 18% (straw fiber 12%, hemp fiber 5%, carbon fiber 1%), epoxy soybean oil 2%, pentaerythritol 2%, stearic acid 3%.
[0026] Wherein, the modified fiber is prepared by the following method:
[0027] (1) Modification of straw fiber and hemp fiber:
[0028] a. Straw fiber and hemp fiber are mixed in proportion, washed with water, soaked in 10% sodium hydroxide solution at room temperature for 3 hours, washed several times with distilled water, adjusted to neutral pH with acetic acid, and put into a drying box Drying in medium temperature for 8 hours, the oven temperature is 80°C.
[0029] b. Soak the above alkali-treated fibers with 4% silane (vinyltriethoxysilane) aqueous solution at room temperature for 3 hours, wash with distilled water for 3 times, and dry them in a drying oven for 8 hours. The temperature of the drying oven is 80...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Preparation of polylactic acid composite material
[0033] The ratio of raw materials is: polylactic acid 70%, modified fiber 23% (straw fiber 15%, hemp fiber 6%, carbon fiber 2%), epoxy soybean oil 2%, pentaerythritol 2%, stearic acid 3%.
[0034] Wherein, the modified fiber is prepared by the following method:
[0035] (1) Modification of straw fiber and jute fiber:
[0036] a. Straw fiber and hemp fiber are mixed in proportion, washed with water, soaked in 10% sodium hydroxide solution at room temperature for 3 hours, washed several times with distilled water, adjusted to neutral pH with nitric acid, and put into a drying box During 8 hours of medium drying, the oven temperature was 80°C.
[0037] b. Soak the alkali-treated fibers above for 3 hours at room temperature with 4% silane (vinyltrimethoxysilane) aqueous solution, wash with distilled water 3 times, and dry them in a drying oven for 8 hours at a temperature of 80°C.
[0038] (2) Carbon fiber...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: Preparation of polylactic acid composite material
[0041] The ratio of raw materials is: polylactic acid 79%, modified fiber 14% (straw fiber 9%, hemp fiber 3%, carbon fiber 2%), epoxy soybean oil 2%, pentaerythritol 2%, stearic acid 3%.
[0042] Wherein, the modified fiber is prepared by the following method:
[0043] (1) Modification of straw fiber and jute fiber:
[0044] a. Straw fiber and jute fiber are mixed in proportion, washed with water, soaked in 10% sodium hydroxide solution at room temperature for 3 hours, then washed several times with distilled water, and then adjusted to neutral pH with nitric acid, then put into a drying box During 8 hours of medium drying, the oven temperature was 80°C.
[0045] b. Soak the alkali-treated fibers above for 3 hours at room temperature with 4% silane (vinyltrimethoxysilane) aqueous solution, wash with distilled water 3 times, and dry them in a drying oven for 8 hours at a temperature of 80°C.
[0046] (2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com