Catalytic cracking method for producing low-carbon olefins and light aromatic hydrocarbons
A technology of catalytic cracking and low-carbon olefins, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, only multi-stage series refining and cracking process treatment, hydrocarbons, etc., can solve the problems of increased and limited yield of light aromatics, and achieve an increase in production efficiency, high BTX yield, and high-efficiency conversion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0070] The present invention also provides a preparation method of the catalytic cracking catalyst provided by the present invention, the preparation method comprising: mixing the preparation raw material of the catalytic cracking catalyst with water and performing beating and spray drying; The dry basis weight of the raw materials for preparation is based on the basis, and the raw materials for preparation include 15-65% by weight of the natural mineral, 10-60% by weight of the precursor of the inorganic oxide binder and 25-75% by weight of Said hybrid molecular sieve, said hybrid molecular sieve includes Y molecular sieve and phosphorus-containing IMF structure molecular sieve.
[0071] Preferably, the preparation step of the phosphorus-containing IMF structure molecular sieve comprises: a, sodium-type IMF structure molecular sieve is desiliconized in an alkaline solution to obtain a desiliconization molecular sieve; b, the desilication molecular sieve obtained in step a is s...
Embodiment
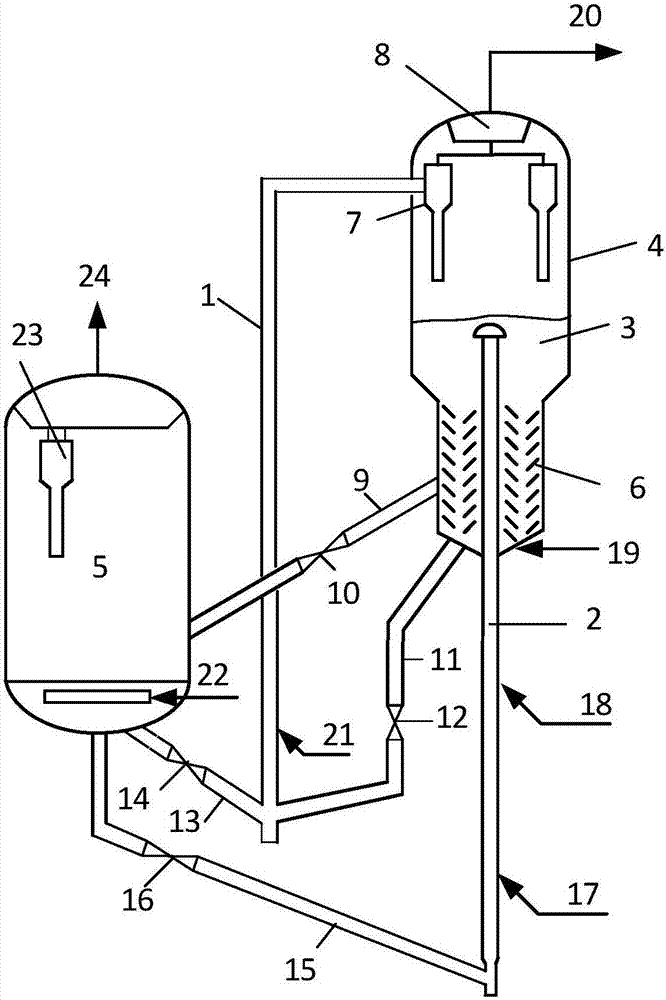
[0118] according to figure 1 The process is tested, the feed oil is vacuum distillate oil, MMC-2 catalyst is used, and the test is carried out on a medium-sized device. The three reactors are all operated under normal pressure. The hydrocracking tail oil enters the riser 1, and the reaction temperature is 580 ℃, reaction time 2.0 seconds, the weight ratio of regenerated catalyst and raw catalyst mixture (wherein the raw catalyst accounts for 20% by weight of the catalyst mixture) to raw oil is 10, and the weight ratio of water vapor to raw oil is 0.25 to carry out the cracking reaction , the reaction oil gas and water vapor and the spent catalyst enter the cyclone separator from the reactor outlet.
[0119] Aromatic raffinate oil (saturated hydrocarbon content is 87% by weight) enters the bottom of the riser 2, and at a reaction temperature of 625°C and a reaction time of 1.8 seconds, the weight ratio of the regenerated catalyst to the feedstock oil is 15, and the weight ratio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com