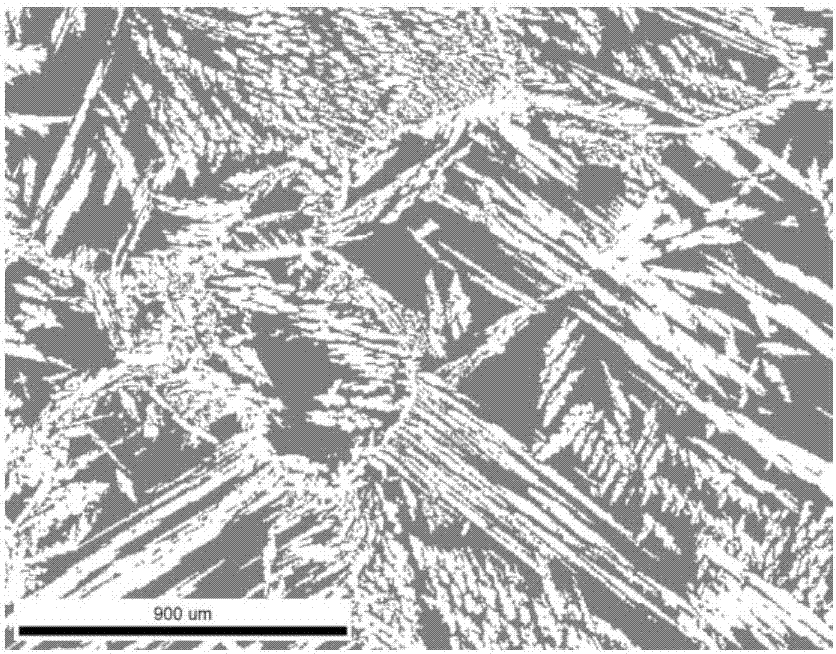
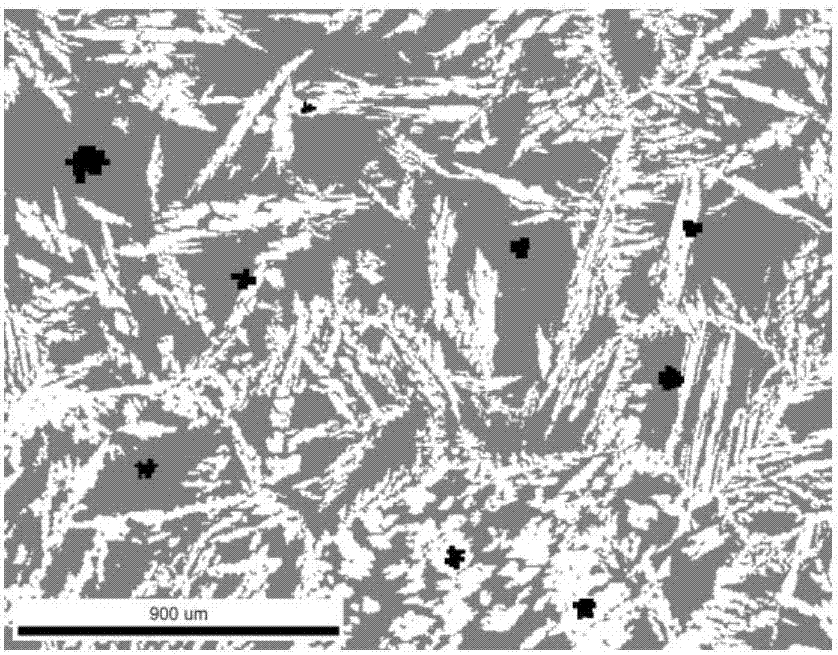
Analysis and detection method of two-phase proportion in as-cast structure of duplex stainless steel
A technology of duplex stainless steel and as-cast structure, which is applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, and material analysis using measurement of secondary emissions, etc. High-level problems are required to achieve the effect of easy identification, high accuracy and clear boundaries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
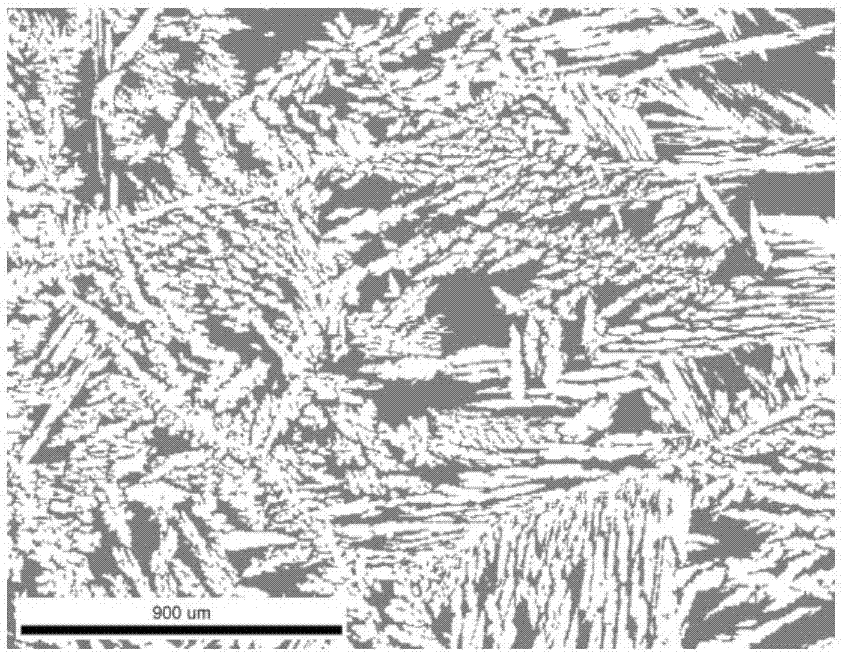
[0027] The method for analyzing and detecting two phase ratios in the as-cast structure of ferrite / austenite duplex stainless steel according to the present invention includes the following steps:
[0028] Step ①: Carry out cutting, rough grinding, fine grinding and mechanical polishing on the duplex stainless steel sample in sequence. The cutting is: the sample can be processed by wire EDM, and the sample size is a thin slice of 10mm×5mm×3mm; the rough grinding is: the observation surface of the sample is sequentially on 60Cw, 150Cw, 400Cw and 600Cw sandpaper Polished with water as a lubricant; the fine grinding is: wet grinding the rough ground sample on 800Cw, 1000Cw, 1200Cw, 1500Cw and 2000Cw sandpaper in sequence; the mechanical polishing is: the finely ground sample is Wet polish the velvet polishing cloth with 2.5μm diamond polishing paste for 3 to 5 minutes, until the mirror effect is achieved, ensuring that there are no obvious scratches by naked eye observation.
[0029]...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The sample cutting, rough grinding, fine grinding and mechanical polishing process are the same as in Example 1, and the scanning electron microscope and EBSD analysis process after electropolishing are the same as in Example 1. The difference is that the sample is electropolished with a voltage of 10V and a current of 1A. It is observed that the surface of the sample is smoother than that in Example 1. At this time, the effect of the residual stress layer is not obvious, and effective EBSD analysis can still be performed without affecting the final result.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The sample cutting, rough grinding, fine grinding and mechanical polishing process are the same as in Example 1, and the scanning electron microscope and EBSD analysis process after electropolishing are the same as in Example 1. The difference is that the sample is electropolished with a voltage of 20V and a current of 2A. It is observed that the surface of the sample is uneven compared to that in Example 1, but a suitable EBSD analysis area can still be found without affecting the final result.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com