Organic material decomposing agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of organic materials and decomposing agents, applied in the field of agricultural production, can solve problems such as weak product functionality, unstable product properties, and insufficient reasonable processing capacity, and achieve product stability and activity, low cost, and low equipment requirements Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Trichoderma harzianum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Bacillus subtilis were carried out in liquid fermentation, and the single-species fermented liquid was mixed evenly according to the weight ratio of 10:20:20:50 to make a composite liquid bacterial classification (the Trichoderma harzianum The number of live bacteria of liquid fermentation strains and Saccharomyces cerevisiae liquid fermentation strains is ≥10 8 cfu / mL, the number of live bacteria of Lactobacillus plantarum liquid fermentation strain and Bacillus subtilis liquid fermentation strain ≥10 9 cfu / mL).
[0033] Mix 60 parts of rice husk powder, 16 parts of bran, 10 parts of corn flour, 1 part of sucrose, and 8 parts of soybean meal in parts by weight to form a solid medium; Mix well in the base; make up water until the weight ratio of water to material is 1:2.
[0034] Put the inoculated material into the woven bag and put it into the fermentation room for fermentation.
[0035] ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Trichoderma harzianum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Bacillus subtilis were carried out in liquid fermentation, and the single-species fermented liquid was mixed evenly according to the weight ratio of 12:20:18:50 to make a composite liquid bacterial classification (the Trichoderma harzianum The number of live bacteria of liquid fermentation strains and Saccharomyces cerevisiae liquid fermentation strains is ≥10 8 cfu / mL, the number of live bacteria of Lactobacillus plantarum liquid fermentation strain and Bacillus subtilis liquid fermentation strain ≥10 9 cfu / mL).
[0040] Mix 65 parts of rice husk powder, 15 parts of bran, 6 parts of corn flour, 2 parts of sucrose, and 7 parts of soybean meal to form a solid medium; dissolve 5 parts of the compound liquid strain in water and add it to the solid medium, mix Uniform; make up water to the weight ratio of water to material 2:3.
[0041] Put the inoculated material into the woven bag and put it i...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Trichoderma harzianum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Bacillus subtilis were carried out in liquid fermentation, and the single-species fermented liquid was mixed evenly according to the weight ratio of 5:25:15:60 to make a composite liquid strain (the Trichoderma harzianum The number of live bacteria of liquid fermentation strains and Saccharomyces cerevisiae liquid fermentation strains is ≥10 8 cfu / mL, the number of live bacteria of Lactobacillus plantarum liquid fermentation strain and Bacillus subtilis liquid fermentation strain ≥10 9 cfu / mL).
[0047] Mix 55 parts of rice husk powder, 20 parts of bran, 5 parts of corn flour, 2 parts of sucrose, and 5 parts of soybean meal in parts by weight to form a solid medium; Mix well in the base; make up water until the weight ratio of water to material is 1:2.
[0048] Put the inoculated material into the woven bag and put it into the fermentation room for fermentation.
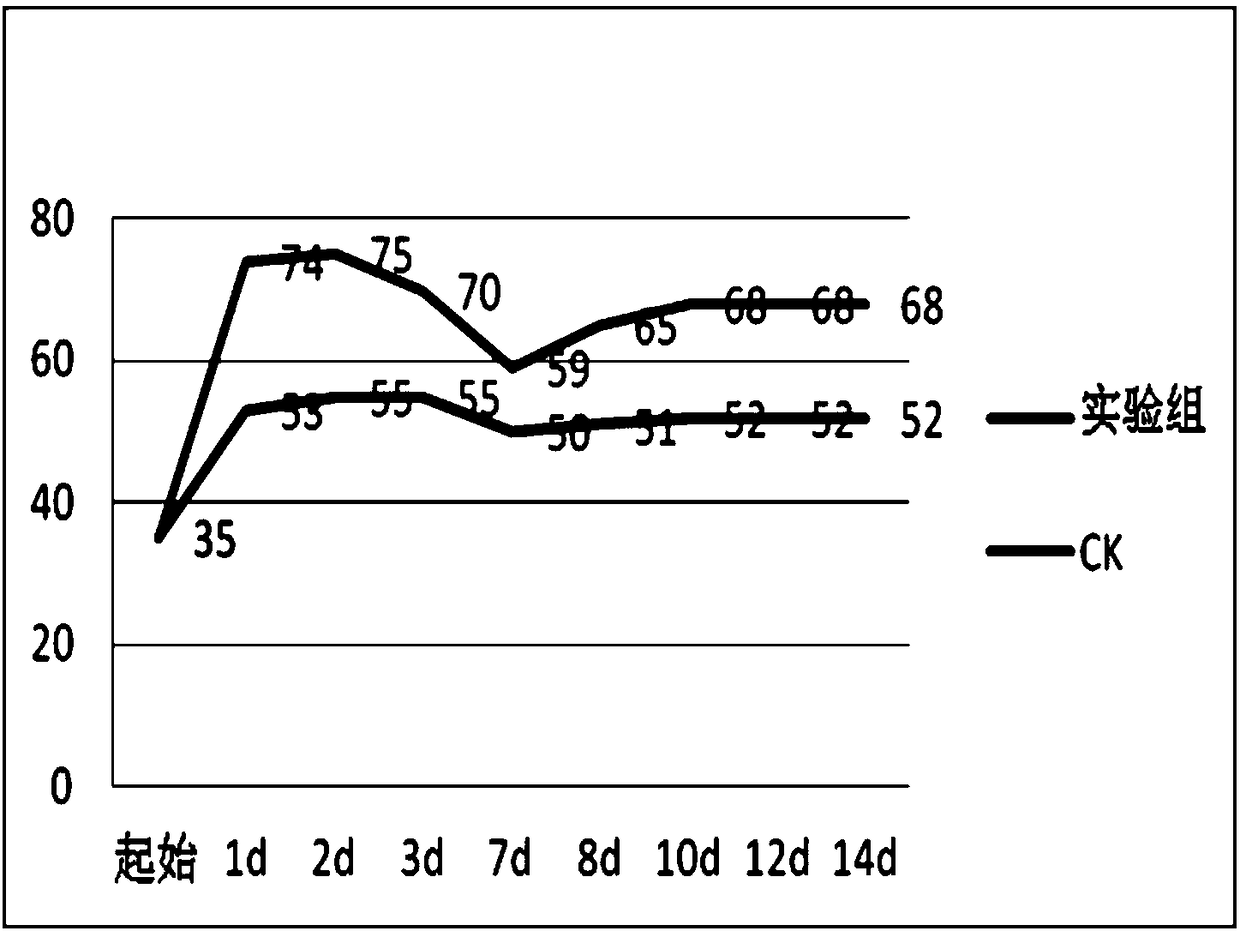
[0049] The initial ferment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com