A vertically grown molybdenum disulfide array electrode material and its preparation method
A molybdenum disulfide, vertical growth technology, applied in the direction of molybdenum sulfide, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems such as complex preparation process of molybdenum disulfide electrode
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
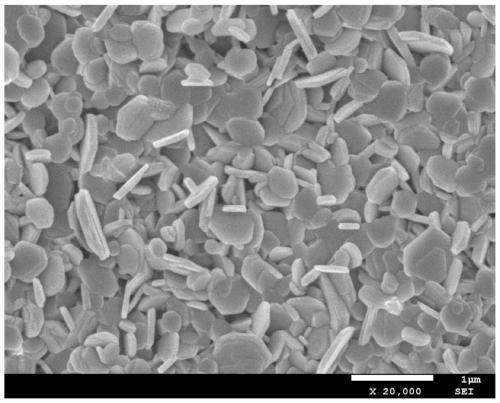
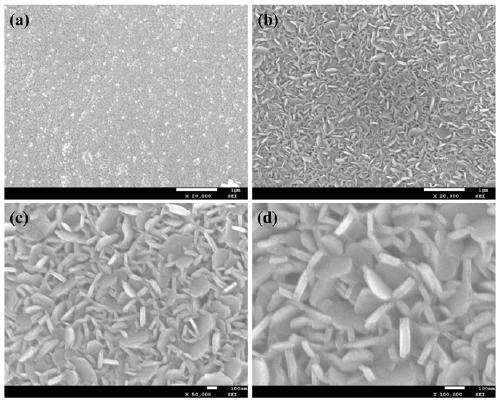
[0026] At room temperature, dissolve 1 mmol of molybdenum chloride in 3 mL of ethanol solution, then add 0.05 mmol of nickel chloride, and stir to dissolve. The precursor liquid was drop-coated on a flat graphite paper substrate surface, and dried on a hot stage at 90 °C for 10 min. Put the coated substrate into a tube furnace, react at 500 °C for 30 min in an Ar+S atmosphere, then react at 800 °C for 30 min, and take it out after natural cooling. figure 1 (b-d) are the SEM images of the sample prepared in Example 1. It can be seen from the figure that a large-area uniform molybdenum disulfide array was prepared in this example, and about 90% of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets grew almost perpendicular to the substrate. figure 1 (a) The molybdenum disulfide film was prepared using the same preparation process conditions as in Example 1, except that the precursor solution did not contain nickel chloride additives. It can be seen from the figure that molybdenum disulfide is ...
Embodiment 2
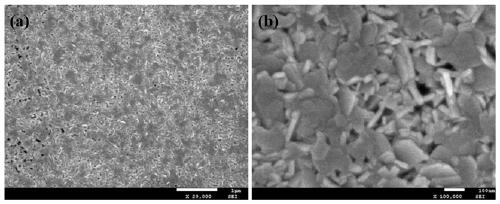
[0028] At room temperature, dissolve 0.9 mmol of molybdenum chloride in 3 mL of ethanol solution, then add 0.1 mmol of nickel chloride, and stir to dissolve. The precursor liquid was drop-coated on a flat graphite paper substrate surface, and dried on a hot stage at 90 °C for 10 min. Put the coated substrate into a tube furnace, react at 500 °C for 30 min in an Ar+S atmosphere, then react at 800 °C for 30 min, and take it out after natural cooling. figure 2 It is the SEM image of the sample prepared in Example 2. It can be seen from the figure that a large-area uniform molybdenum disulfide array is prepared in this example, and about 40% of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets grow perpendicular to the substrate. It should be pointed out that no Ni element was detected in the energy spectrum analysis of the sample in Example 2, indicating that the Ni element was almost evaporated at 800°C for 30 min, and the prepared sample was molybdenum disulfide.
Embodiment 3
[0030] At room temperature, dissolve 0.9 mmol of molybdenum chloride in 3 mL of ethanol solution, then add 0.1 mmol of nickel chloride, and stir to dissolve. The precursor liquid was drop-coated on a flat graphite paper substrate surface, and dried on a hot stage at 90 °C for 10 min. Put the coated substrate into a tube furnace, react at 700 °C for 2 h in an Ar+S atmosphere, and take it out after natural cooling. image 3 This is the SEM image of the sample prepared in Example 3. It can be seen from the figure that a large-area uniform molybdenum disulfide array was prepared in this example, and about 40% of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets grew perpendicular to the substrate. It should be pointed out that the energy spectrum analysis of the sample in Example 2 did not detect the Ni element, indicating that the Ni element was almost evaporated at 700°C for 2 h, and the prepared sample was molybdenum disulfide.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com