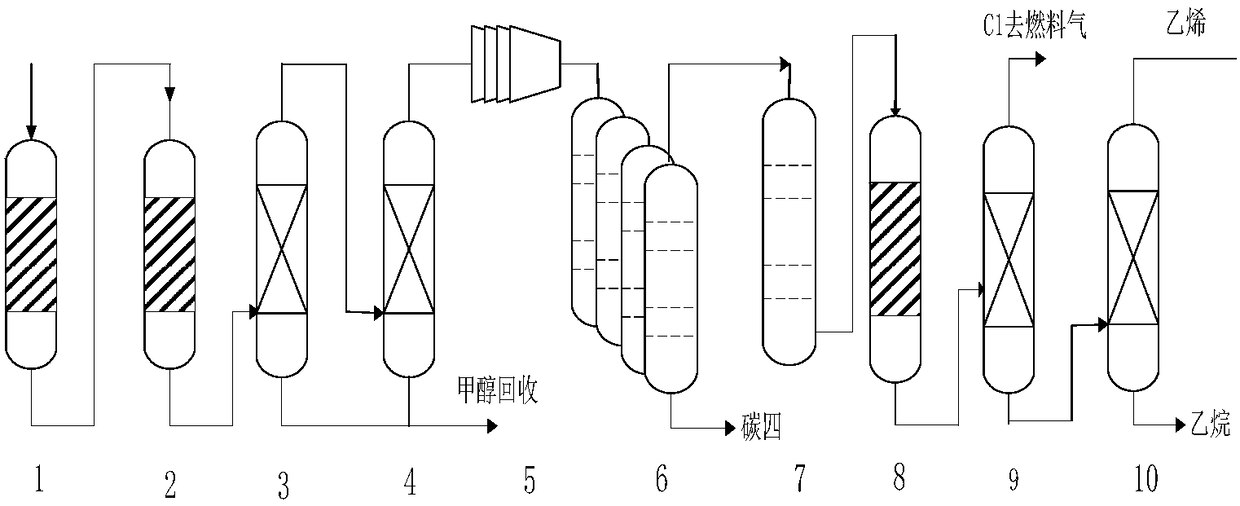
Selective hydrogenation method for methanol to olefin product
A technology for producing olefins from methanol and selective hydrogenation, which is applied to the selective hydrogenation of propyne and propadiene, and the field of iron-based hydrogenation catalysts for trace acetylene. , low conversion rate of acetylene, etc., to achieve the effects of excellent anti-coking performance, moderate reactivity and low ethylene loss rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Weigh a clover-shaped alumina carrier of Φ4.5×4.5mm. Take an appropriate amount of ferric nitrate, dissolve it in 60ml of deionized water by heating, adjust the pH value to 2.5, impregnate the equal volume on the surface of the carrier at the temperature of the impregnating solution at 50°C, flip the carrier quickly and impregnate for 6 minutes, let it rest for 30 minutes until the adsorption equilibrium, and age at 60°C for 30 minutes, then Follow the program in the oven: Dry the catalyst, and then use the temperature programming method to activate the catalyst. The activation procedure: Weigh an appropriate amount of cobalt nitrate, and impregnate according to the above preparation steps.
[0100] Evaluation method:
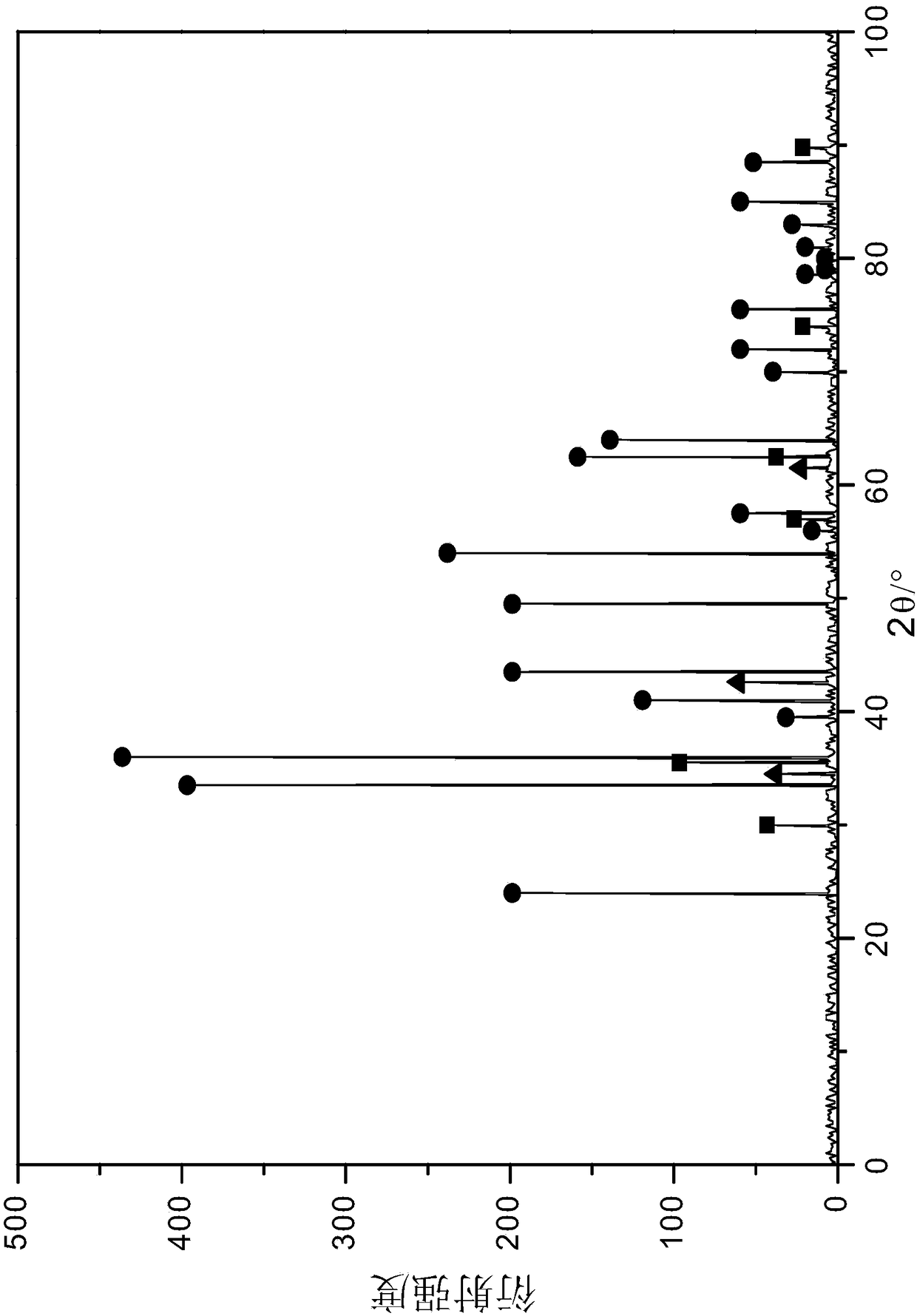
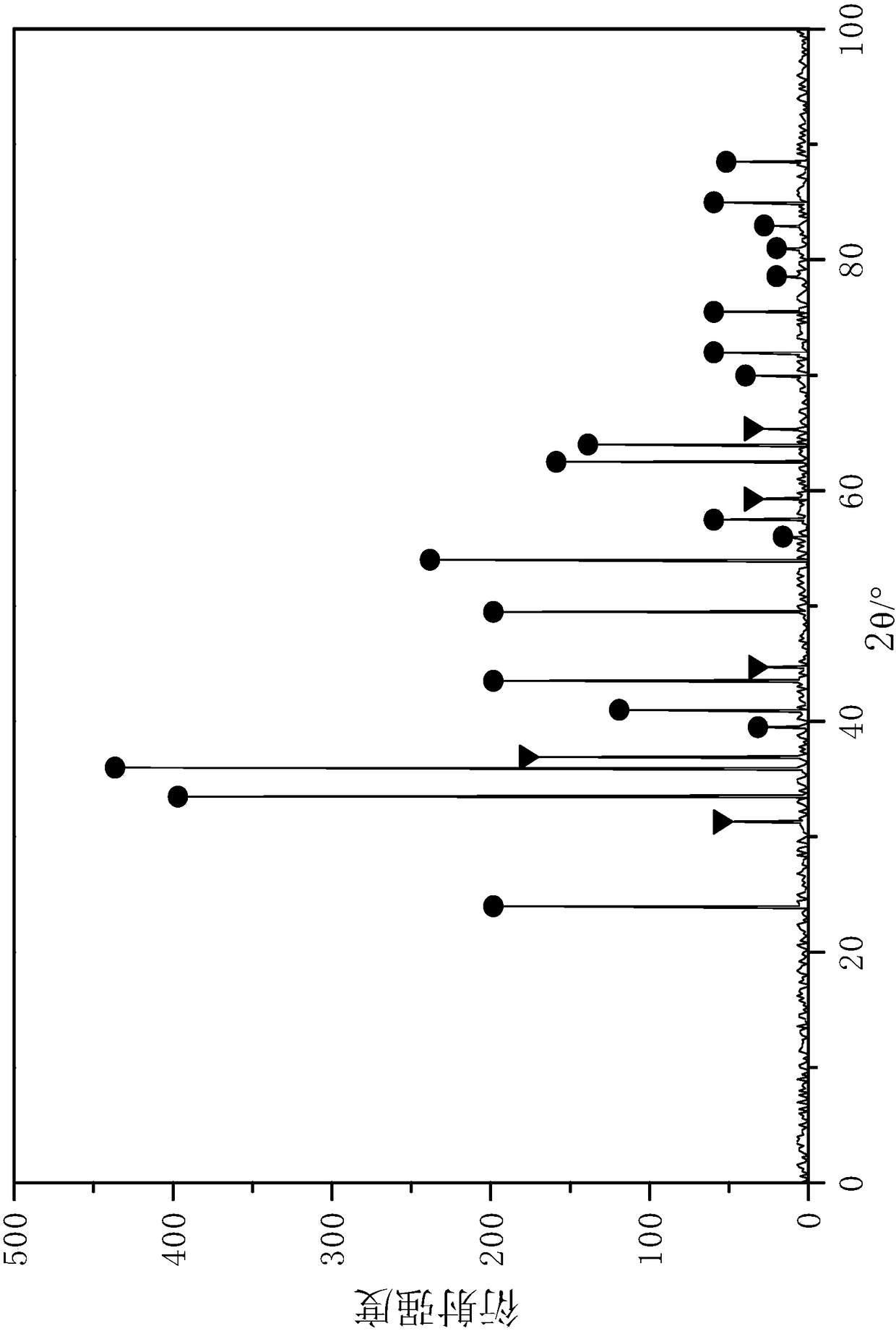
[0101] Before the catalyst is used, it is reduced with 40% hydrogen + 60% nitrogen in the reduction furnace. The reduction temperature is 300°C and the pressure is 0.5MPa. figure 2 shown. Reduction time 4h. Attached figure 1 In the hydrogenati...
Embodiment 2
[0107] At 50°C, a certain amount of NaAlO 2 solution and ZrCl 4 The solution was stirred and mixed, then neutralized with nitric acid solution, stirred for 10 hours, and uniform Al-Zr particles were formed by co-precipitation. The resultant was filtered and the Na in it was washed with deionized water + and Cl - Ions, and then add an appropriate amount of polyvinyl alcohol with a mass concentration of 15% as a pore-forming agent, and knead it into shape. Dry at 130°C for 2h, and calcined at 650°C for 4h to obtain a Zr-Al composite support. The mass ratio of alumina to zirconia in the carrier is 4:1.
[0108] The catalyst was prepared with alumina-zirconia composite carrier. Take an appropriate amount of ferric chloride and cobalt chloride, heat and dissolve in deionized water, adjust the pH value to 2.0, and impregnate the excess on the carrier at a temperature of 80°C, shake the beaker for 10 minutes, and filter off the excess impregnating liquid. Aging in a water bath ...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Weigh 100ml of a Φ1.5mm spherical α-alumina carrier. Dissolve an appropriate amount of ferric nitrate in 40ml of deionized water, adjust the pH value to 3.0, soak the liquid at a temperature of 40°C, spray the watering can onto the carrier, load it in the drum for 10 minutes to load the active components evenly, and control the loading process to 6 minutes to complete, then Follow the program in the oven: Dry the catalyst, move the catalyst into an evaporating dish, and activate the catalyst in a muffle furnace using a temperature-programmed method. The activation procedure: Obtain a catalyst dip.
[0114] Using the same method as the first step, take an appropriate amount of cobalt nitrate, dissolve it, spray it on the surface of the dipped catalyst, dry it, and roast it to obtain the final catalyst. Drying procedure: The physical properties of the carrier and catalyst, and the content of each component of the catalyst are shown in Table 3.
[0115] Before the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pore volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com