Hindered Lewis Acid-Base Pair--flp Catalyzed Living Polymerization of Vinyl Polar Monomers
One--FLP, polar monomer technology, applied in the field of active controllable polymerization system, can solve the problems of low initiation efficiency, limited degree of polymerization, monomer adaptability, etc., achieve mild reaction conditions, narrow molecular weight distribution, monomeric The effect of wide applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
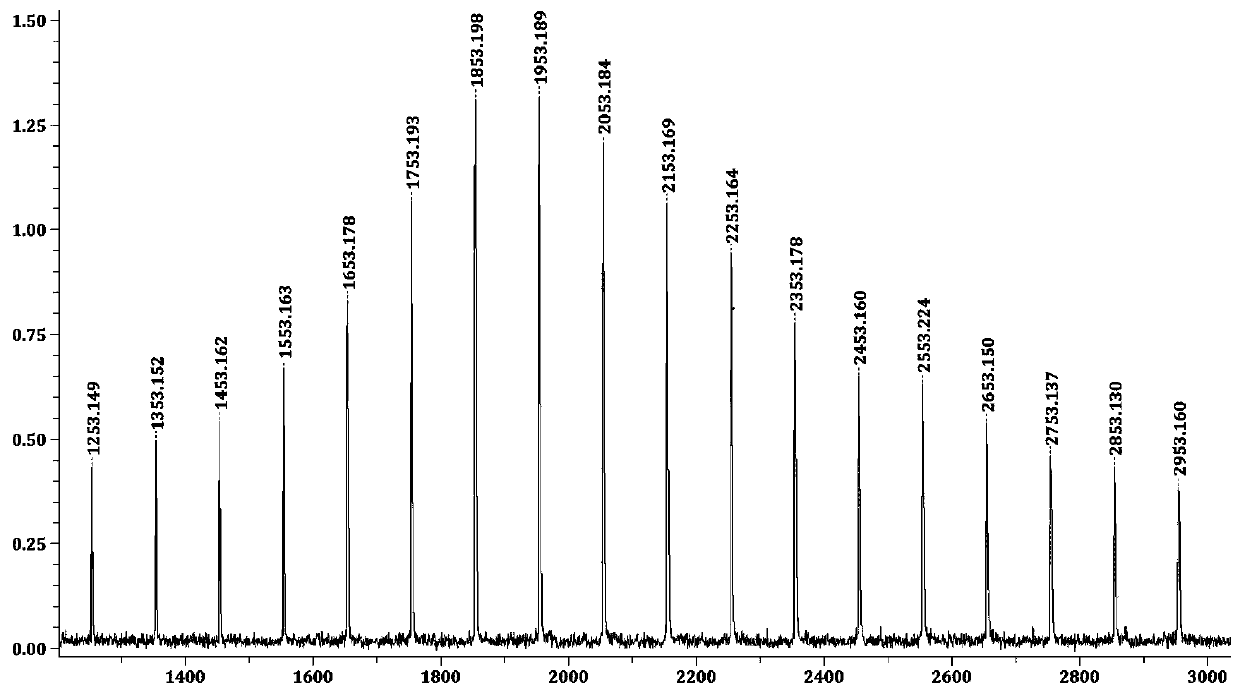
[0044] The conjugate addition polymerization of embodiment 1 methyl methacrylate (MMA)
[0045] There are two feeding methods in the polymerization process: 1. Lewis acid and Lewis base are pre-mixed for 5 minutes, and then monomer is added; 2. Lewis acid and monomer are pre-mixed, and then Lewis base is added. Regardless of the feeding method, the conjugated addition polymerization of the vinyl polar monomer can be well realized.
[0046] The polymerization reaction was carried out in a glove box, and methyl methacrylate (0.5mL, 4.68mmol) was measured, and an appropriate amount (making the total solution volume 5mL) toluene was added to a 20 ml reaction bottle, Lewis base and Lewis acid were added respectively, and Start timing, stir for a period of time until the monomer is completely converted, take the reaction bottle out of the glove box, and add 5% HCl / methanol solution to terminate the polymerization reaction. The polymer was filtered off, washed thoroughly with methan...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Conjugate addition polymerization of allyl methacrylate (AMA) and N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMAA)
[0055] The polymerization reaction was carried out in a glove box, and an appropriate amount of toluene was weighed (to keep the total volume of the solution at 5 mL) in a 20 mL reaction bottle, and Lewis base and Lewis acid were added (in molar ratio, Lewis acid: Lewis base=2:1), Stir for 10 minutes, then add allyl methacrylate (633 μL, 4.68 mmol) or N,N-dimethylacrylamide (482 μL, 4.68 mmol), and start timing, stir for a period of time until the monomer is completely converted, and then add The reaction bottle was taken out from the glove box, and 5% HCl / methanol solution was added to terminate the polymerization reaction. The polymer was filtered off, washed thoroughly with methanol, and dried under vacuum at 50°C to constant weight. The resulting polymer was 1 H identification (see attached Figure 8 ), indicating that the reaction selectively occurs at the...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The chain extension of embodiment 3MMA
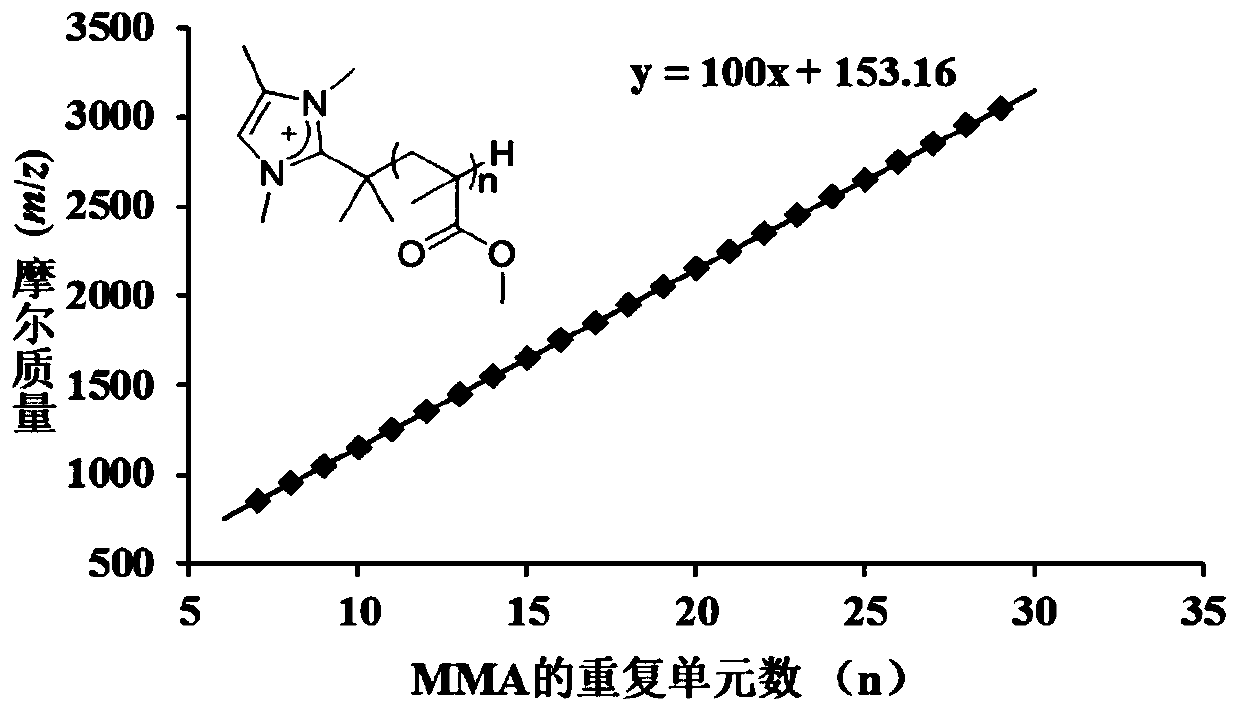
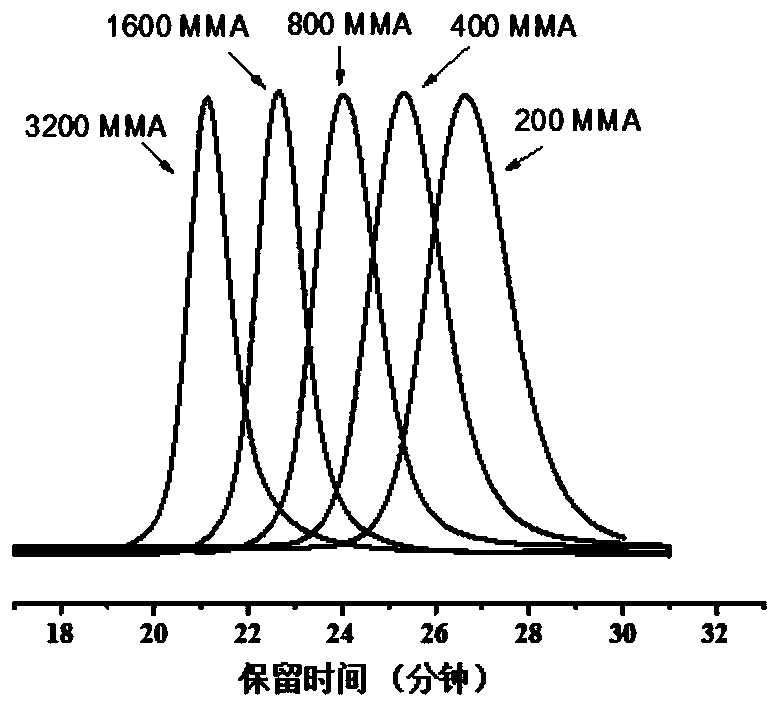
[0060] The polymerization reaction was carried out in the glove box, and MeAl(BHT) was weighed 2 (22.5mg, 4.68×10 -2 mmol) in a 20 ml reaction flask, add MMA (0.5mL, 4.68mmol), add an appropriate amount of toluene (the total volume of the solution is 5mL), after the monomer and Lewis acid fully react, add the NHO1 (3.6 mg, 2.34×10 -2 mmol), and start timing, after stirring for a period of time, after the complete conversion of the monomers, add the same amount of MMA (0.5mL, 4.68mmol) as the first addition, and repeat this several times. After all the monomers are completely converted, add The reaction bottle was taken out from the glove box, and 5% HCl / methanol solution was added to terminate the polymerization reaction. The polymer was filtered off, washed thoroughly with methanol, and dried under vacuum at 50°C to constant weight. The molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the resulting polymers were determi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com