Particulate carbon material that can be produced from renewable raw materials and method for the production of said carbon material
A granular, carbon material technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biofuels, carbon preparation/purification, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
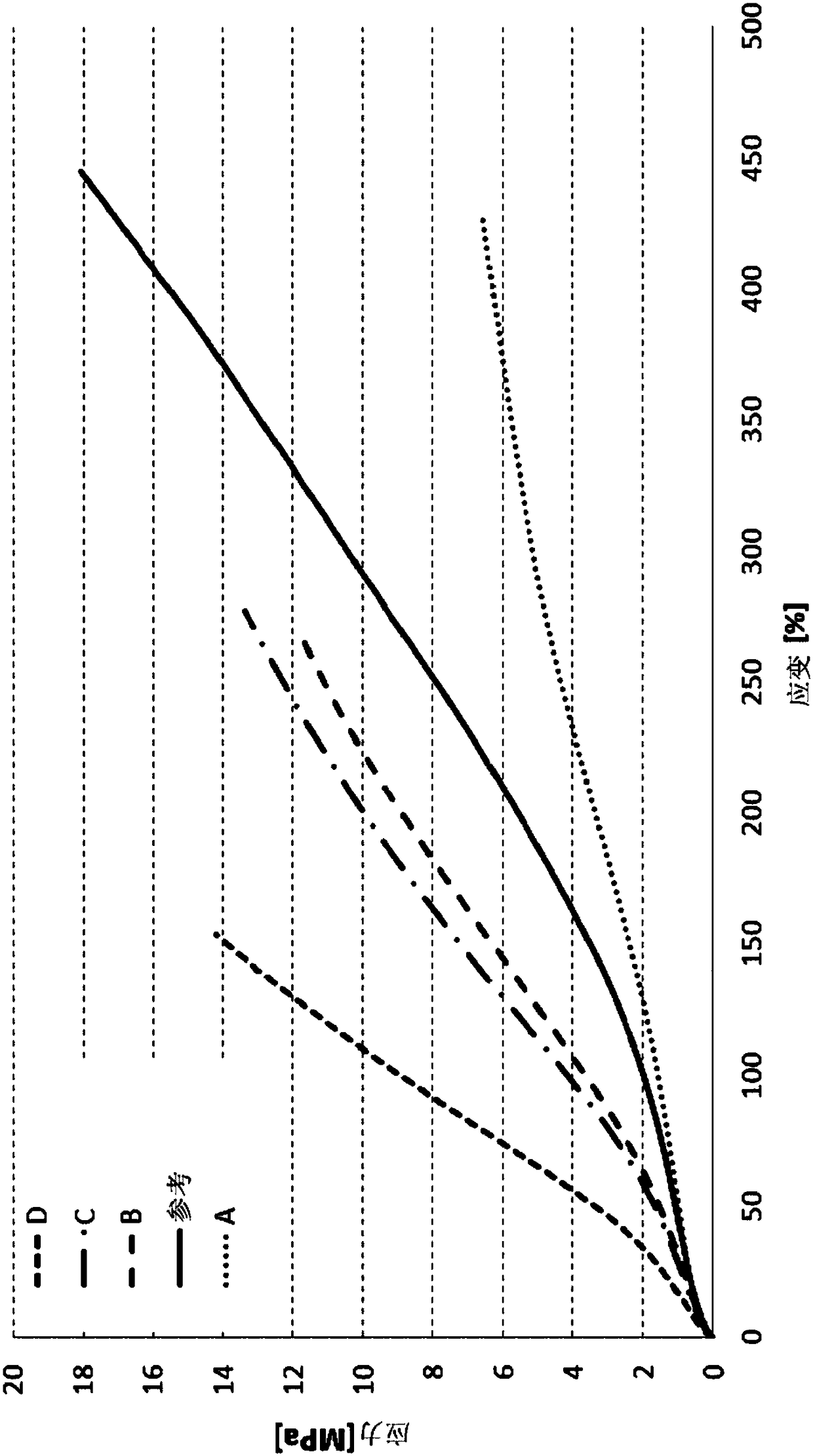
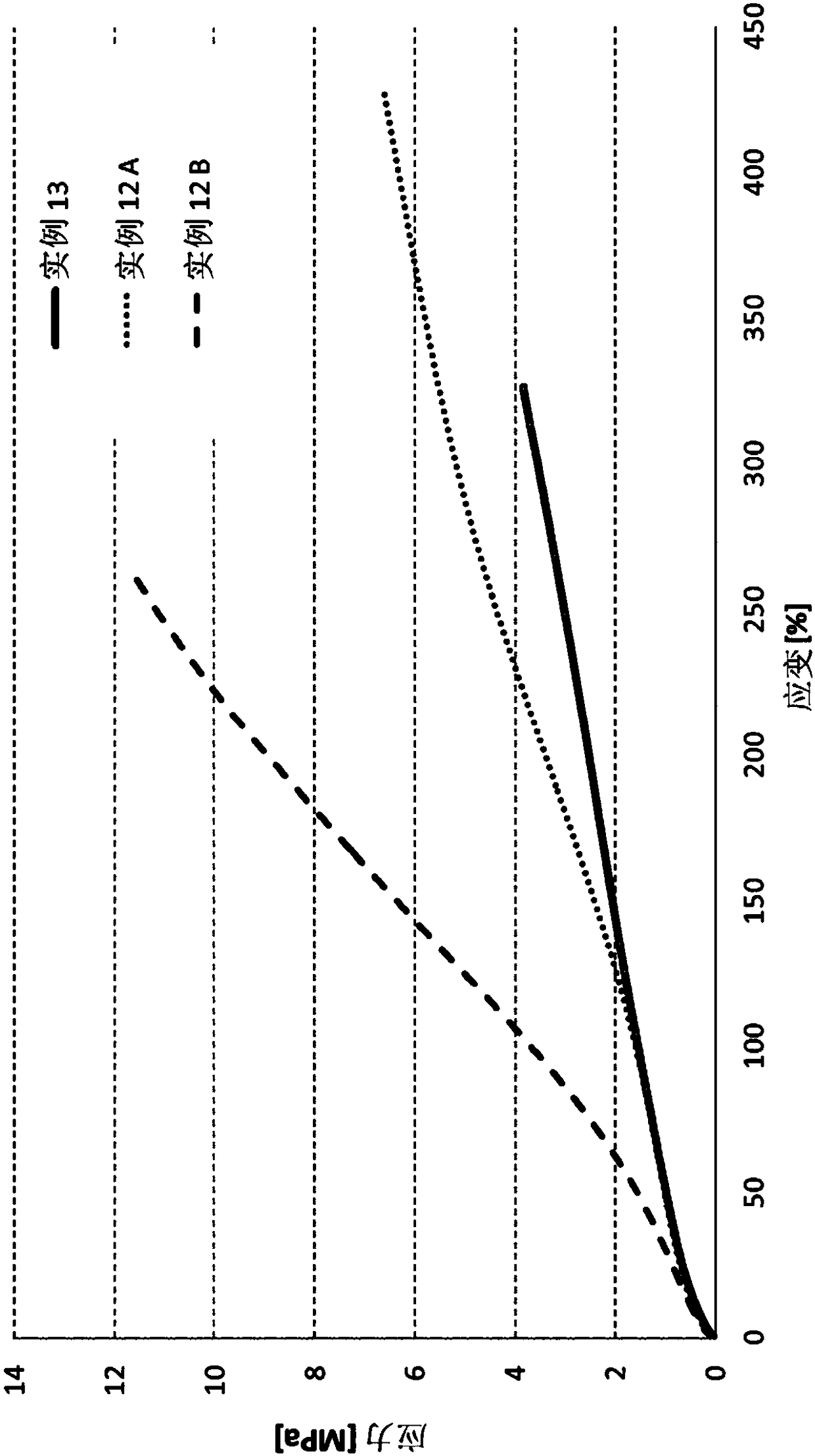
Examples
example 12A to example 12D
[0294] For the preparation of rubbers composed of SBR and granular carbon materials from Examples 1 and 2 or with carbon black N660 Examples 12A to 12D of articles and reference examples
[0295] The carbon material obtained according to Example 1 and Example 2 was introduced as filler material into the rubber mixture and vulcanized with the aid of further additives. The components of the rubber mixture are shown in Table 7.
[0296]
[0297] phr: parts per hundred parts of rubber, the amount based on the amount of elastomer
[0298] DPG, CBS: vulcanization accelerator
[0299] Si69: coupling agent
[0300] Table 7
[0301] Lanxess' SBR solution (sSBR) Buna VSL 4526-0 was used as SBR. The SBR is a copolymer composed of 26% by mass of styrene in addition to butadiene. Its Mooney viscosity is 65ME (ASTM D 1646). Zinc oxide, stearic acid and sulfur were from Fischer Scientific. 2-N-Cyclohexylbenzothiazole sulfenamide (CBS) was from Lanxess. 1,3-Diphenylguanidine (D...
example 2
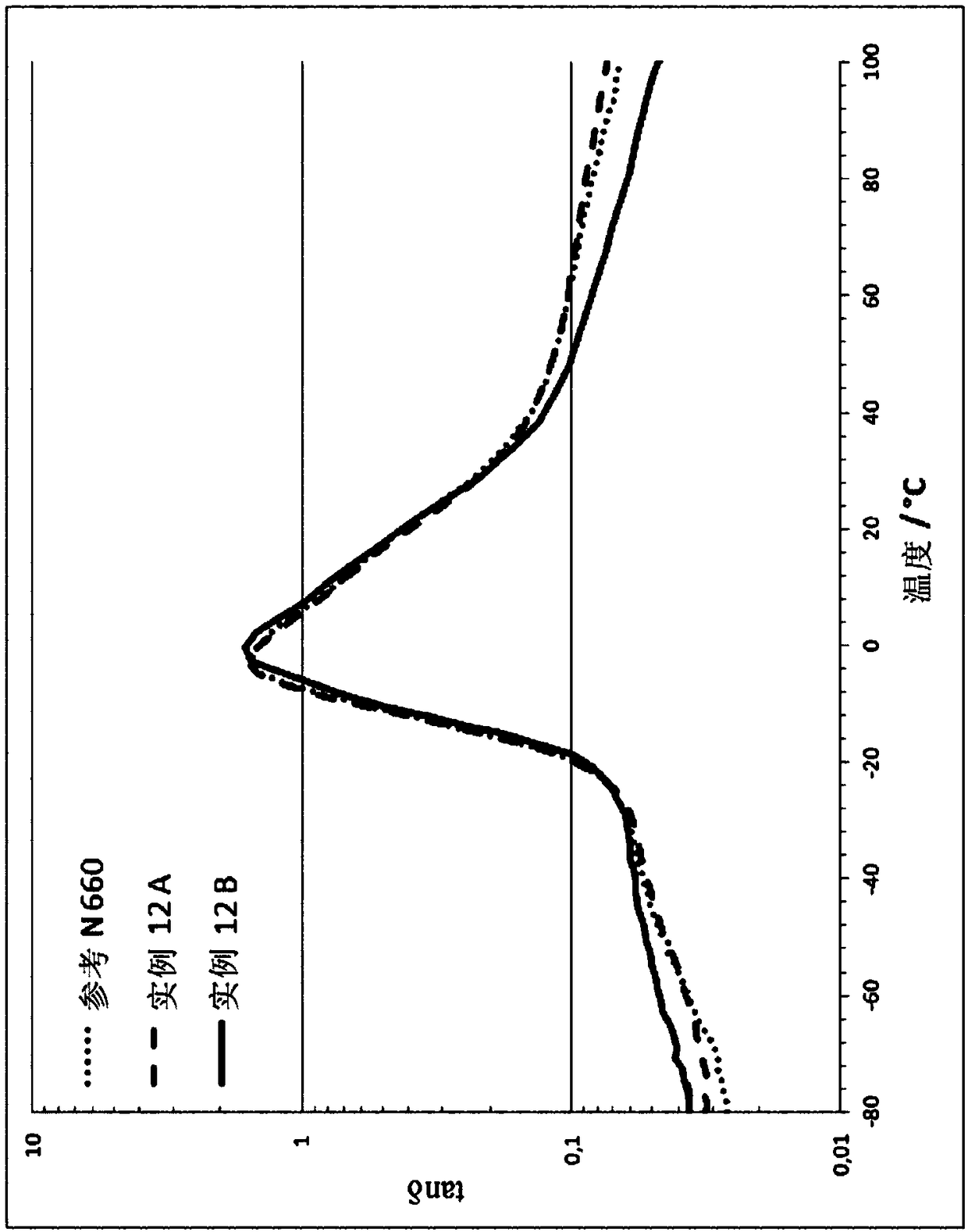
[0309] Application of the particulate carbon material in Example 2 in combination with a coupling agent (Example 12B) caused a noticeable change. Compared to the reference and 12A, the glass transition temperature of the mixture in Example 12 was shifted up to T g,SBR = -0.48°C. Under conditions of weak dynamic strain (0.5%), the energy loss behavior of mixture 12B is clearly improved relative to the reference with N660, which is seen at lower curve changes in the temperature range above the glass transition temperature.
[0310] It can be seen that the elastomeric material comprising the granular carbon material and coupling agent in Example 2 has a smaller value for tan δ above the glass transition temperature relative to the reference with N660, which is shown by the Relatively reduced sliding friction can be expected in the resulting tire.
[0311]
tanδ at 60°C
tanδ at 0°C
Reference with N660
0.1020
1.4342
Example 12A
0.1035
1....
example 14
[0320] to confirm 14 C content, the material in Example 2 was provided to A.Mickiewicz University Foundation, Poznań Ridiocarbon Laboratory, ul. 46, 61-612 Poznań. The method used is described by the head of the laboratory, Tomasz Goslar, on the institute's website. The main components of lignin are summarized below.
[0321] Used to use AMS technology to 14 The processing method of C identification age has the following steps:
[0322] a) Chemical pretreatment
[0323] b) Production of CO 2 and graphitized
[0324] c) AMS 14 C measurement
[0325] d) Calculate and calibrate 14 C's age
[0326] a) In principle, chemically pretreated methods are described in Brock et al., 2010, Radiocarbon, 52, 102-112.
[0327] Samples of plant residues were treated with 1M HCl (80°C, 20+min), 0.025M to 0.2M NaOH (80°C), and then, 0.25M HCl (80°C, 1h). After treatment with the corresponding reagents, the samples were rinsed with distilled water (Millipore) until pH=7. If bubble f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mooney viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com