Alloy and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for alloys and alloy ingots, which is applied in the field of powder metallurgy and can solve the problems of reducing the density and closed pores of high-temperature alloy parts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In this example, the mass percent of each component of the superalloy is: 20% nickel, 15.5% iron, 16% chromium, 11.5% molybdenum, 5.0% niobium, 3.2% tungsten, 0.45% carbon, and the rest is cobalt.
[0029] Put the raw materials of the above components into a vacuum induction melting furnace, melt the alloy ingot of this component, and then cast it into the first bar with a specification of Φ80×600, cut off the shrinkage cavity of the first bar, and turn the first bar Processed into the second bar with a specification of Φ75×400.
[0030] Using the second bar as raw material, superalloy powder was prepared by plasma rotating electrode atomization method. Specifically, in the plasma rotating electrode atomization method, the rotational speed of the second rod is 14500 r / min, and the melting current is 1800A.
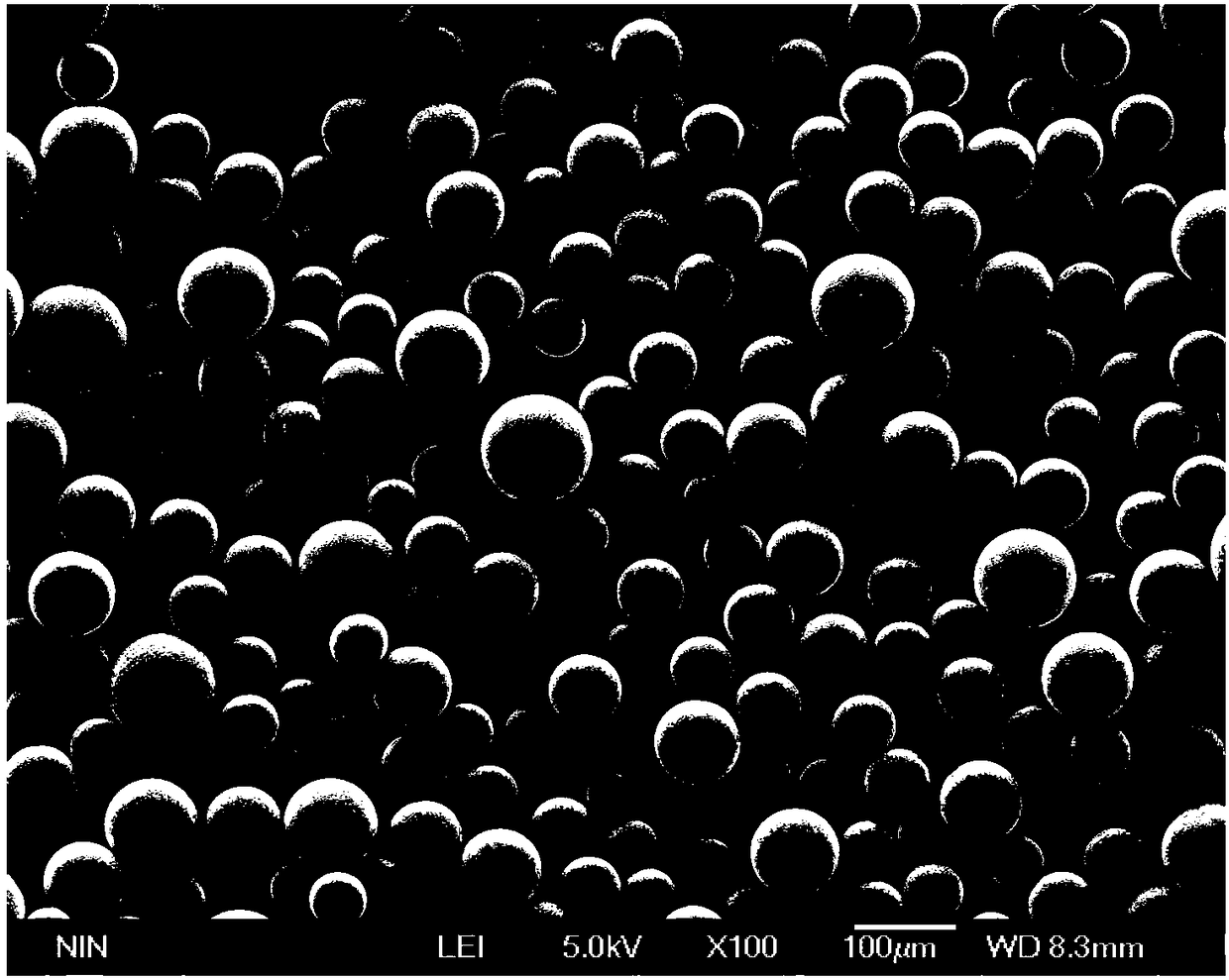
[0031] It should be noted that the alloy powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0032] Further, the...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this example, the mass percent of each component of the superalloy is: 21.5% nickel, 16.5% iron, 17% chromium, 12% molybdenum, 5.8% niobium, 4% tungsten, 0.50 carbon, and the rest is cobalt.
[0037] Put the raw materials of the above components into a vacuum induction melting furnace, melt the alloy ingot of this component, and then cast it into the first bar with a specification of Φ80×600, cut off the shrinkage cavity of the first bar, and turn it into a specification of Φ75× 400 for the second bar stock.
[0038] Using the second bar as raw material, superalloy powder was prepared by plasma rotating electrode atomization method. Specifically, in the plasma rotating electrode atomization method, the rotational speed of the second rod is 14500r / min, and the melting current is 1800A. The prepared alloy powder is sieved to obtain -150 mesh powder, the powder is loaded into a graphite mold, and vacuum hot-pressed sintering is carried out to obtain a high-density powd...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In this example, the mass percent of each component of the superalloy is: 22% nickel, 17.5% iron, 18.5% chromium, 13% molybdenum, 6.5% niobium, 4.5% tungsten, 0.60 carbon, and the rest is cobalt.
[0043] Put the raw materials of the above components into a vacuum induction melting furnace, melt the alloy ingot of this component, and then cast it into the first bar with a specification of Φ80×600, cut off the shrinkage cavity of the first bar, and turn the first bar Processed into the second bar with a specification of Φ75×400.
[0044] Using the second bar as raw material, superalloy powder was prepared by plasma rotating electrode atomization method. Specifically, in the plasma rotating electrode atomization method, the rotational speed of the electrode rod is 14500 r / min, and the melting current is 1800A. The prepared alloy powder is sieved to obtain -150 mesh powder, the powder is loaded into a graphite mold, and vacuum hot-pressed sintering is carried out to obtai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com