Gene fine mapping method adopting map-based cloning principle and based on plant genome sequencing and inter-subspecies hybrid segregation populations
A plant genome and whole genome sequencing technology, applied in the fields of genomics, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of inability to carry out genetic work, time-consuming verification, and expansion of human and material costs, etc. To achieve the effect of saving manpower, accurate and reliable statistical analysis results, and accurate and reliable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1. Obtaining phenotypic mutant strains by mutagenesis and preparing offspring populations of mutant strains and wild strains
[0040] 1. Obtaining phenotypic mutant strains by mutagenesis
[0041] 1. Using rice kittake seeds as raw materials, carry out EMS mutagenesis (take the seeds, first soak them in clear water for 16 hours, and then soak them in 0.5% EMS solution for 8 hours).
[0042] 2, the seed that step 1 obtains is sowed and cultivated into a plant, and the plant harvests the seed after selfing (M 1 substitute seeds).
[0043] 3, the seeds that step 2 is obtained are sown and cultivated as plants, harvest seeds after plant selfing (M 2 substitute seeds).
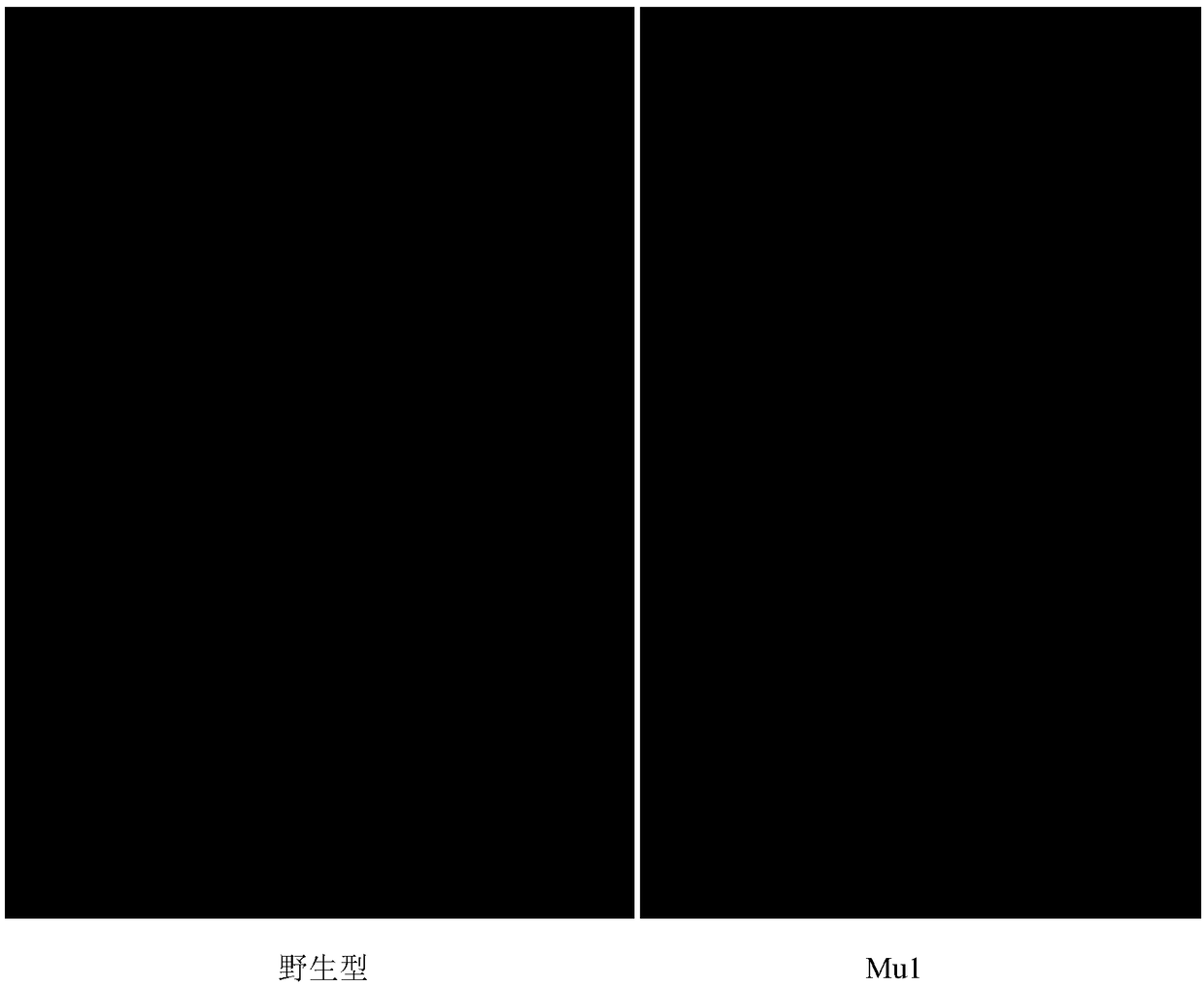
[0044] 4. The seeds obtained in step 3 were sown and grown into plants, and a mutant with a single tiller phenotype was screened out, and named mutant Mu1.
[0045] Two months after transplanting, the phenotype photos of rice kittake and mutant Mu1 are shown in figure 1 .
[0046] 2. Preparatio...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2, map position cloning gene location
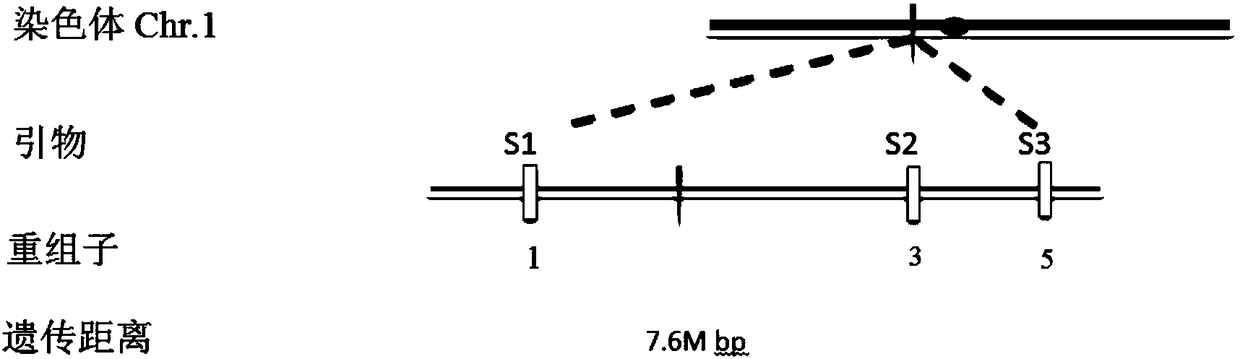
[0054] 1. The F obtained from Example 1 2 In the generation segregation population, the leaves of 50 plants with single tiller phenotype were randomly selected, and the leaves were mixed with equal mass to extract genomic DNA to obtain a single tiller DNA pool.
[0055] 2. Preliminary positioning
[0056] The single tiller DNA pool constructed in step 1 was amplified by PCR using 180 pairs of SSR markers, and a molecular marker S2 closely linked to the single tiller phenotype was screened.
[0057] S2-F (5'-3'): TATAAGGAAAAGAACGCTGC;
[0058] S2-R (5'-3'): TGAAATCATGCACCATTAAC.
[0059] 3. Fine positioning
[0060] Develop new molecular marker S1 (located at the position of chromosome 1 13M, detection primer is composed of primer S1-F and primer S1-R) and molecular marker S3 (detection primer is composed of primer S3-F and primer S3-R composition).
[0061] S1-F (5'-3'): GACCTAGTGGTCTTCAATCT;
[0062] S1-R (5'-3'...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3, Large-scale Genome Sequencing Gene Mapping
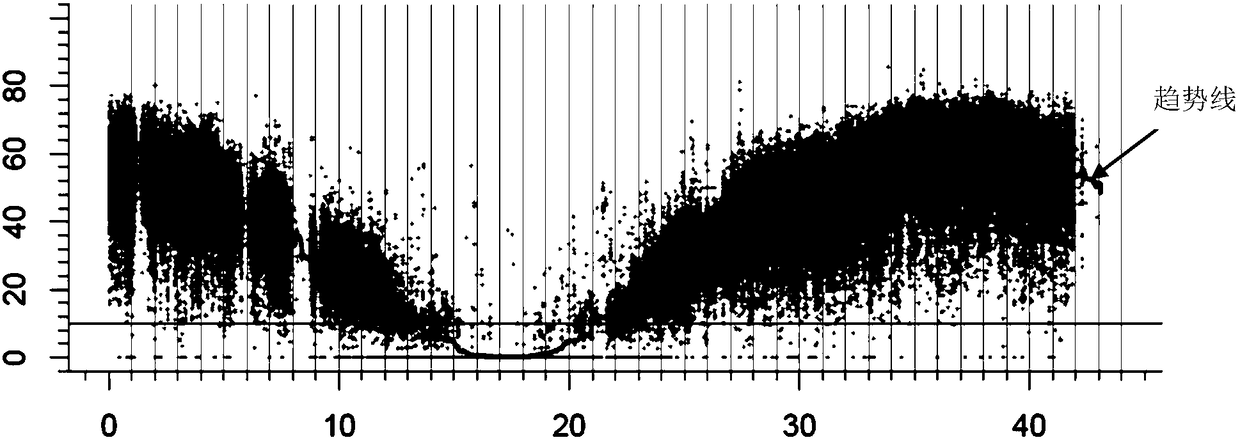
[0067] 1. The F obtained from Example 1 2 In the generation segregation population, the leaves of 50 plants with the phenotype of single tiller number were randomly selected, and the leaves were mixed with equal mass to extract DNA to obtain a single tiller DNA pool.
[0068] 2. Perform whole-genome sequencing on the mutant Mu1, the indica rice maintainer line Q1B, and the single tiller DNA pool obtained in step 1 (reads with a sequencing depth greater than 10 times should cover more than 90% of the genome is the best), and obtain the full-length DNA of the mutant Mu1 respectively. Genome sequencing results, whole-genome sequencing results of the indica maintainer line Q1B, and whole-genome sequencing results of the single tiller DNA pool.
[0069] 3. Compare each whole-genome sequencing data obtained in step 2 with the rice Nipponbare reference genome (specifically, BWA, GATK, samtools and other software can be u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com