Method for obtaining hollow zirconia fiber by microwave sintering of Metaplexis japonica (Thunb.) Makino. fiber
A zirconia fiber, microwave sintering technology, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibers, textiles and papermaking, inorganic raw material rayon, etc., can solve the problems of low sintering efficiency, difficult to prepare hollow fibers, etc., to improve the thermal insulation performance and speed up the reaction process. , good continuity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
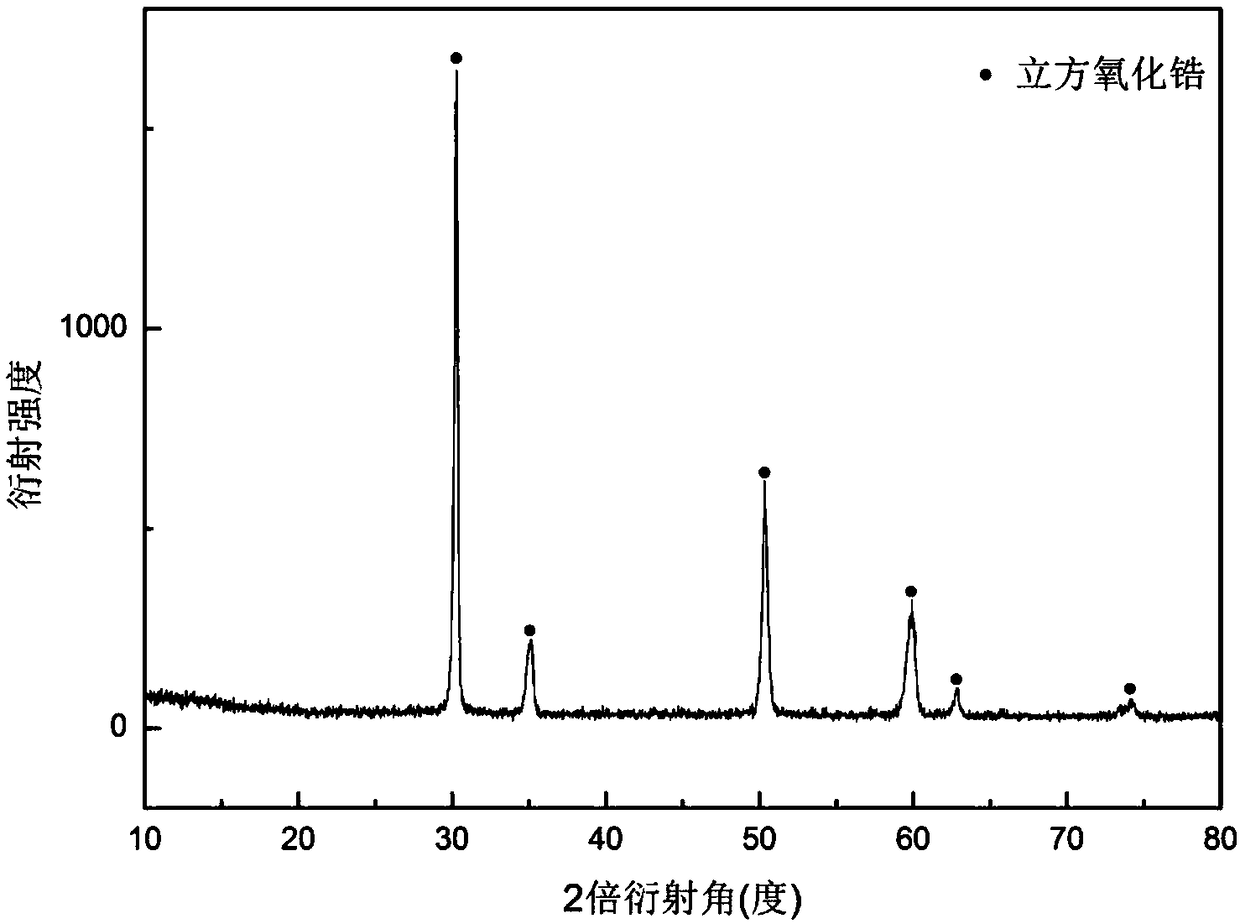
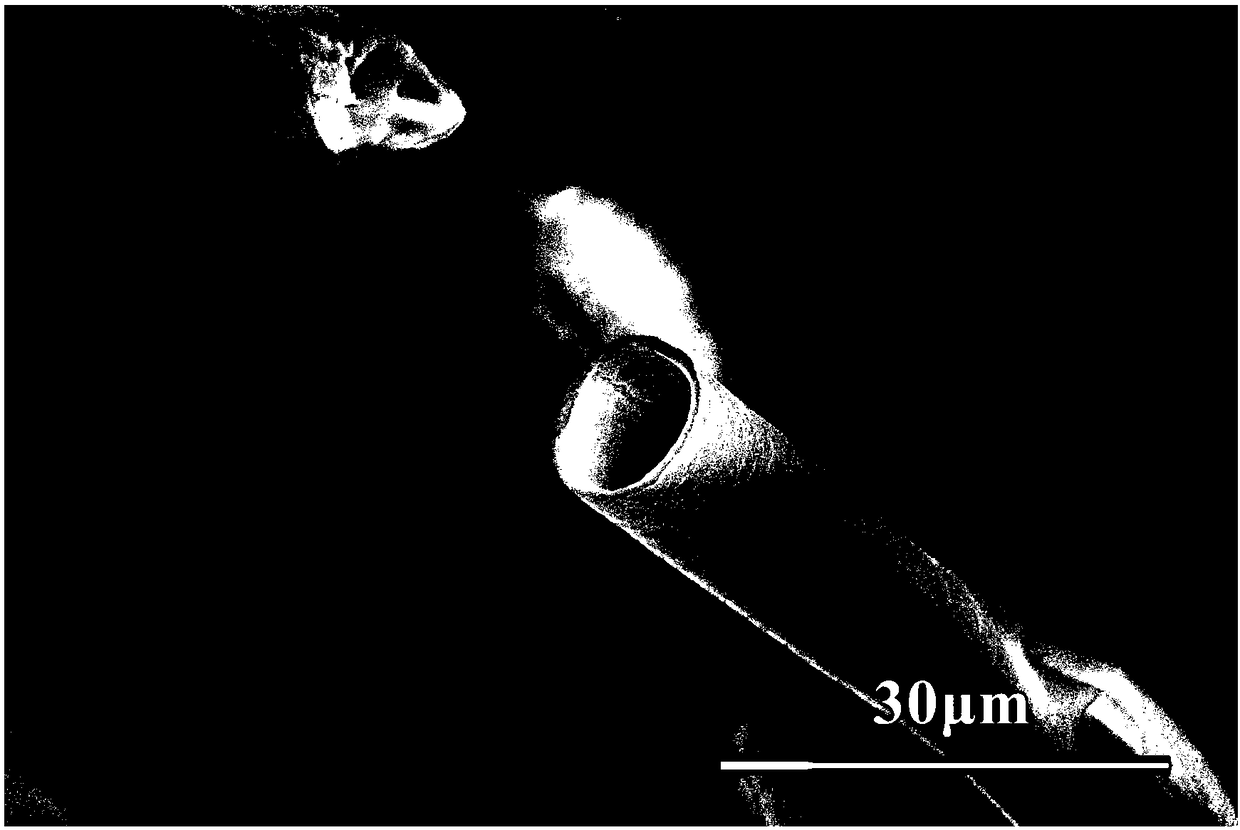
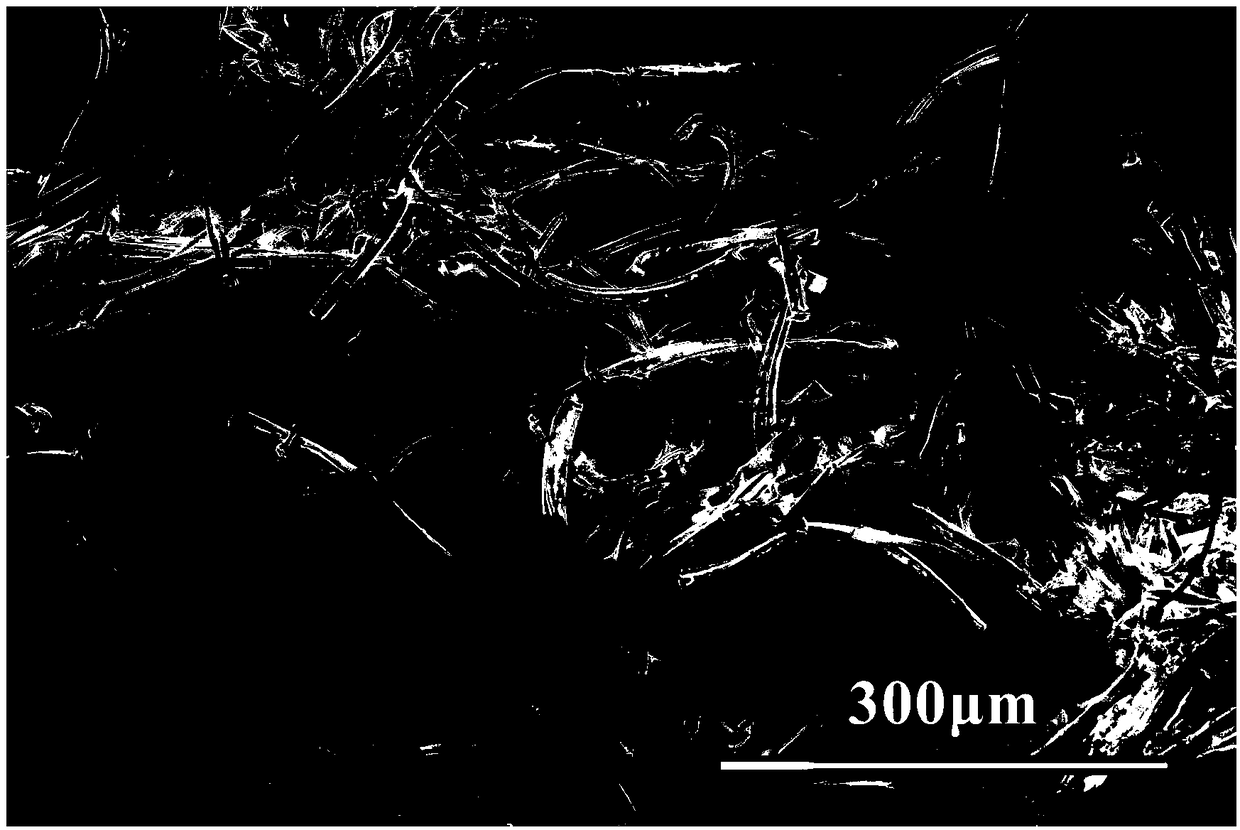
[0034] Get 4.41g of zirconium oxychloride octahydrate and dissolve it in 20ml of 50% ethanol aqueous solution by volume fraction, add 0.42g of yttrium nitrate hexahydrate stabilizer and 1g of zinc bromide microwave sintering aid, and prepare a 10% oxygen Zirconium chloride precursor solution. Immerse the radish fiber in the above solution for 10 minutes, then take it out and dry it; place the dried precursor fiber in a microwave oven with a microwave frequency of 2.45 GHz, and heat it with a power of 700 W for 10 minutes to prepare a hollow zirconia fiber. From figure 1 The X-ray diffraction pattern in the material shows that the cubic phase of the material is zirconia. figure 2 Shown is a high-magnification photo of the prepared zirconia fiber scanning electron microscope, it can be seen that the fiber is hollow, and there are tubular micropores inside the fiber, and its porosity is greatly improved compared with the solid fiber. image 3 Shown is a low-magnification photo...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Dissolve 1.99g of zirconium oxychloride octahydrate into 20ml of 50% ethanol aqueous solution by volume fraction, add 0.22g of calcium chloride dihydrate stabilizer and 0.5g of zinc bromide microwave sintering aid, and prepare a mass fraction of 5% zirconium oxychloride precursor solution. Immerse the radish fiber in the above solution for 10 minutes, then take it out and dry it; put the dried precursor fiber in a microwave oven with a microwave frequency of 2.45 GHz, and heat it with a power of 700 W for 5 minutes to prepare a hollow zirconia fiber. Figure 4 Shown is a high-magnification photo of the prepared zirconia fiber scanning electron microscope, it can be seen that the fiber is hollow, and there are tubular micropores inside the fiber, and its porosity is greatly improved compared with the solid fiber. Figure 5 Shown is a low-magnification photo of the zirconia fiber scanning electron microscope. It can be seen that the fibers are interlaced and have good con...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Get 7.44g of zirconium oxychloride octahydrate and dissolve it in 20ml of 50% ethanol aqueous solution by volume fraction, add 1.5g of cerium nitrate hexahydrate stabilizer and 1.5g of zinc bromide microwave sintering aid, and prepare 15% of Zirconium oxychloride precursor solution. Immerse the radish fiber in the above solution for 10 minutes, then take it out and dry it; place the dried precursor fiber in a microwave oven with a microwave frequency of 2.45 GHz, and heat it with a power of 700 W for 20 minutes to prepare a hollow zirconia fiber. Figure 6 Shown is a high-magnification photo of the prepared zirconia fiber scanning electron microscope, it can be seen that the fiber is hollow, and there are tubular micropores inside the fiber, and its porosity is greatly improved compared with the solid fiber. Figure 7 Shown is a low-magnification photo of the zirconia fiber scanning electron microscope. It can be seen that the fibers are interlaced and have good continu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com