Preparation method and application of high temperature-resistant and salt-resistant kitchen waste decomposing compound bacteria agent
A compound bacterial agent and high-temperature-resistant technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of narrow application range, unsatisfactory treatment effect, inability to survive and reproduce, etc., and achieve the effect of wide selection range, remarkable decomposing effect and strong application ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
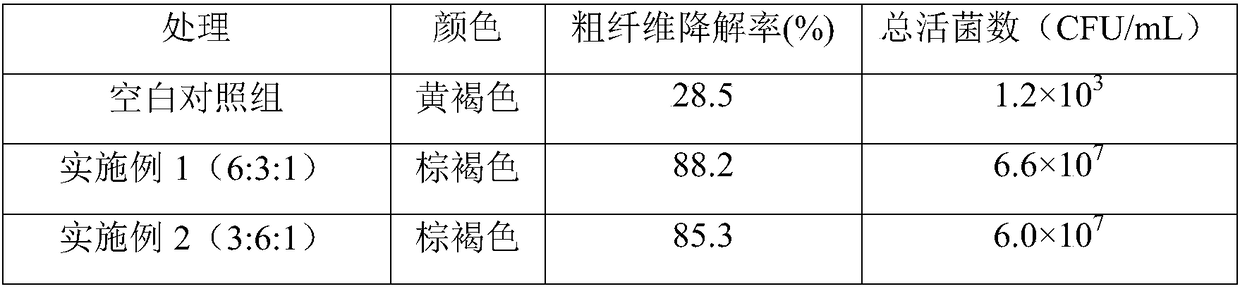
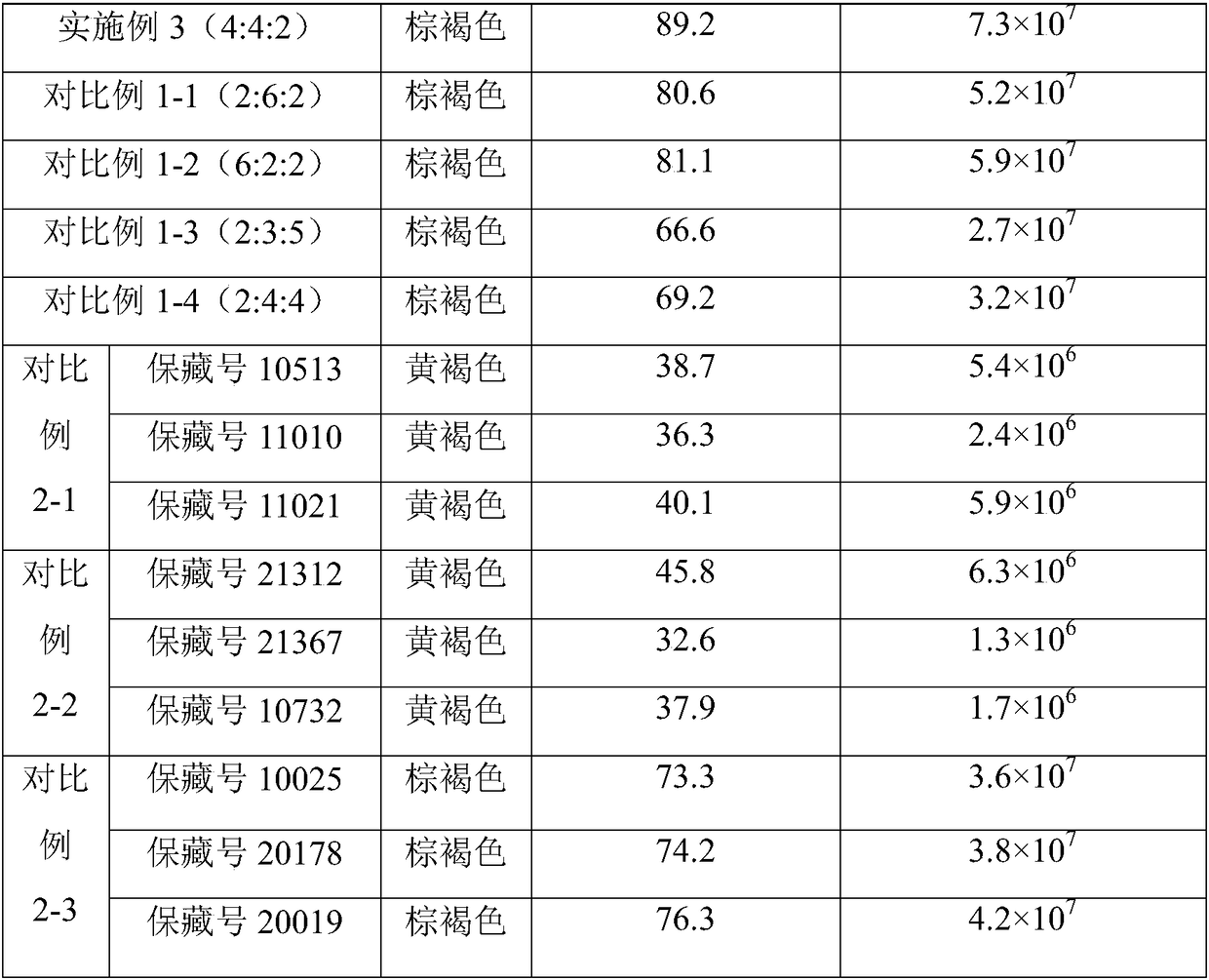
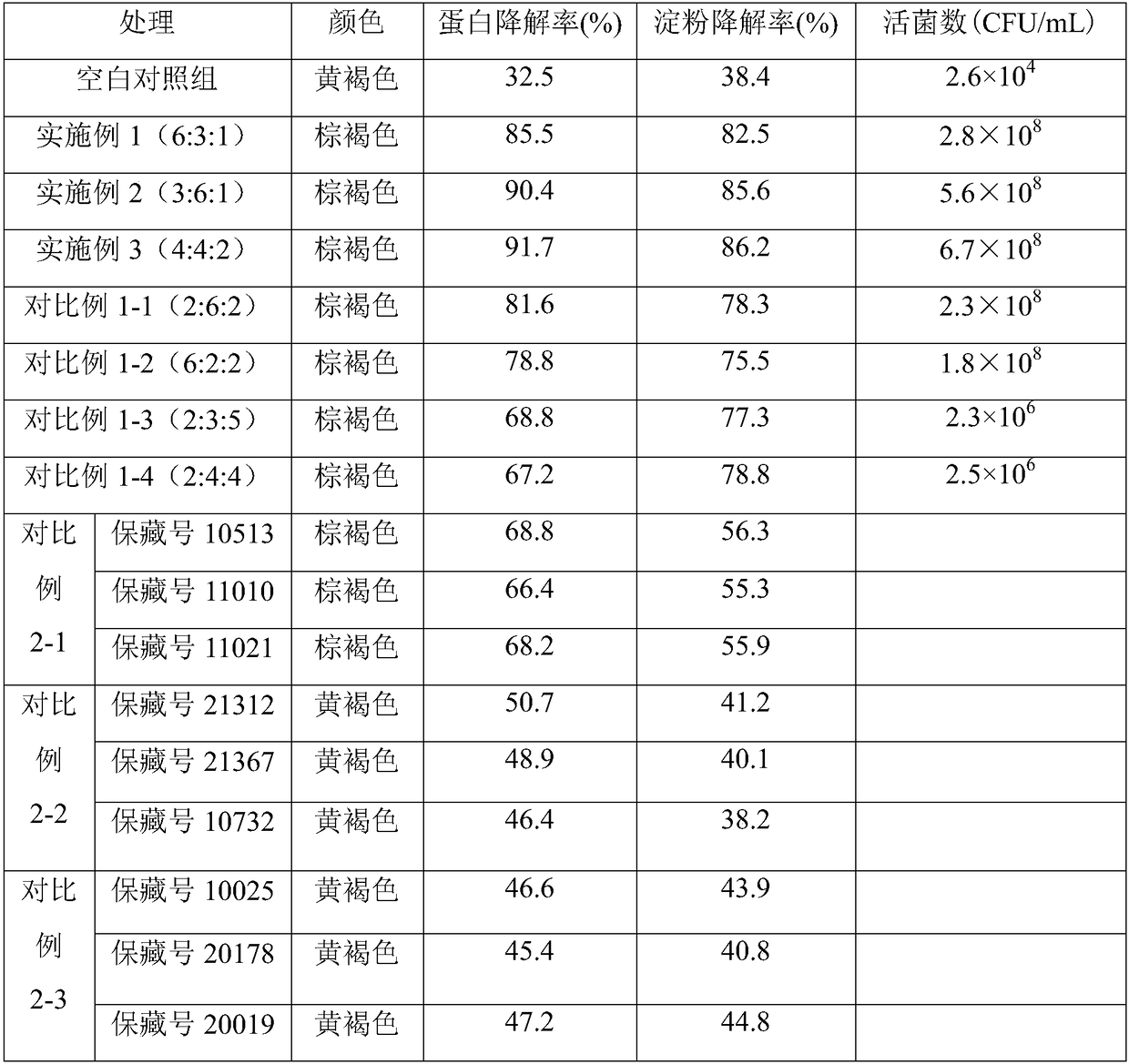
[0059] Embodiment 1, high-temperature and salt-resistant kitchen decomposing compound bacterial agent, is made up of solid decomposing bacteria, composite bacterial liquid and enzyme preparation, and solid decomposing bacteria is made up of streptomyces sp. (Streptomyces sp.) and solid fermented material, and solid fermented material is A mixture of oats, rice bran, and bran; the compound bacterial solution is a mixture of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae; the enzyme preparation is cellulase and protease , a mixture of amylase and lipase (the above enzymes are resistant to high temperature).
[0060] The preparation method of the high-temperature and salt-resistant kitchen decomposing composite bacterial agent (hereinafter referred to as composite bacterial agent) specifically comprises the following steps:
[0061] (1), preparation of solid decomposing bacteria:
[0062] Include the following steps:
[0063] (1.1), preparation meth...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Embodiment 2, the embodiment 1 step (1.2) oats, rice bran and bran are evenly mixed according to the ratio of 5:3:2 and changed to mix by volume ratio 3:1:4; Bacillus subtilis in step (2.4) The bacterial liquid, the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacterial liquid and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial liquid are mixed in a volume ratio of 6:3:1 to be mixed in a volume ratio of 3:6:1; and in step (3), cellulase, protease, The mixing ratio of amylase and lipase powder is changed from 4:2:2:2 to 1:4:4:1, and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0084] Embodiment 3, the embodiment 1 step (1.2) oats, rice bran and bran are evenly mixed according to the ratio of 5:3:2 and changed to mix by volume ratio 4:3:4; Bacillus subtilis in step (2.4) The bacterial liquid, the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacterial liquid and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial liquid are mixed in a volume ratio of 6:3:1 to be mixed in a volume ratio of 4:4:2; and in step (3), cellulase, protease, The mixing ratio of amylase and lipase powder is changed from 4:2:2:2 to 4:1:1:2, and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com